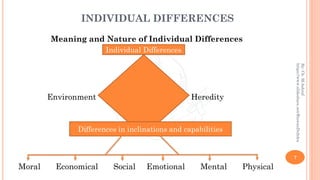
The document discusses individual differences in human development and learning, focusing on understanding their meaning, causes, and educational provisions necessary to address them. It highlights the uniqueness of individuals in terms of various traits and emphasizes the importance of tailored educational approaches for both gifted and slow learners. The conclusion underscores that both heredity and environment significantly influence individual differences in intelligence and other characteristics.