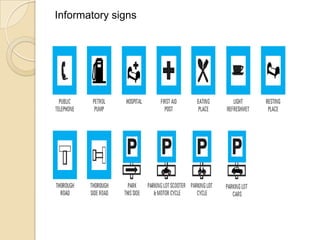
This document summarizes various traffic control devices and rules of the road. It describes common signage like mandatory, warning, and informational signs used to regulate traffic. It also outlines situations requiring extra care around emergency vehicles, buses, railways and street repairs. Key traffic rules are provided regarding keeping left, overtaking, yielding at intersections, and allowing passage of emergency vehicles. Finally, it discusses other traffic control devices like road markings, traffic lights, and channelizing devices used to direct traffic flow.