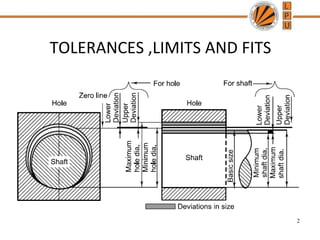
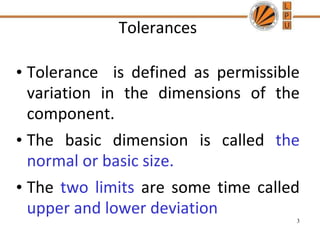
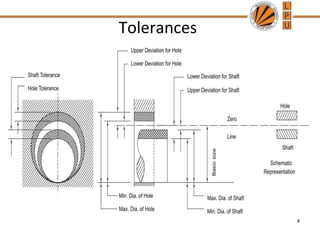
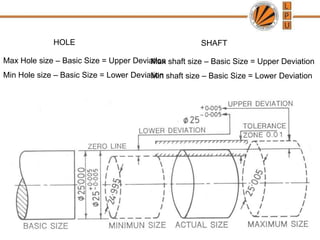
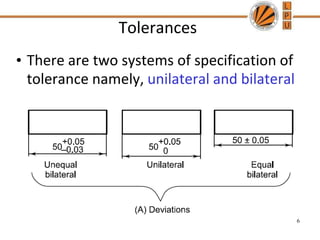
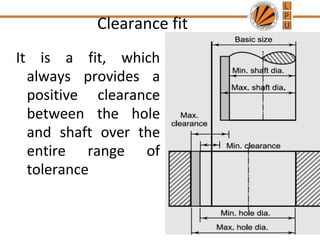
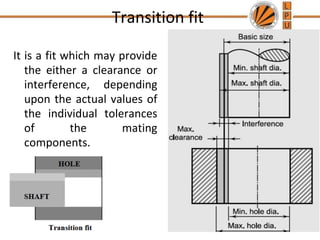
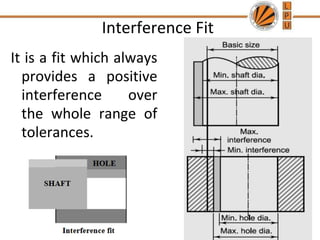
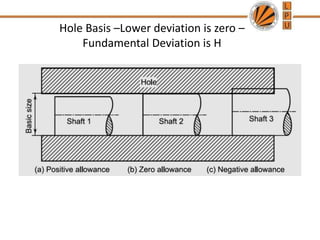
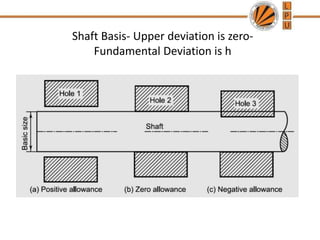
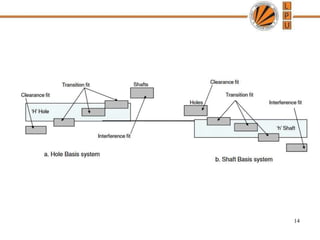
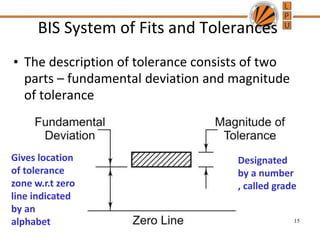
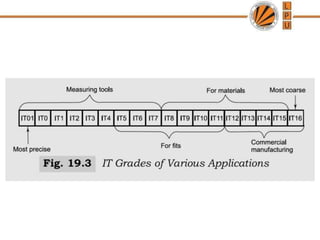
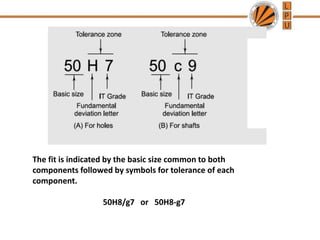
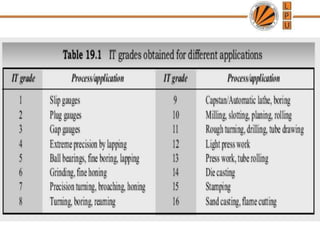
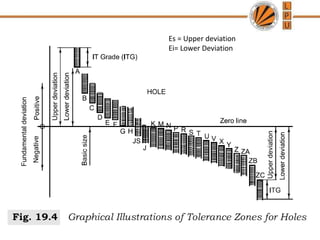
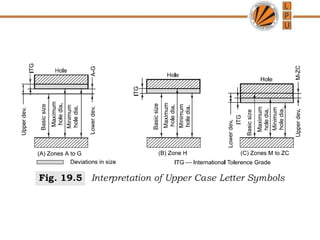
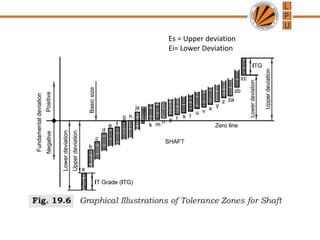
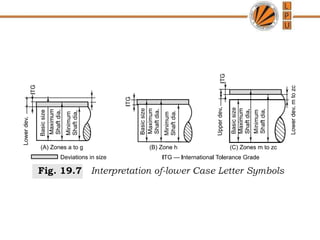
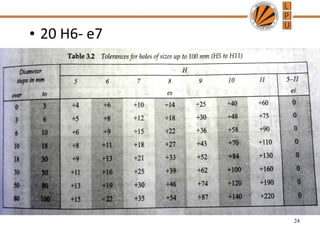
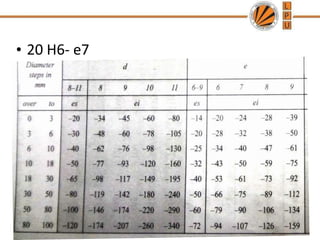
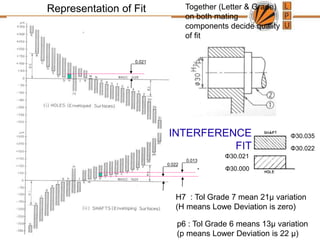
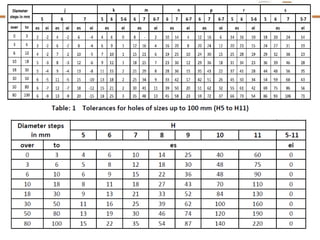
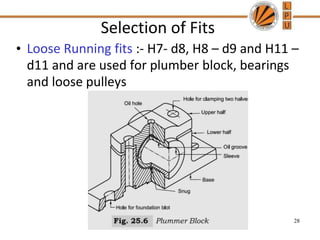
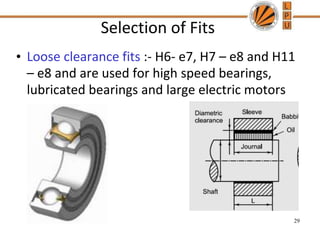
