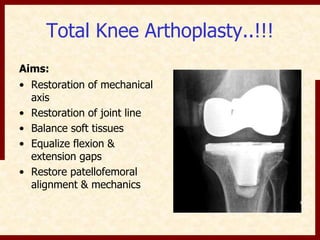
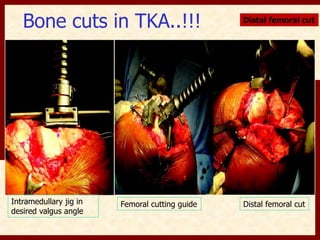
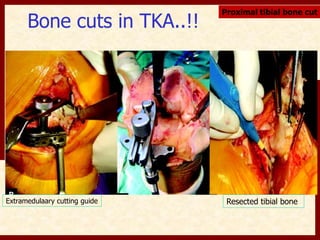
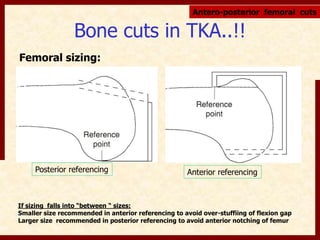
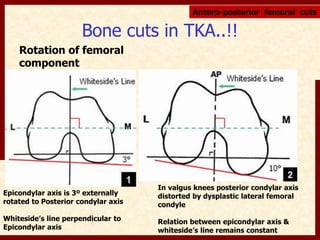
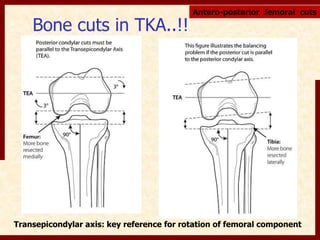
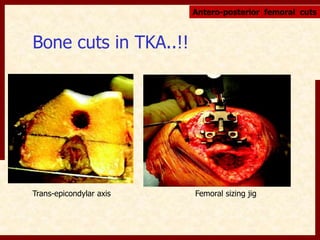
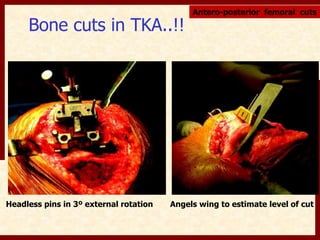
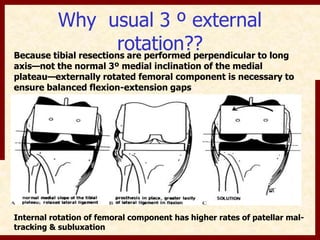
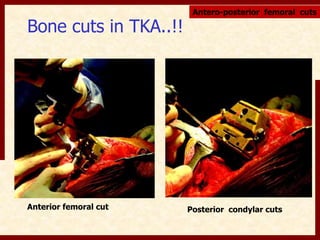
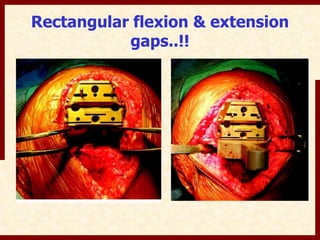
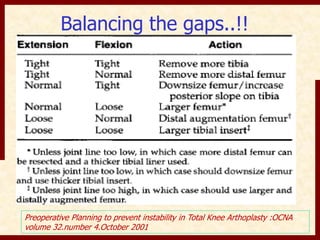
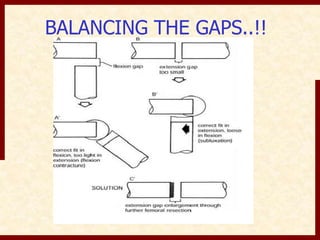
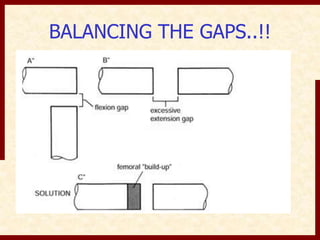
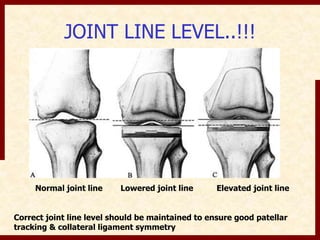
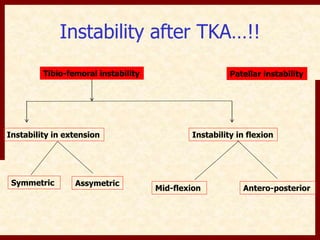
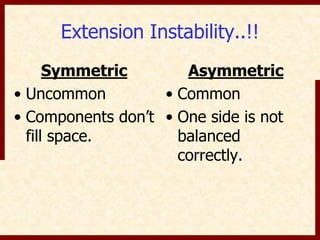
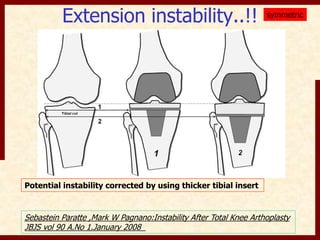
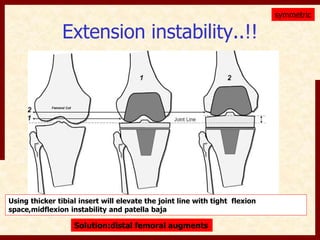
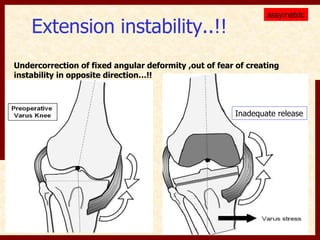
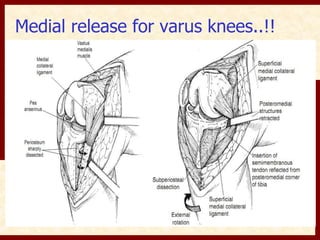
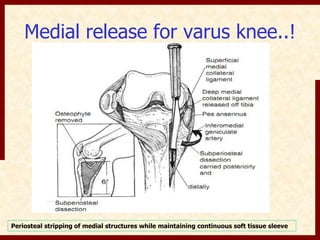
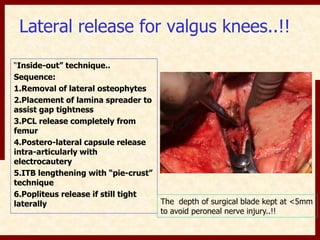
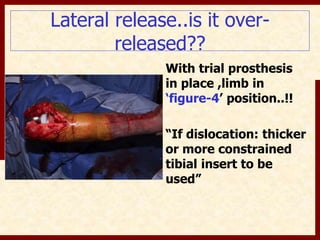
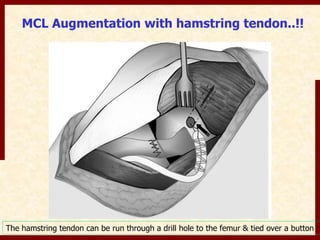
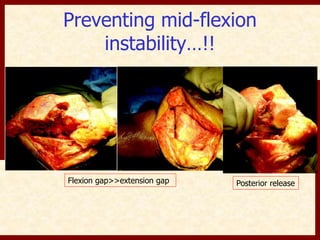
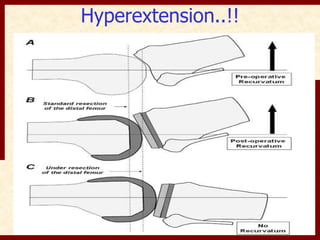
