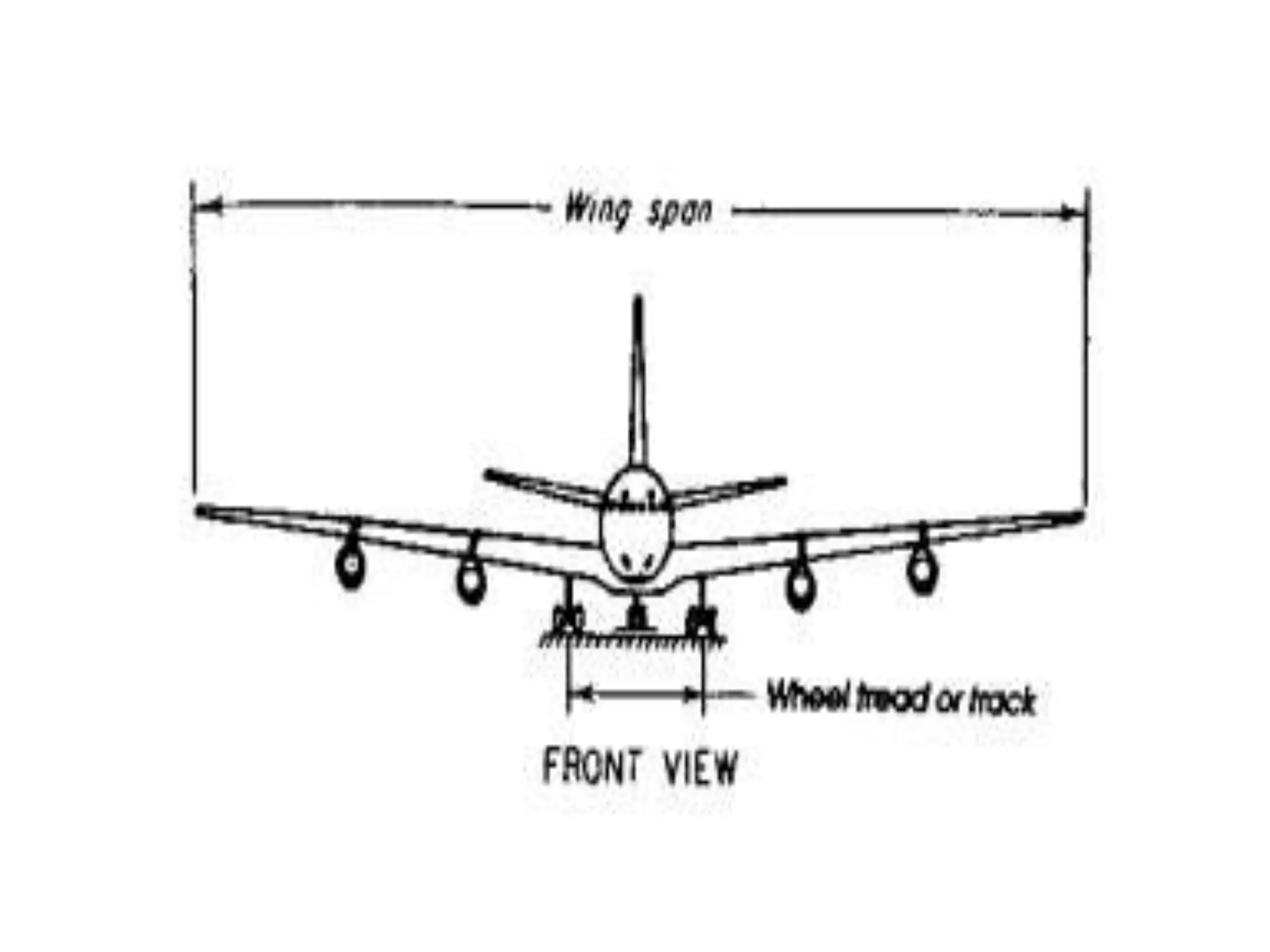
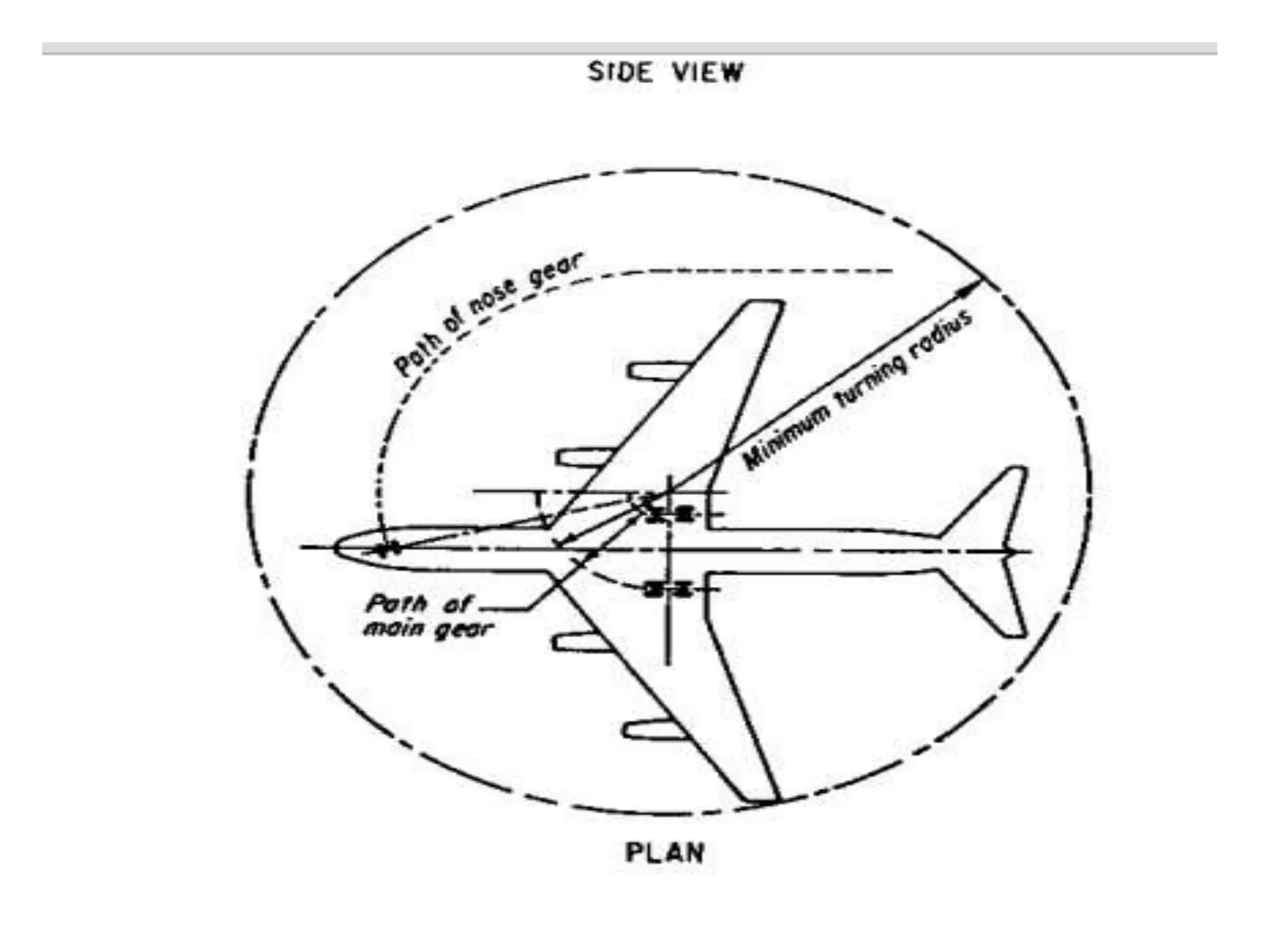
The document discusses airport engineering, covering its planning, design, construction, and the required infrastructure like terminals and runways for passenger and freight services. It highlights the historical development of air transport and the establishment of various regulatory bodies, as well as the classification of airports based on take-off and landing methods and their functions. Key points include significant events in the evolution of aviation in India and the role of the Airport Authority of India in managing air navigation and airport facilities.