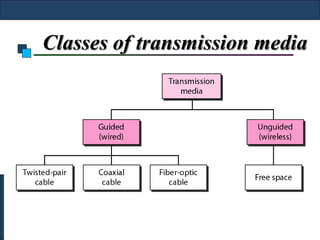
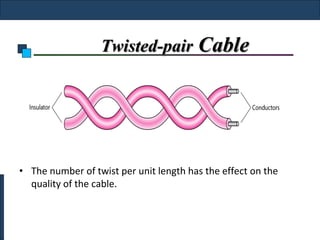
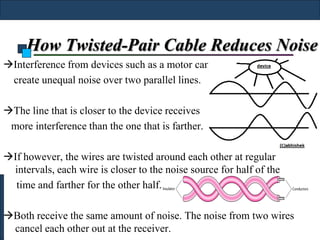
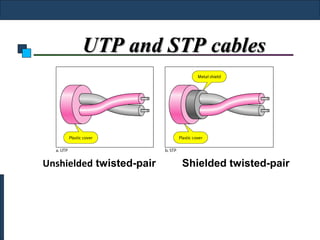
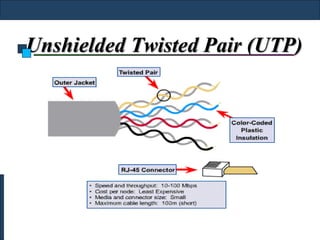
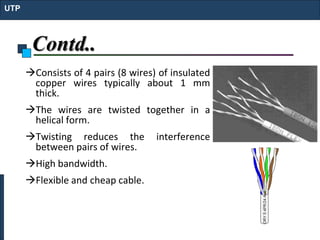
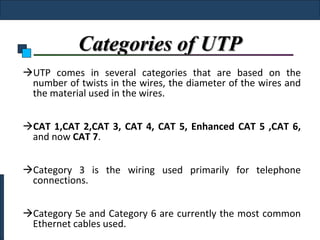
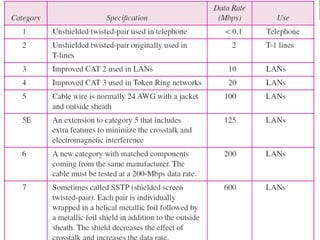
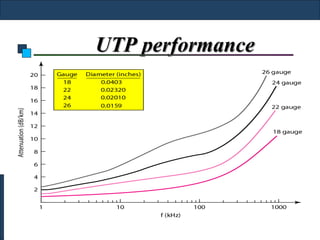
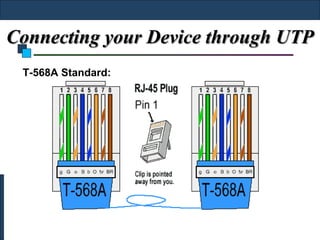
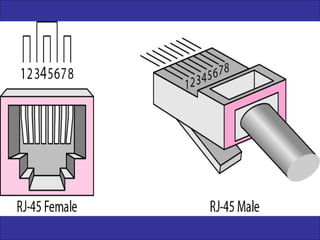
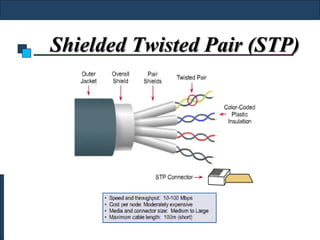
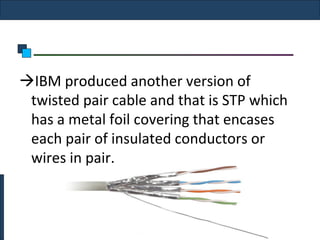
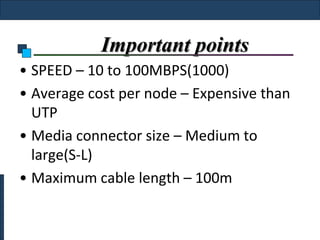
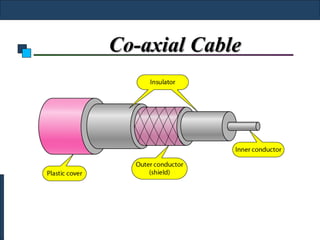
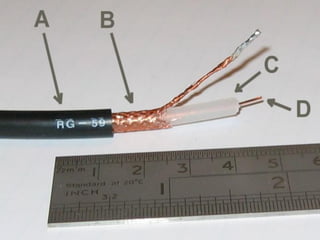
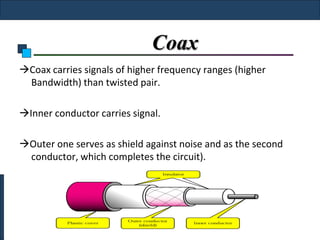
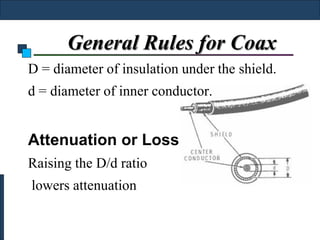
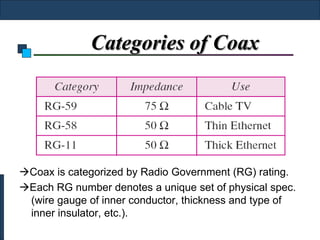
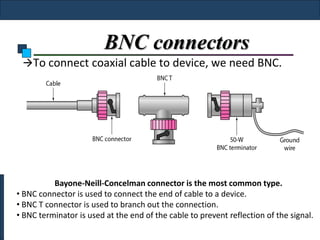
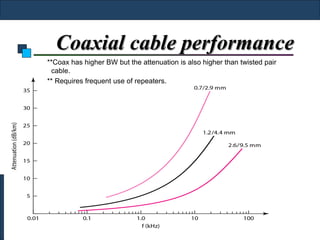
Twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable are guided media that provide a conduit for transmission. Twisted-pair cable reduces noise through regular twisting of the wire pairs. Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable is commonly used for telephone and Ethernet connections while shielded twisted-pair (STP) provides better noise shielding but is more expensive. Coaxial cable uses a central conductor surrounded by insulating and outer conducting layers to carry higher frequency signals than twisted pair over longer distances.