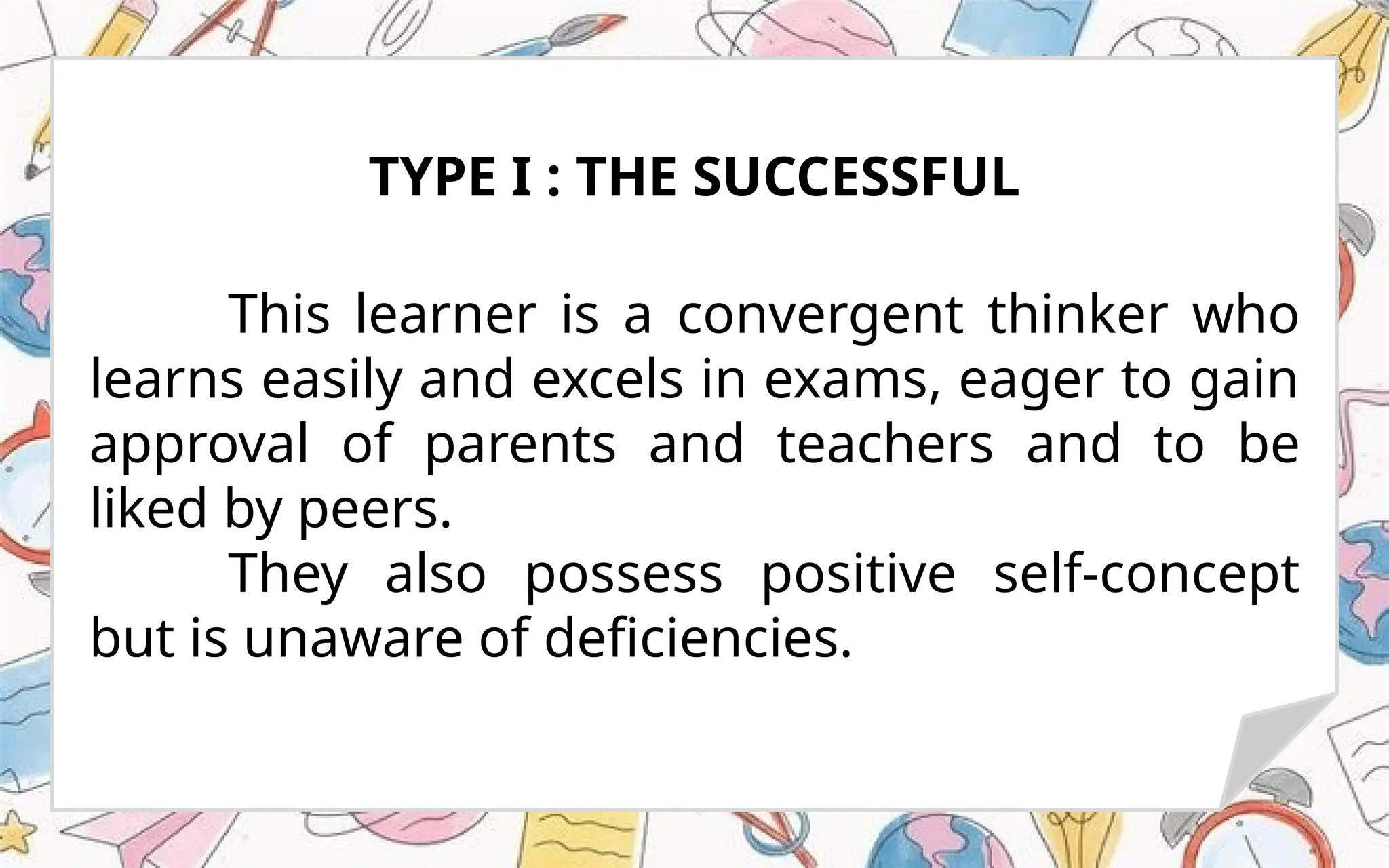
The document outlines the definitions, characteristics, and identification methods for gifted and talented learners, including five categories of giftedness based on various criteria. It addresses the importance of recognizing gifted learners to prevent negative consequences such as demotivation and frustration. Additionally, it categorizes gifted learners into different profiles based on their characteristics and developmental milestones.