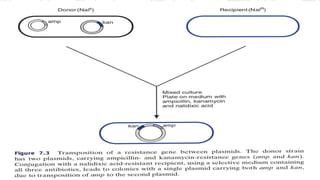
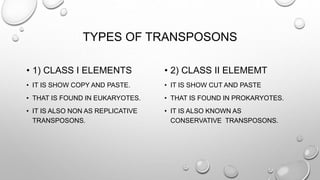
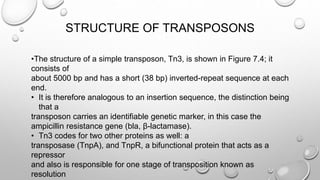
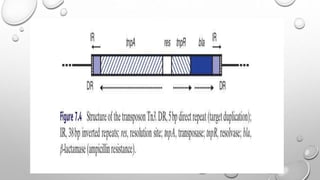
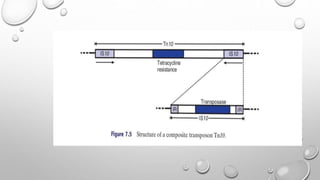
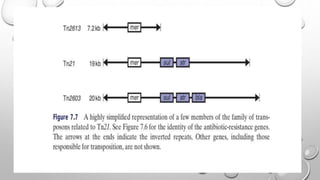
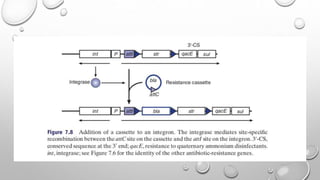
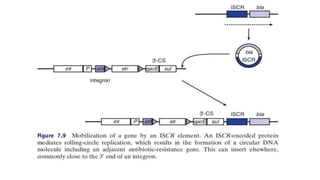
Transposons are mobile genetic elements that can move within genomes. They were first discovered on plasmids carrying antibiotic resistance genes. It was found that resistance genes could move between plasmids via transposition. This explained how unrelated plasmids could acquire the same resistance genes. There are two classes of transposons - class I are "copy and paste" elements found in eukaryotes, while class II are "cut and paste" elements in prokaryotes. Many resistance plasmids have evolved rapidly by acquiring additional genes via transposon movement within and between plasmids and chromosomes. Composite transposons contain insertion sequence elements flanking resistance genes. Larger transposons are built up by inte