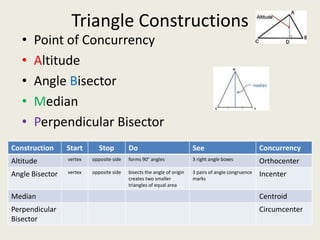
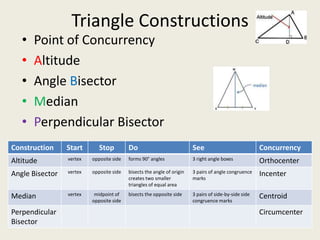
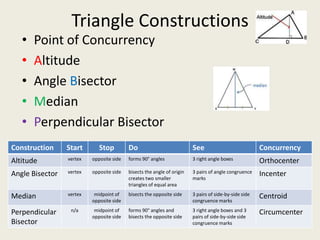
Here are the answers to the triangle concurrency review quiz questions:
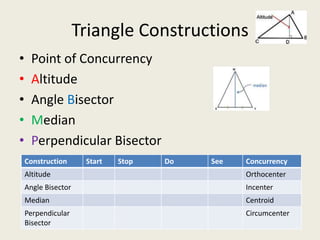
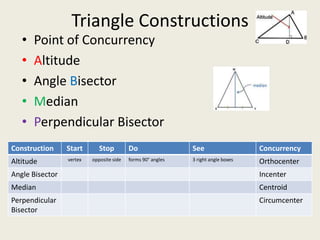
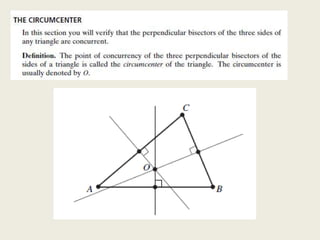
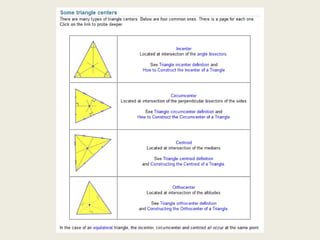
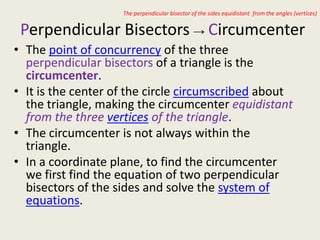
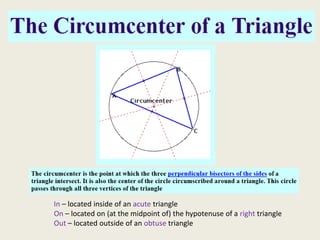
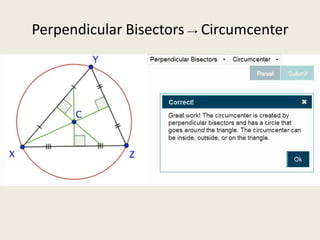
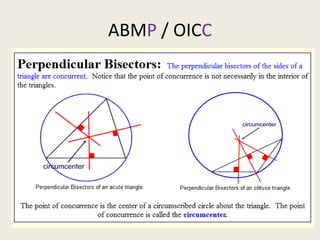
1) Circumcenter
2) At the midpoint of the hypotenuse
3) Vertices
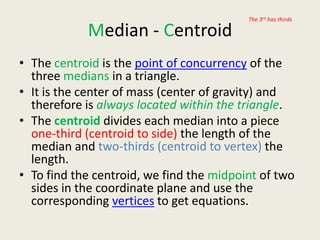
4) 1/3 to 2/3
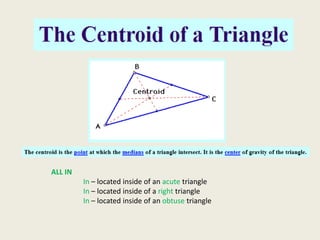
5) Always
6) Vertex
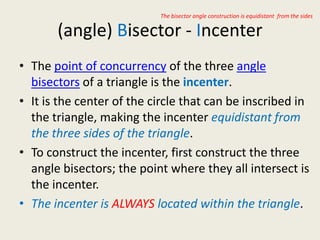
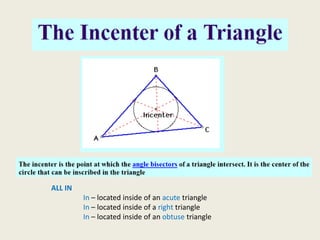
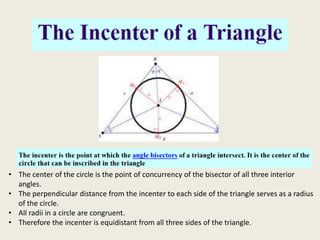
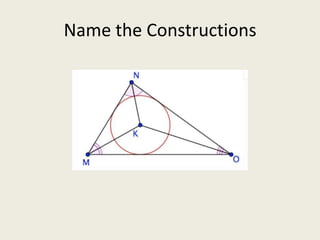
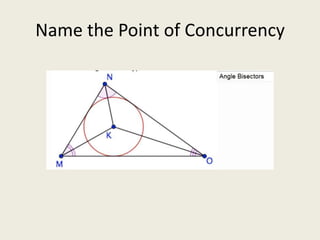
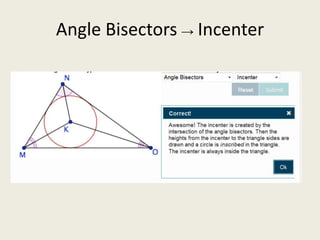
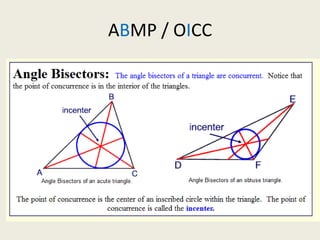
7) Incenter
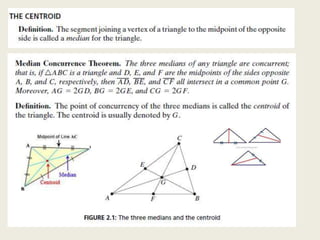
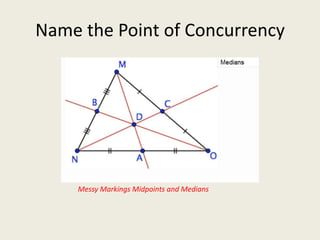
