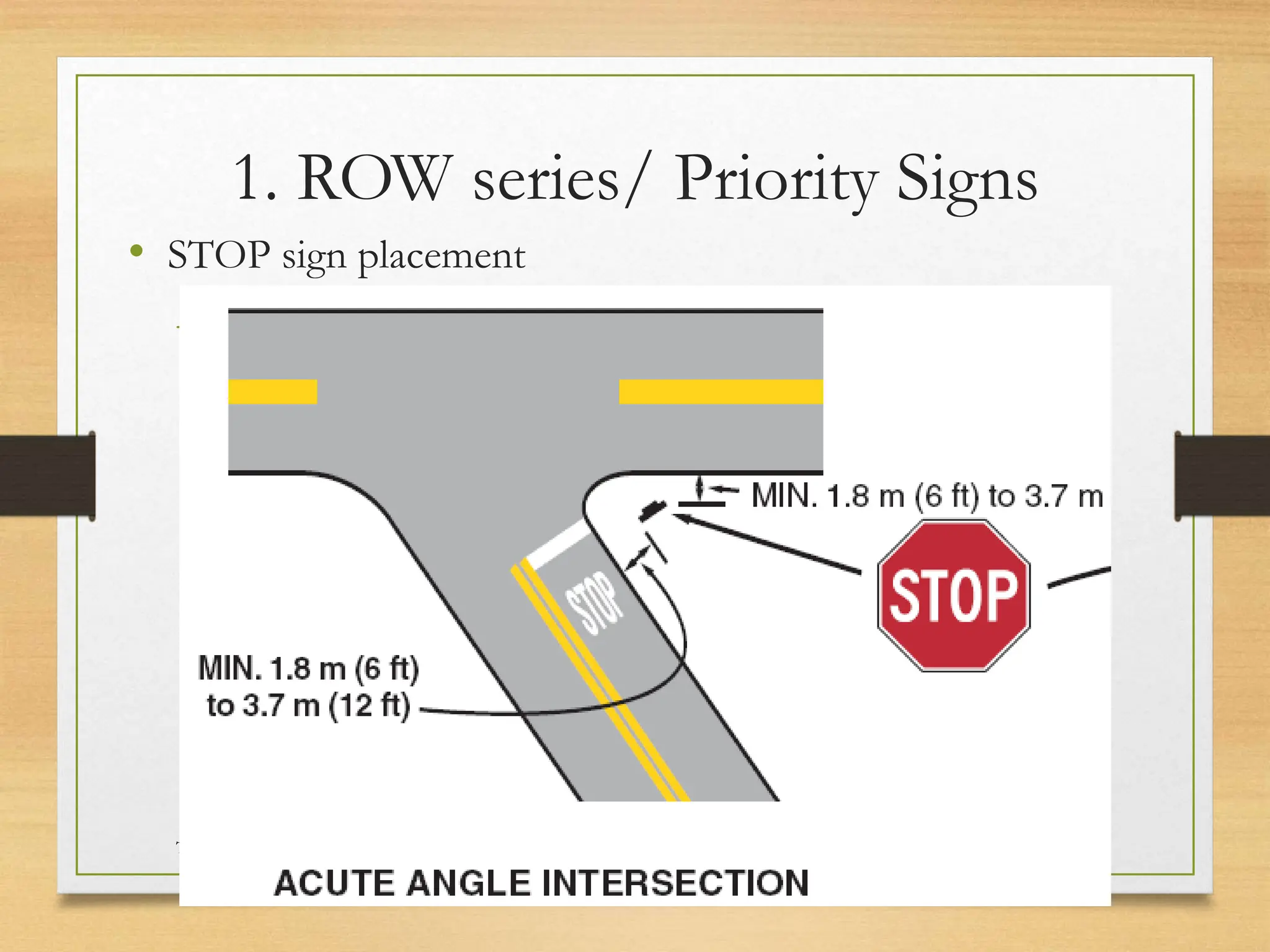
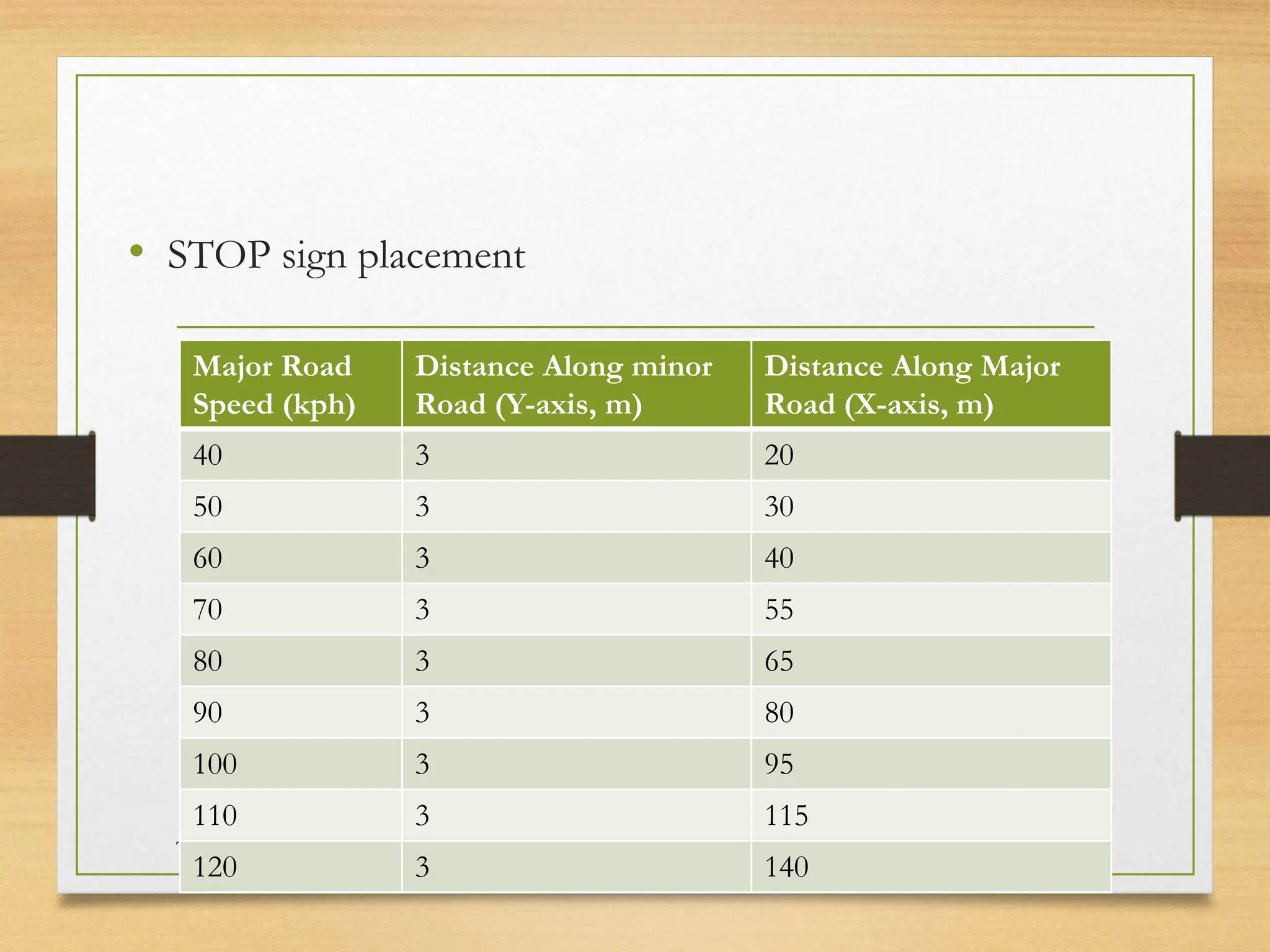
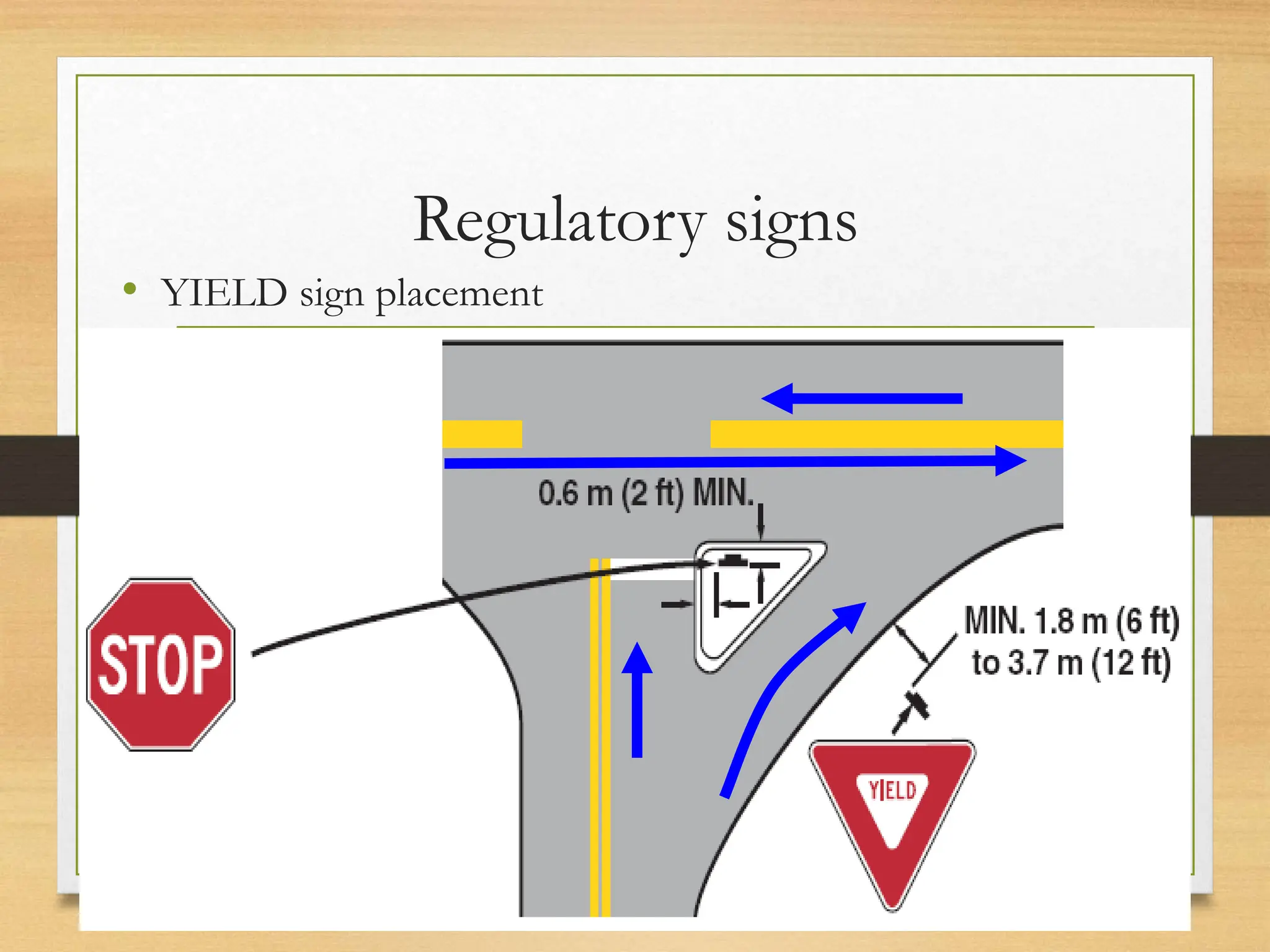
