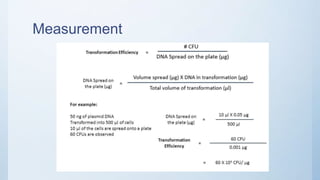
This document defines transformation and transformation efficiency. Transformation is when a cell takes up exogenous genetic material through its membrane. Transformation efficiency is calculated by dividing the number of successful transformants by the amount of DNA used, and it can be measured in transformants or colony forming units per microgram of DNA. Factors like plasmid size, DNA form (single vs double stranded), and DNA damage can affect transformation efficiency.