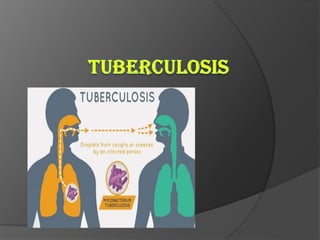
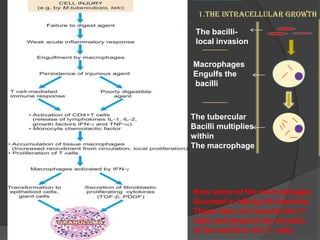
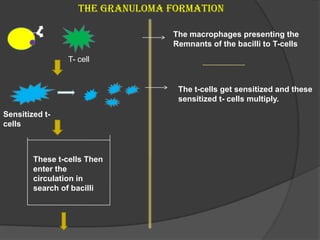
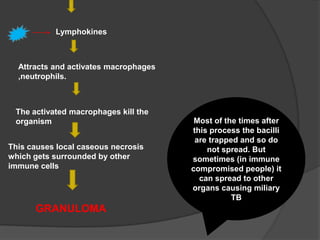
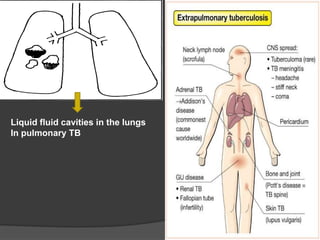
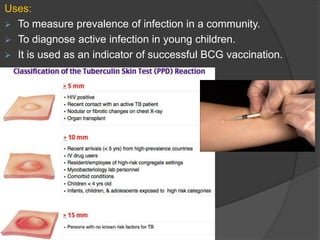
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease primarily affecting the lungs, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which can lead to primary or secondary forms of the disease. The clinical manifestations include asymptomatic infections, pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB, with diagnosis involving tuberculin tests, microscopy, culture, and molecular methods. Treatment typically involves a multi-drug regimen, and challenges such as multi-drug resistant (MDR-TB) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR-TB) forms are significant public health concerns.