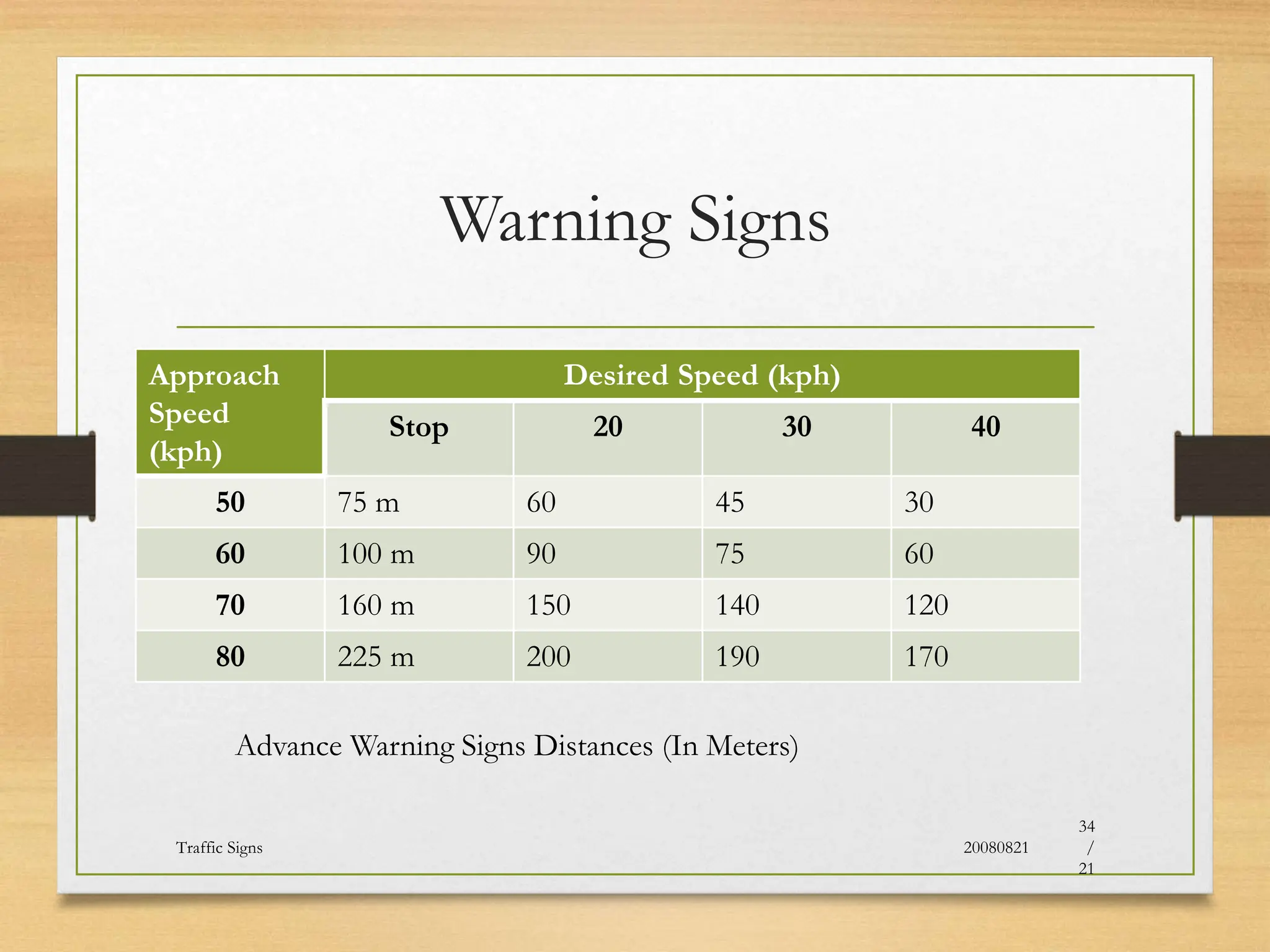
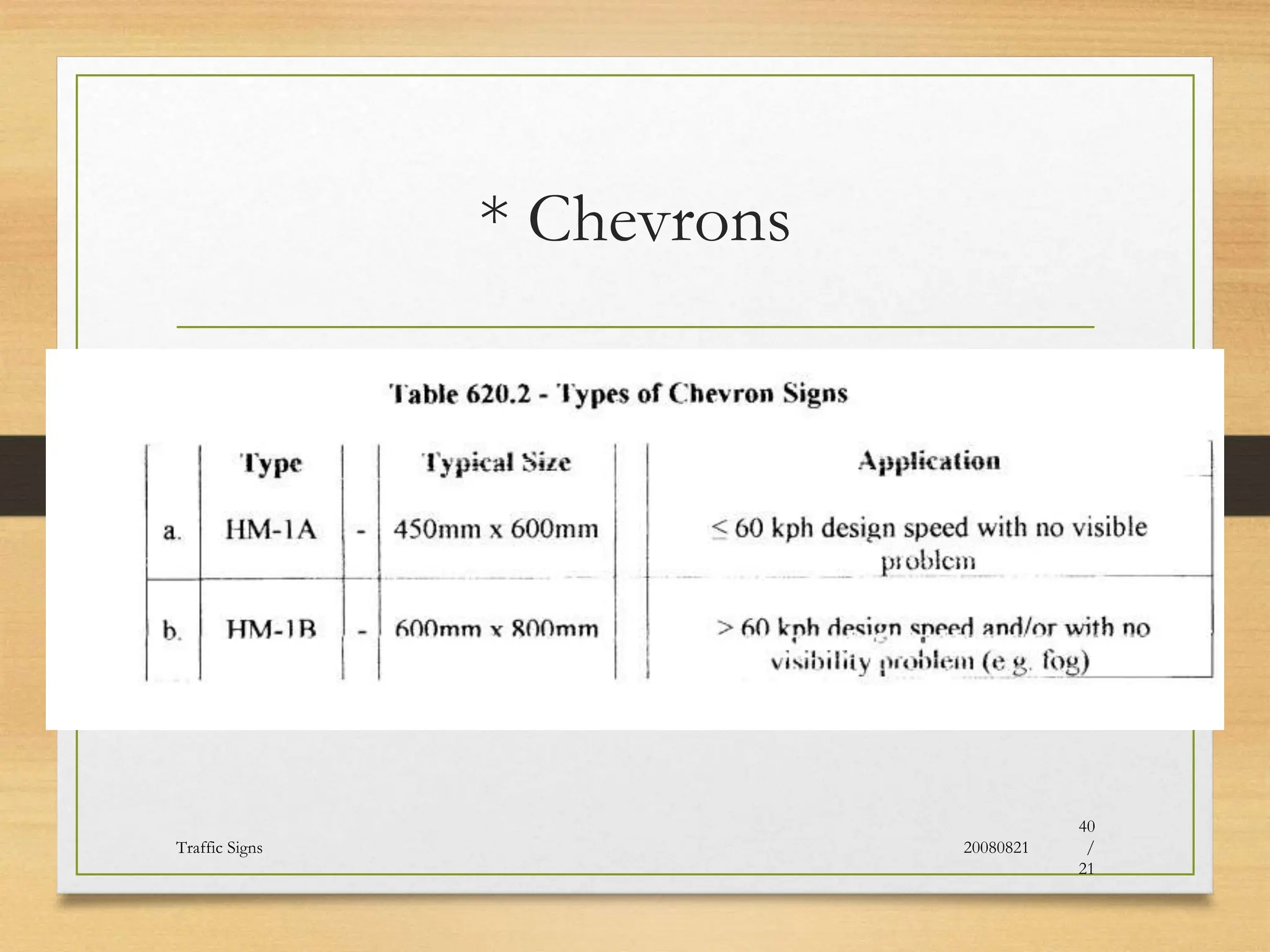
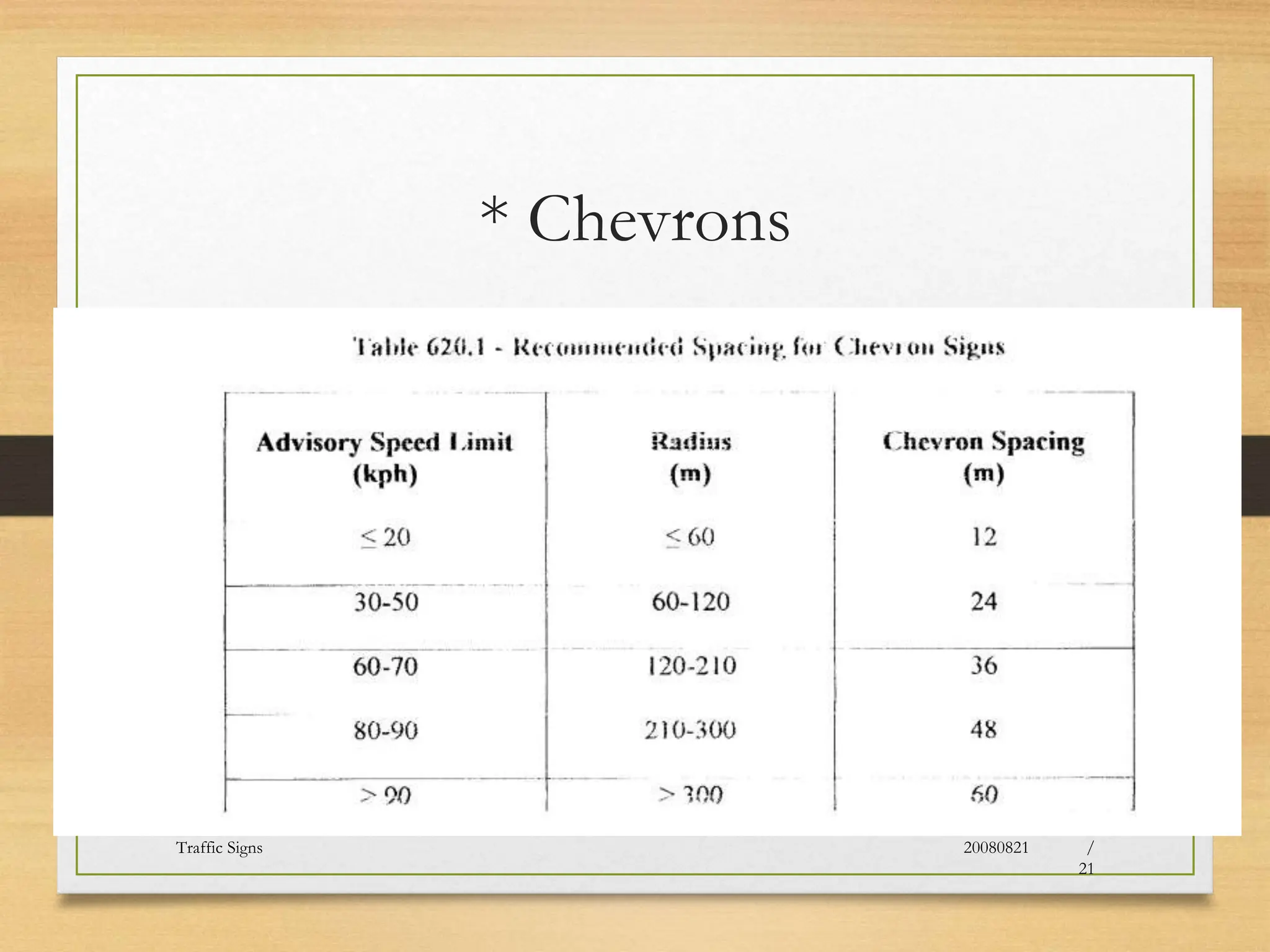
