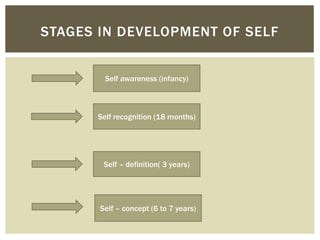
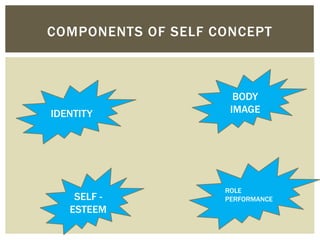
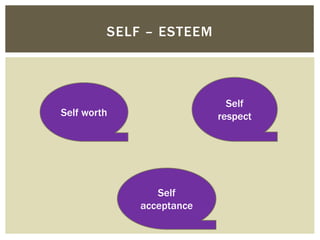
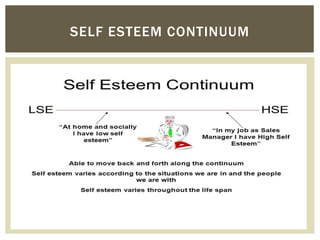
This document discusses the development of self-esteem from infancy through adulthood. It outlines factors that influence self-esteem, such as age, gender, relationships, and experiences. The document also describes different types of self-esteem, including inflated, high, and low self-esteem. Key aspects of developing a positive self-esteem are feeling competent, loved, in control of one's life, and able to meet expectations. Self-esteem is shaped by experiences throughout life and impacts how one views themselves.