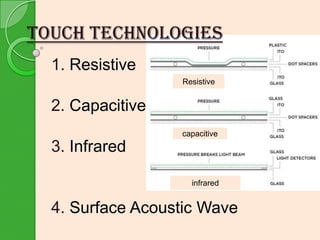
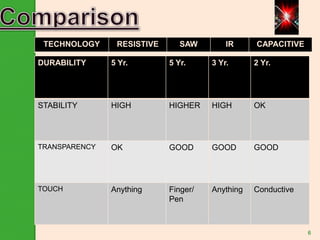
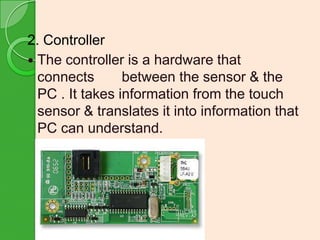
This document provides an overview of touchscreen technology. It begins with definitions of touchscreens and their ability to detect touch locations. Next, it discusses the history of touchscreen development from 1971-1983. Benefits of touchscreens are then outlined, such as intuitive use without training. The document proceeds to describe four main touchscreen technologies: resistive, capacitive, infrared, and surface acoustic wave. It explains the construction of a basic touchscreen including the touch sensor, controller, and software driver. Applications are listed in various industries. Disadvantages involve screen size and dirt. The conclusion discusses the growing adoption of touchscreens in devices and their potential to replace mice and keyboards.