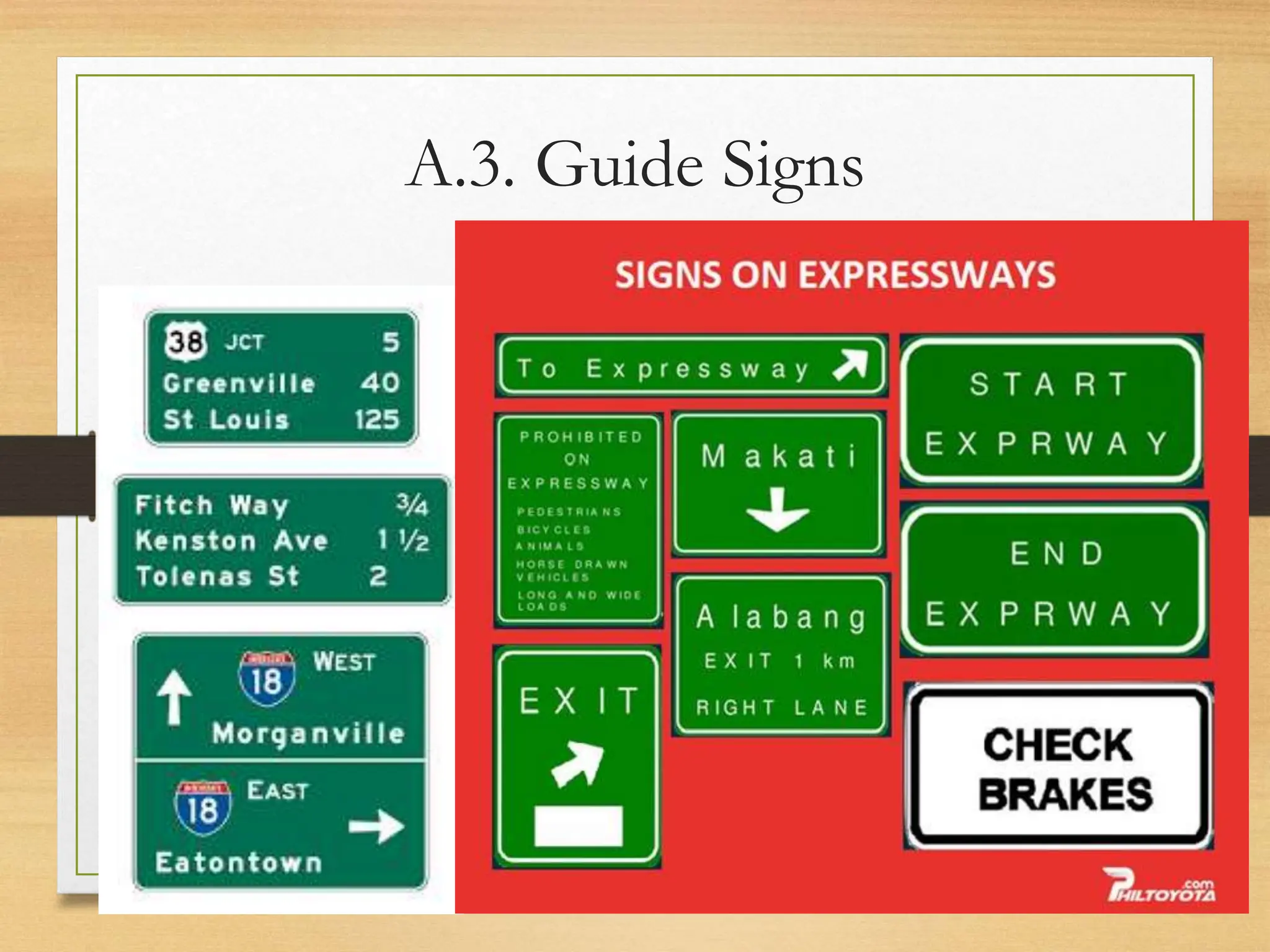
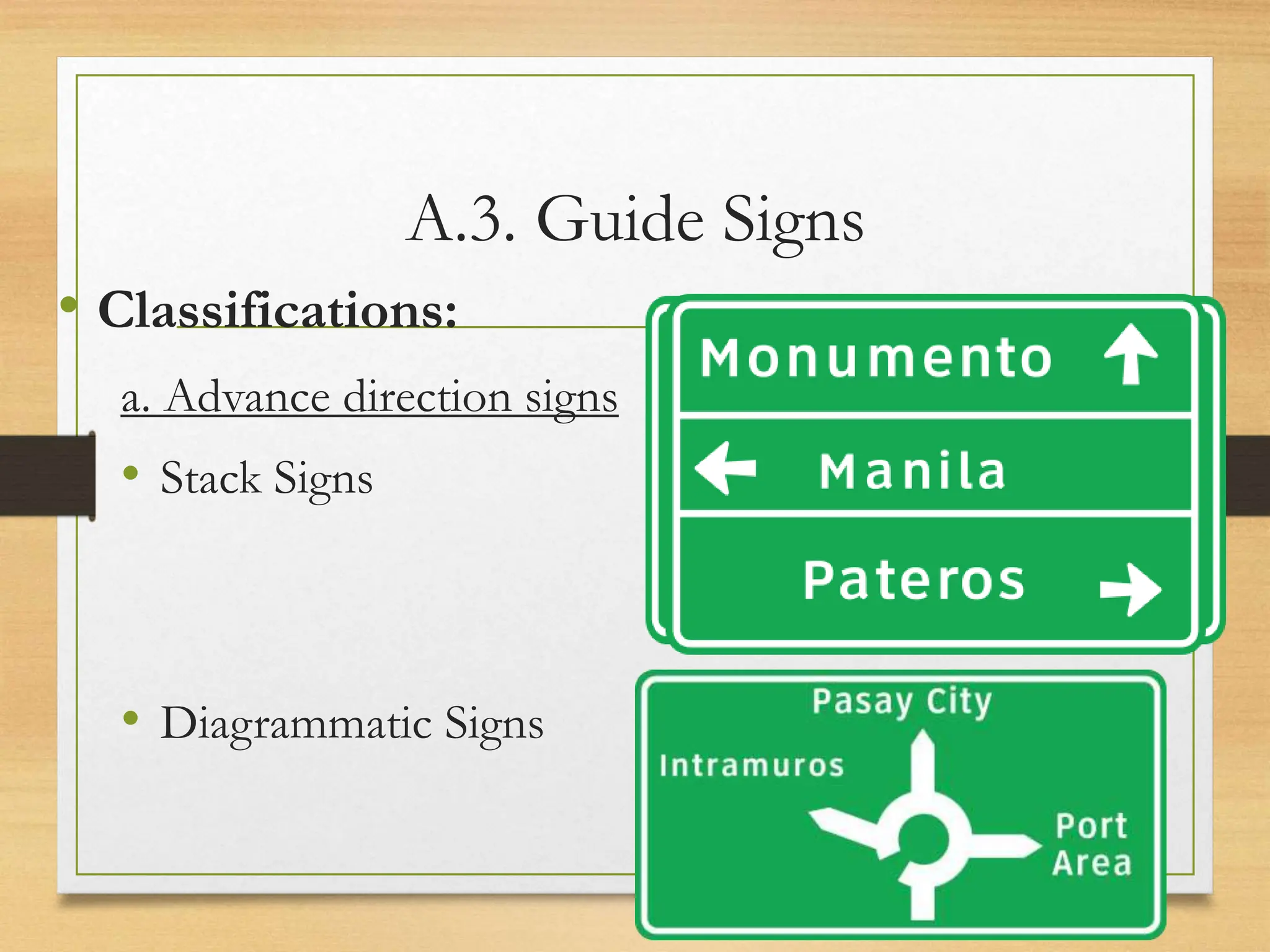
