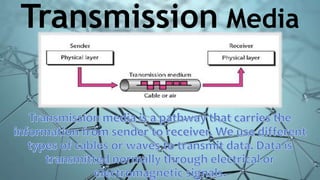
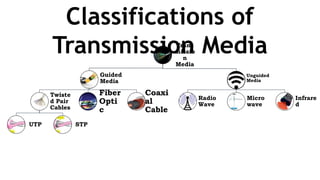
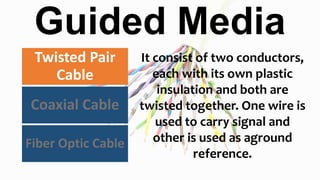
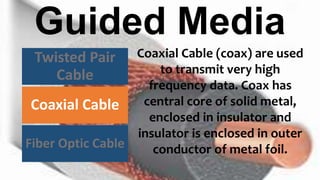
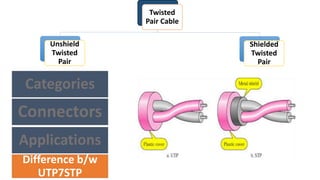
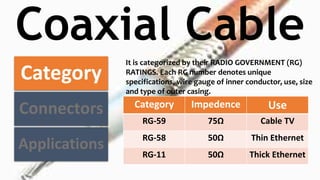
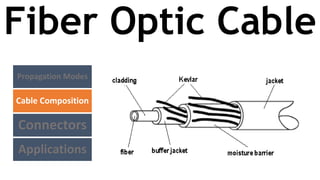
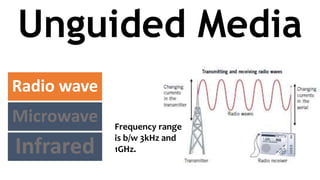
The document classifies and describes different types of transmission media used for data communication, including guided media like twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable which transmit data through a physical medium, as well as unguided media such as radio waves, microwaves, and infrared which transmit electromagnetic waves wirelessly without a physical path. It provides details on the composition, categories, applications and specifications of each type of transmission medium.