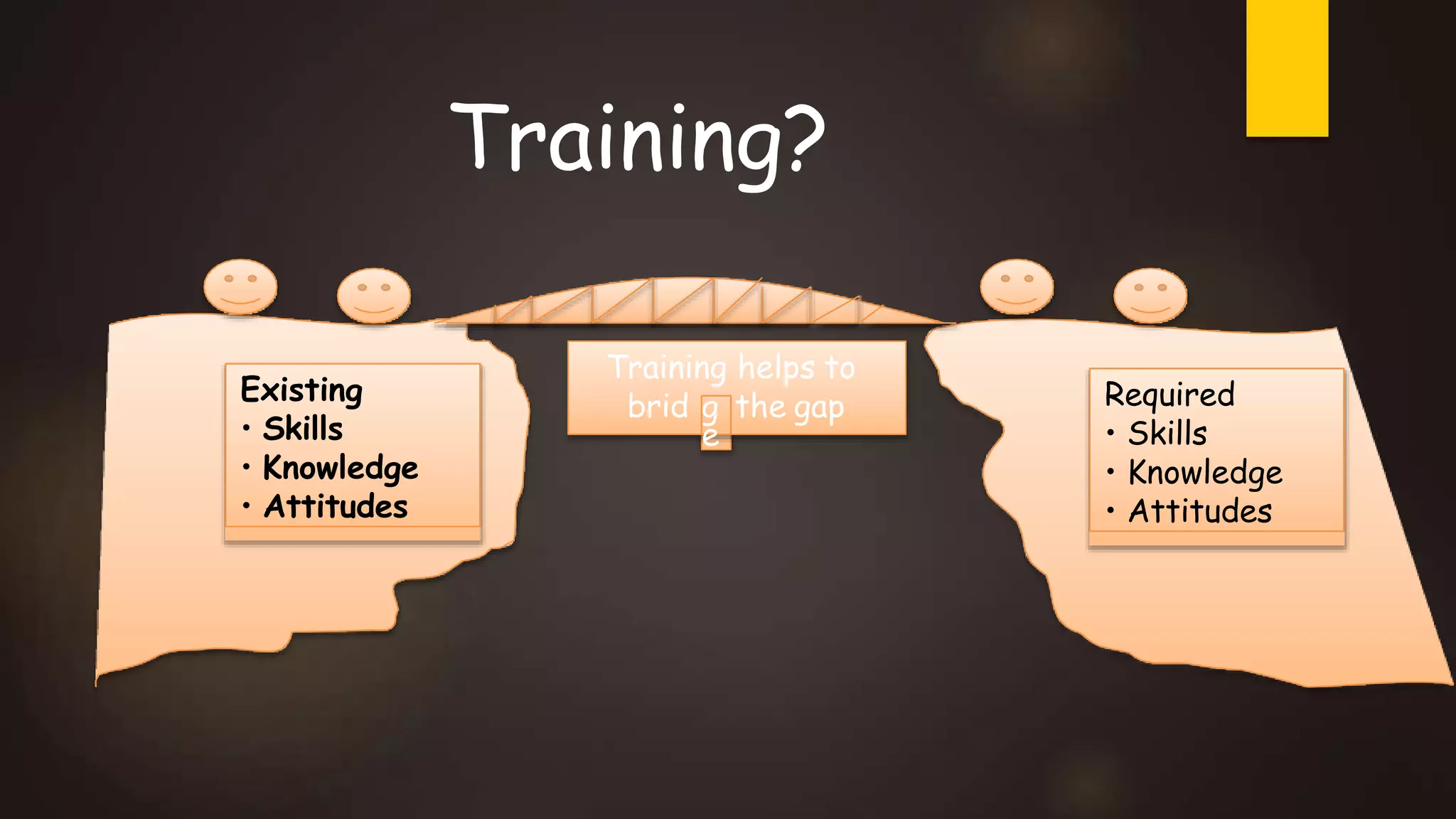
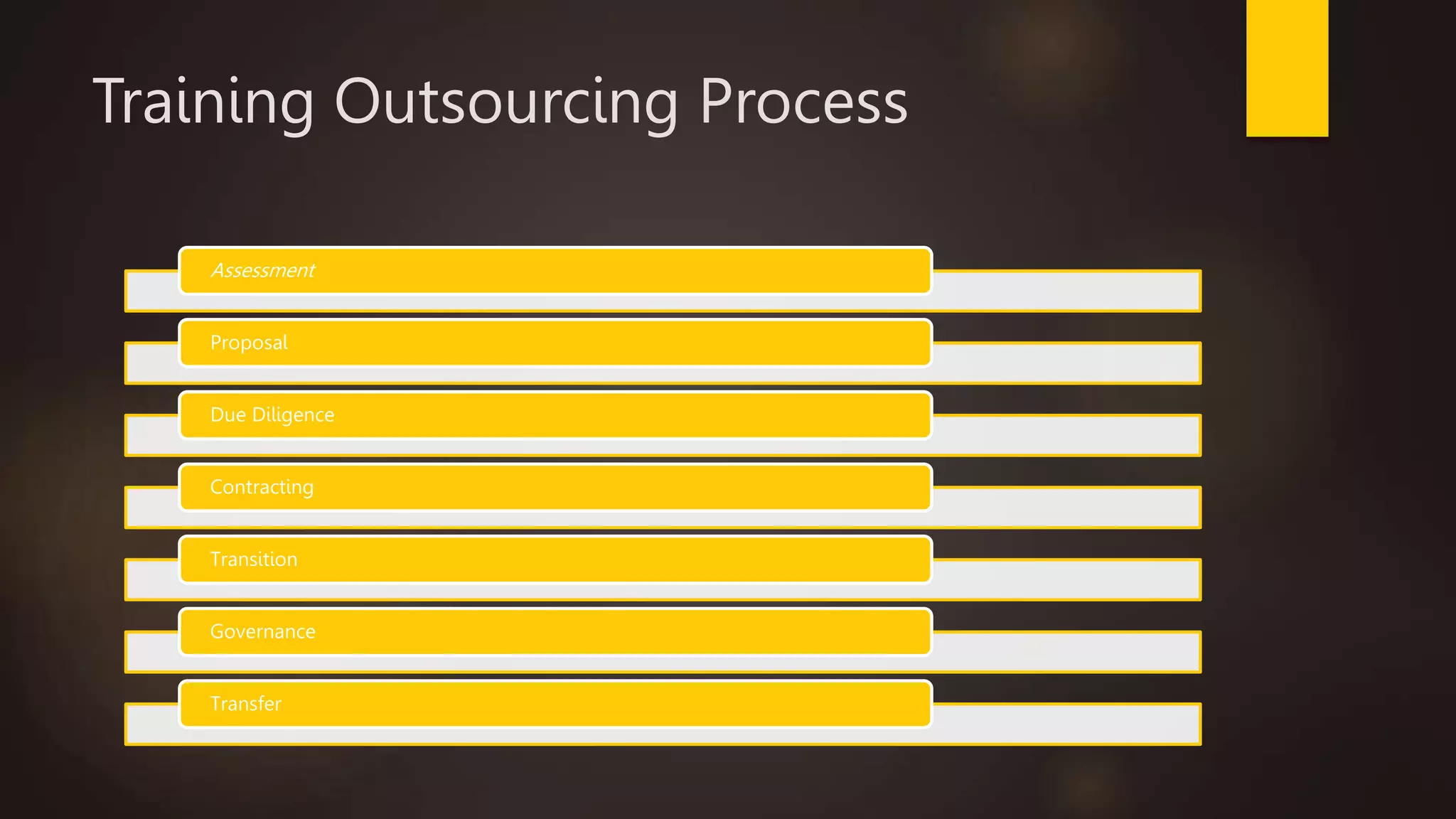
Training and development involves improving organizational and individual effectiveness. Training focuses on immediate changes through instruction, while development addresses longer-term goals. There are various training methods, including on-the-job methods like apprenticeships and job rotations, and off-the-job methods like classroom lectures. Training needs assessment identifies gaps between present and required skills and knowledge. Competency-based training focuses on specific skills, while role-based training applies skills through practical exercises. Outsourcing training can leverage costs and resources.