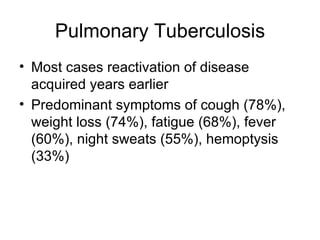
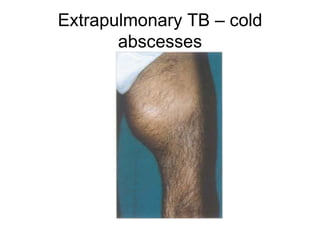
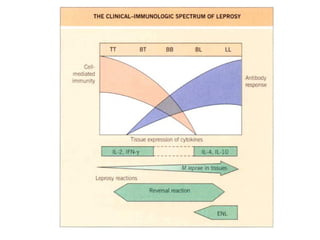
Tuberculosis is a widespread infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It infects one third of humanity and causes over 1.6 million deaths per year, making it one of the leading causes of death from infectious disease worldwide. The highest case rates are found in Asia, with India, China, and Indonesia having the most cases. Tuberculosis is often found concurrently with HIV infection and about half of those coinfected will develop active TB. Treatment involves a combination of antibiotics over several months, but drug resistance is a major problem, especially in Asia.