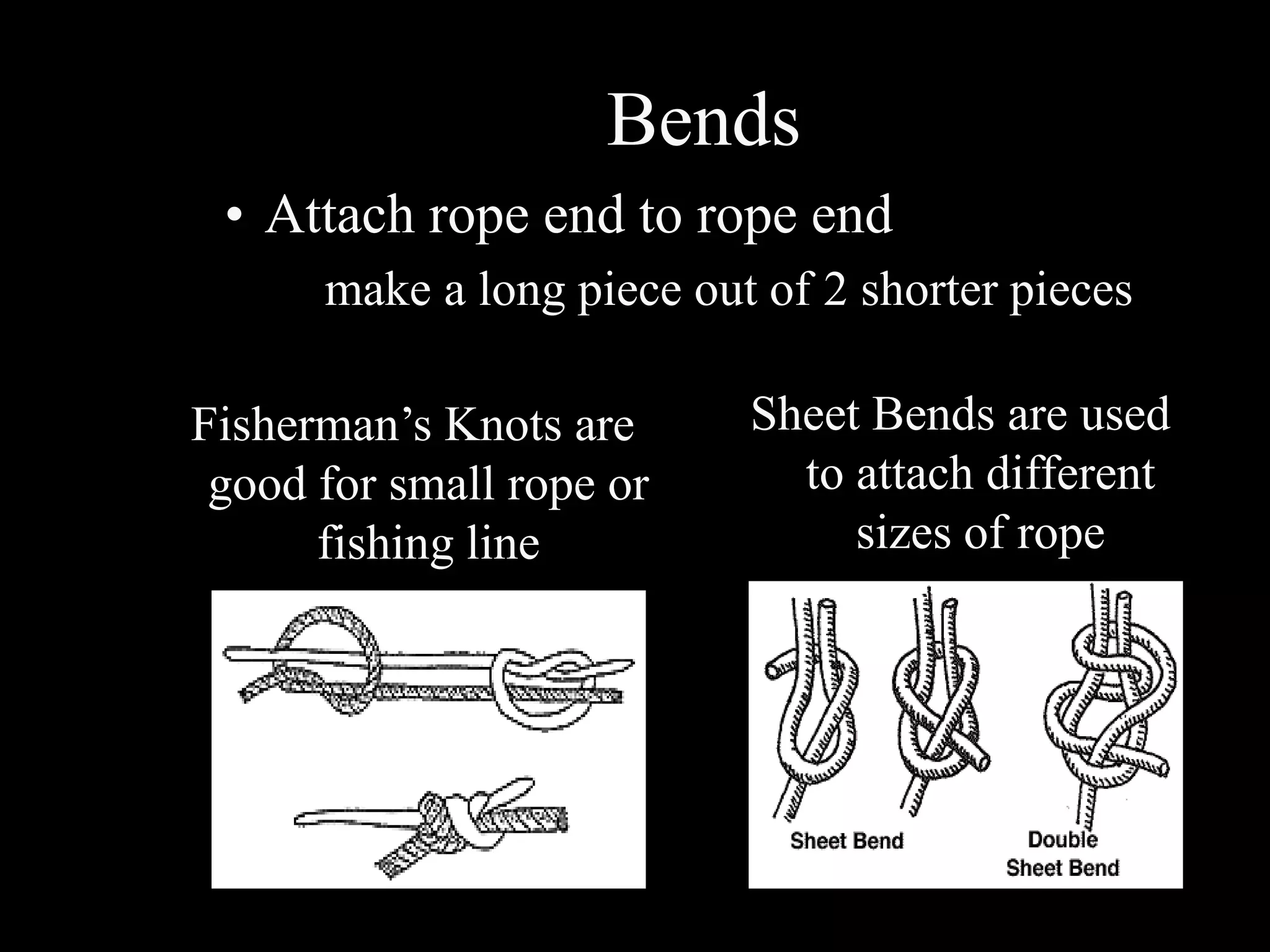
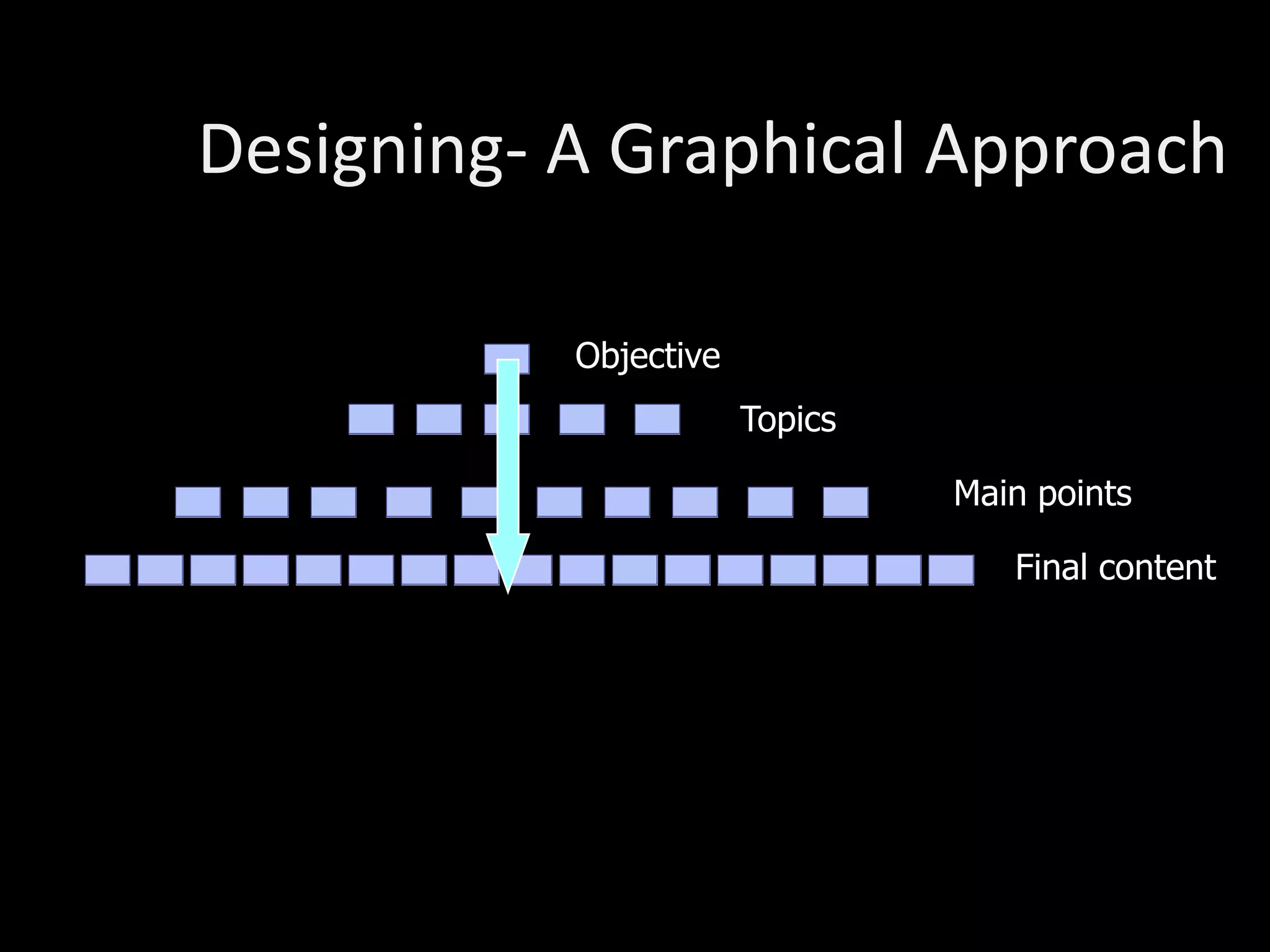
The document provides guidance on training others effectively. It discusses:
1) The key aspects of being a trainer including having subject matter expertise, strong presentation skills, and the ability to engage learners.
2) How to design effective training through needs assessments, setting objectives, and using instructional design principles to structure content and activities.
3) Best practices for delivering training such as using various teaching methods, rehearsing, and focusing on practical applications over just information sharing.