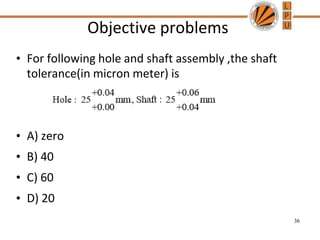
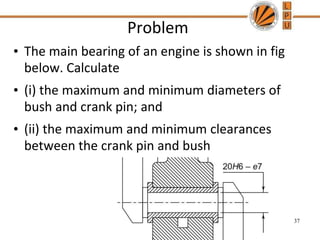
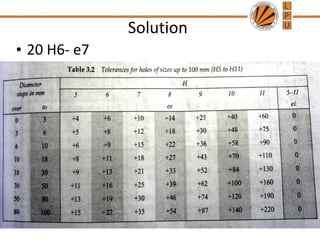
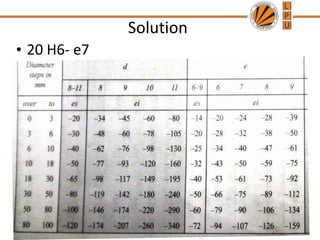
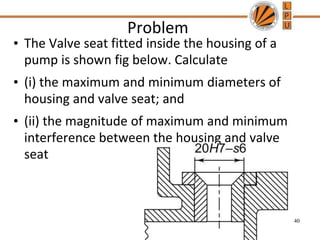
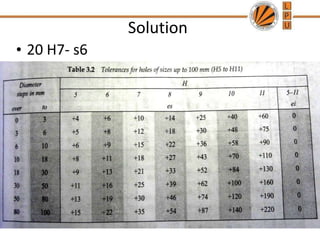
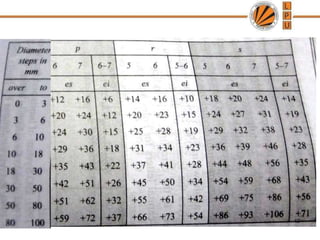
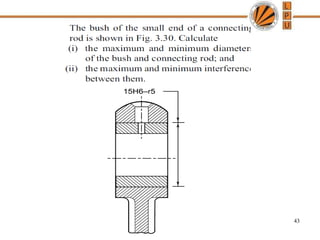
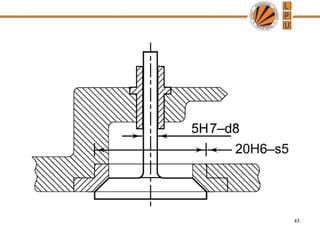
This document discusses tolerances, limits, and fits between machine elements. It defines tolerance as the permissible variation in a component's dimensions, with upper and lower deviation limits. Three common fits are defined - clearance fit which always provides space, transition fit which may provide clearance or interference, and interference fit which always overlaps. Hole and shaft basis systems are described for specifying tolerances. Different grades of fits are explained for various machine applications like loose running, precision, and press fits. Objective problems on fit selection and calculations are presented.