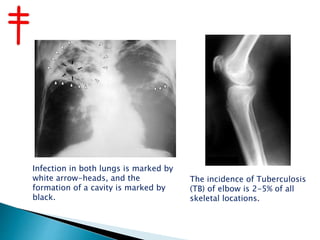
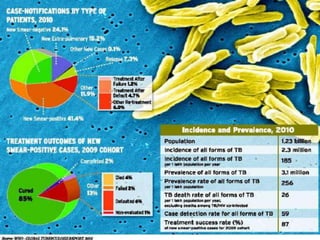
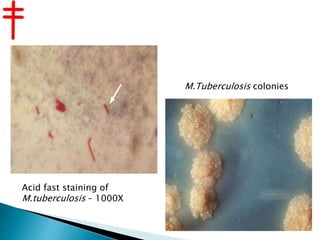
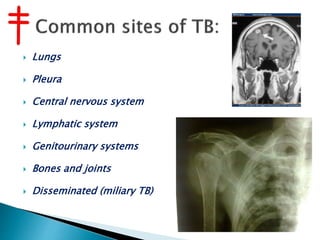
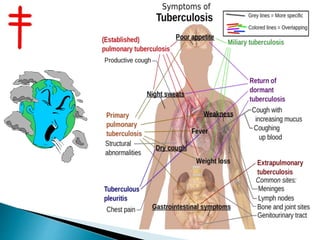
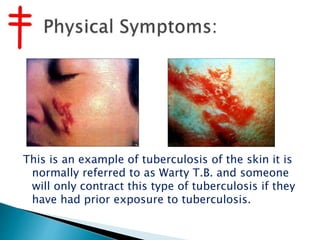
Tuberculosis is caused by various strains of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, which most commonly affects the lungs. It can spread through the body to other organs. TB may be pulmonary (lung-based in 90% of cases) or extra-pulmonary in other parts of the body. While treatable with antibiotics now, TB was once a major global killer and remains a serious public health issue, made worse by the emergence of drug-resistant strains like MDR-TB and XDR-TB which are harder to treat.