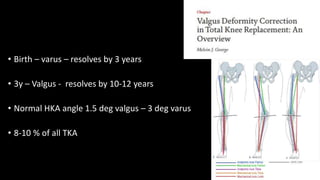
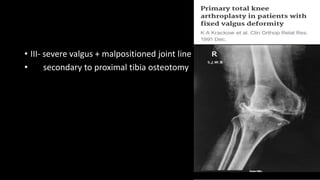
This document discusses total knee arthroplasty (TKA) for valgus knees. It defines valgus knee deformity and classifications. The lateral parapatellar surgical approach is described as advantageous over the medial parapatellar approach for valgus knees, avoiding additional soft tissue releases. Key challenges include lateral femoral hypoplasia, externally rotated tibia, and lateral tibial defects. Surgical techniques involve lateral releases and pie crusting to balance the knee in extension and flexion. Complications can include common peroneal nerve palsy and hindfoot deformities requiring correction.