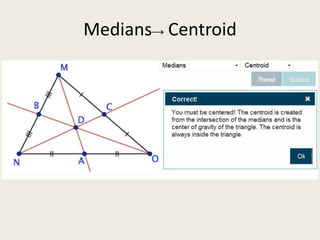
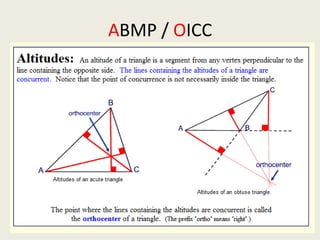
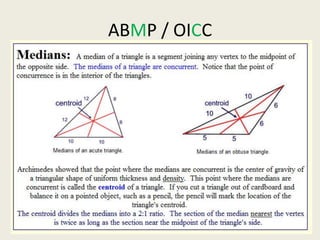
8) Centroid
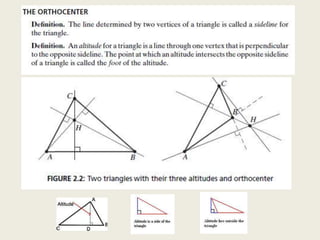
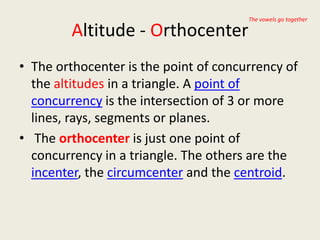
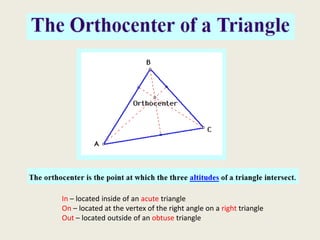
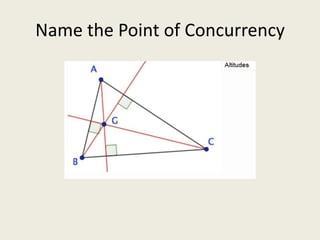
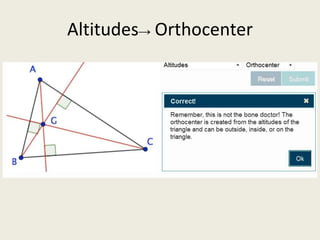
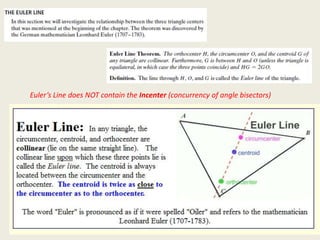
9) Orthocenter
10) Side
11) Sometimes
12) Sides
13) Always
14) Sometimes
15) Vertex of the right angle




![Recapitualtion
• Ready for another quiz?
• You will be presented with a series of fifteen
questions about triangle concurrencies.
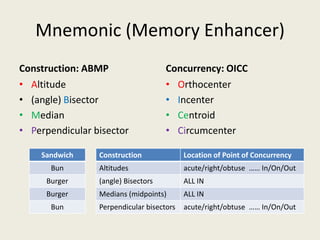
• Brain Dump the mnemonic to help you keep
the concepts straight.
• Remember to use the burger-bun, for the all-
in vs. the [in/on/out] for [acute/right/obtuse].
• Remember which construction was listed in
the third position and why it’s the third.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/triangleconcurrencyabmp-oicc-130330212907-phpapp02/85/Triangle-concurrency-abmp-oicc-47-320.jpg)



