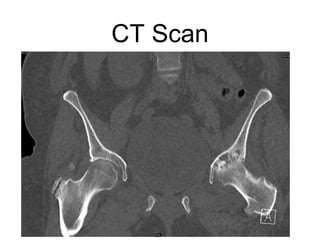
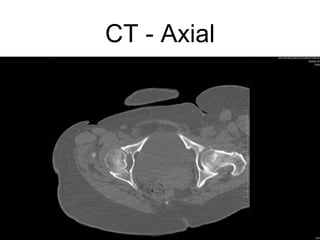
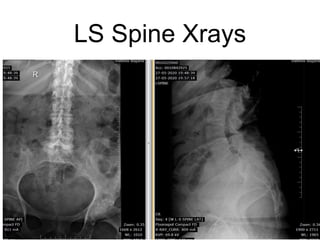
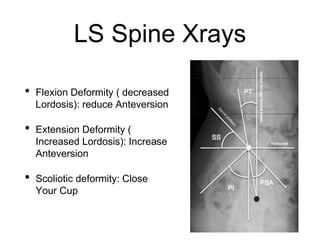
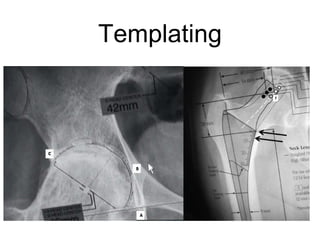
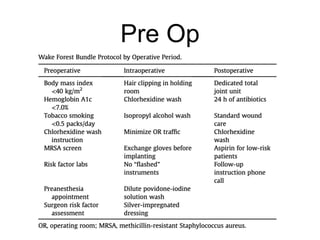
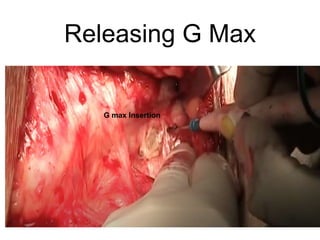
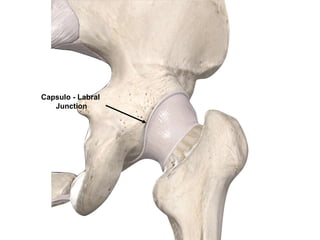
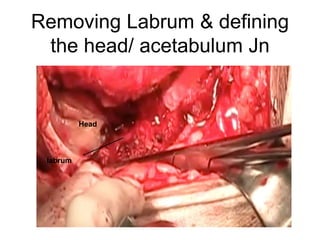
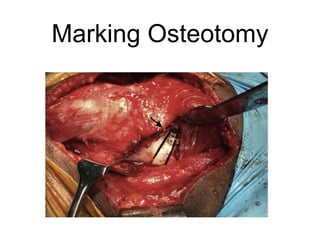
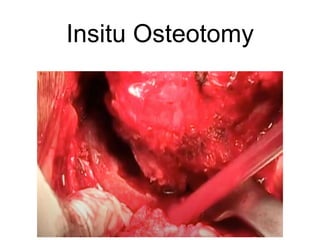
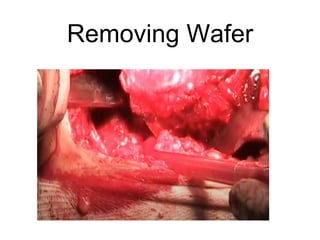
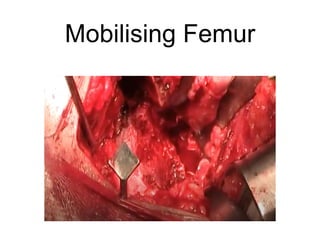
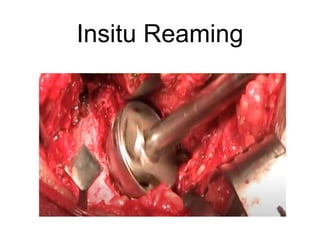
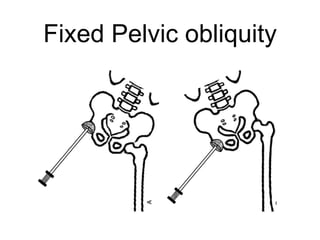
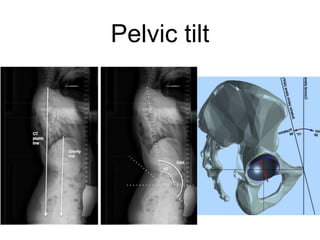
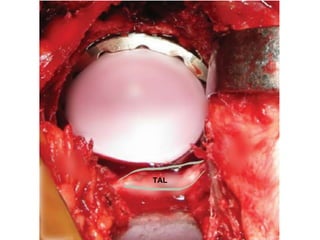
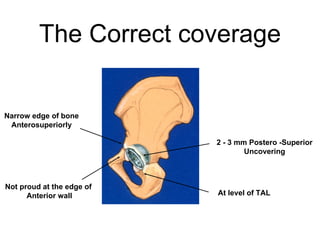
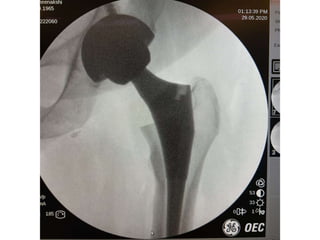
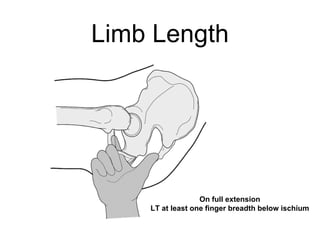
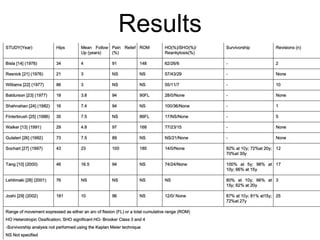
The document outlines surgical tips for addressing ankylosing spondylitis, focusing on preoperative planning, anesthesia, positioning, and exposure techniques. It emphasizes the importance of proper diagnosis and anatomical considerations, including deformities and imaging, to ensure successful hip procedures. Key recommendations include meticulous preparation, adequate exposure and soft tissue preservation, and careful reaming and positioning of components to restore hip biomechanics.