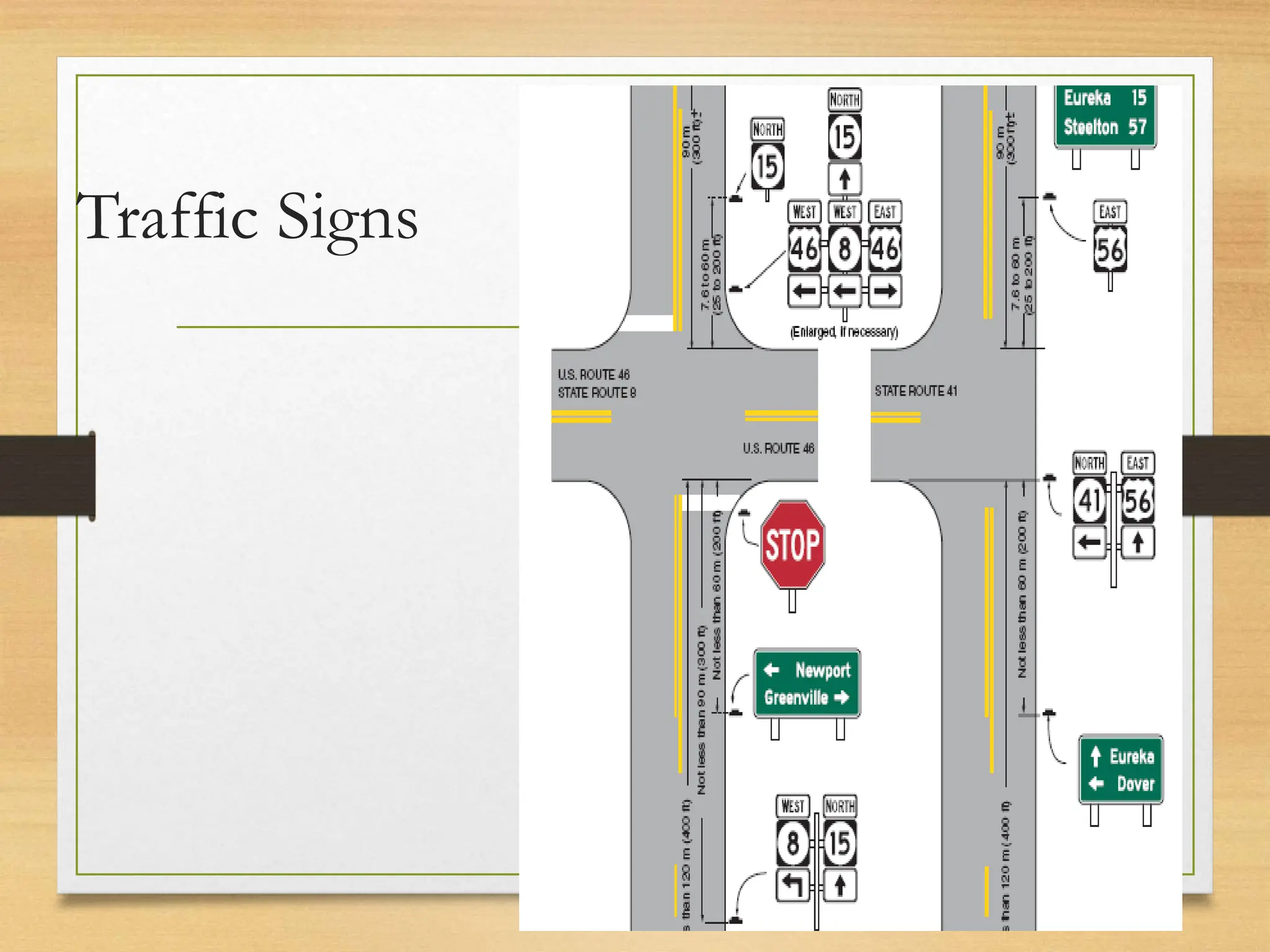
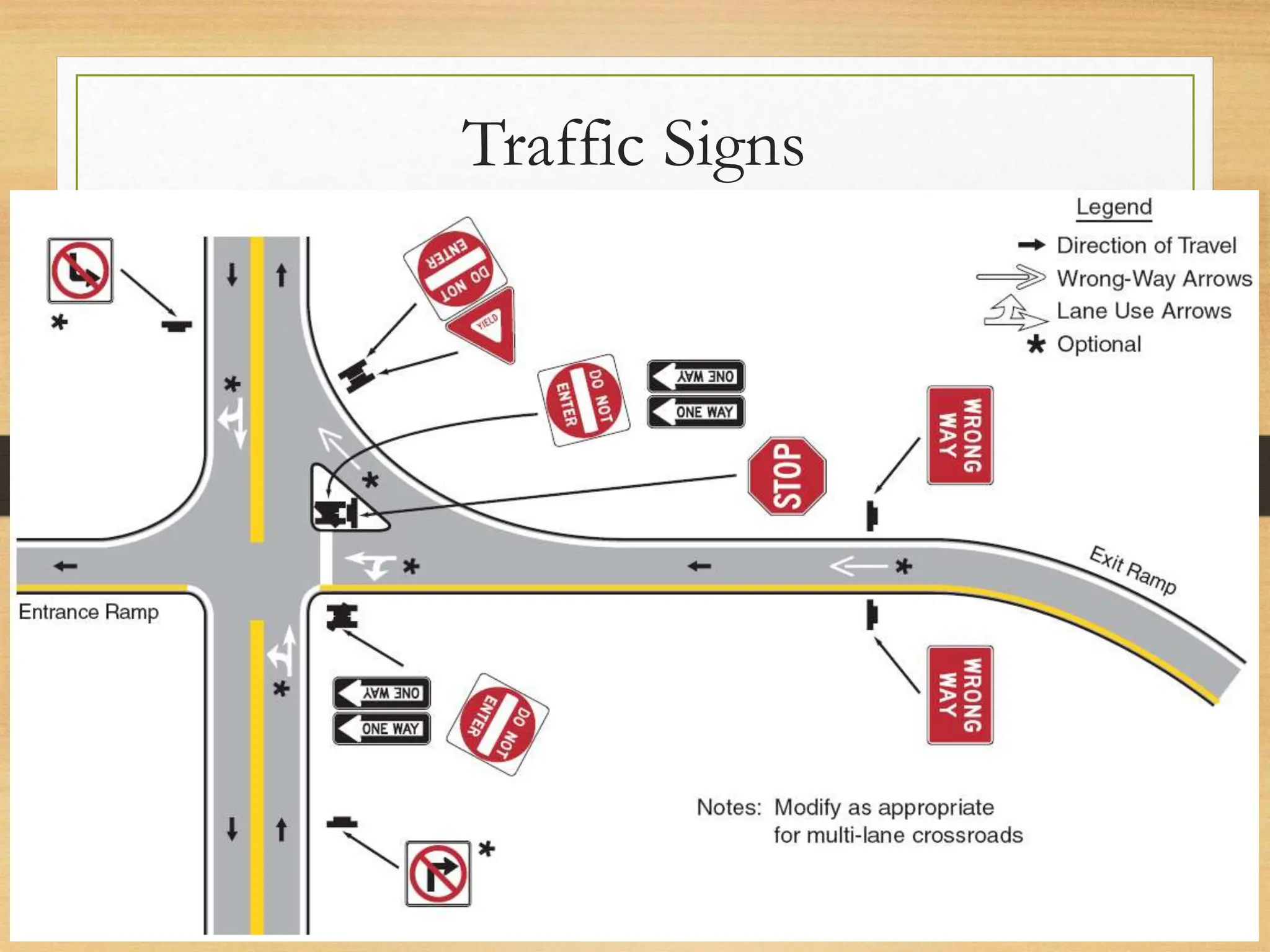
The document provides an overview of traffic control devices, emphasizing their role in highway safety and effective communication between traffic engineers and road users. It outlines the various types of devices, including traffic signs, pavement markings, traffic signals, and other channelizing devices, along with their design principles and classifications. Key principles for effective traffic signs include visibility, clarity, comprehensibility, and consistency to ensure safe and orderly traffic movement.