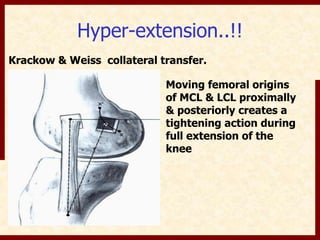
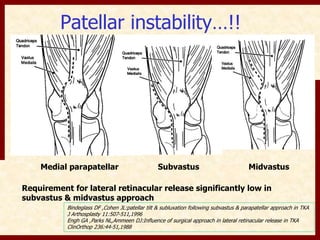
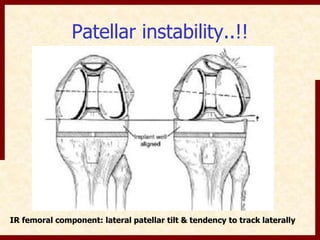
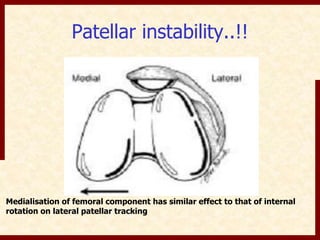
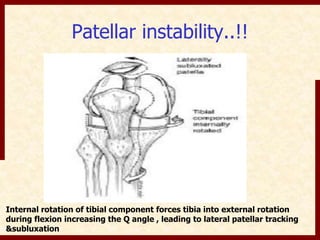
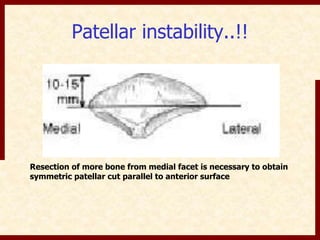
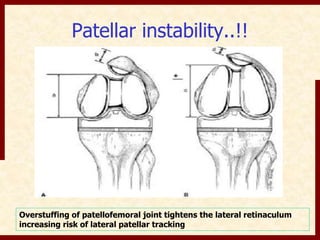
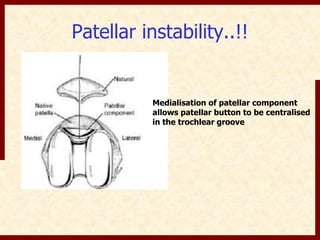
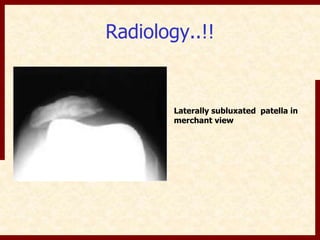
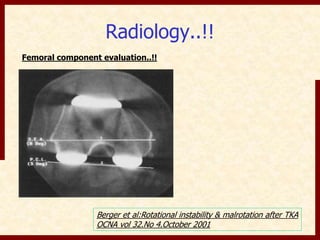
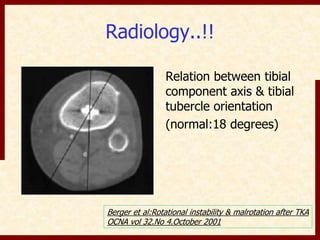
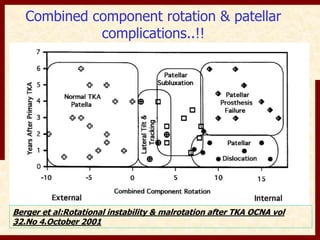
This document discusses instability after total knee arthroplasty (TKA). It begins by outlining the goals and basic principles of TKA. It then describes the bone cuts made during TKA and emphasizes that resection of the proximal tibia influences both flexion and extension gaps. The document discusses various causes of instability after TKA including improper bone cuts, soft tissue imbalance, and component malpositioning. It provides details on managing different types of instability such as instability in extension, flexion, and mid-flexion. Prevention of instability through proper bone cuts and soft tissue balancing is emphasized.