Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times


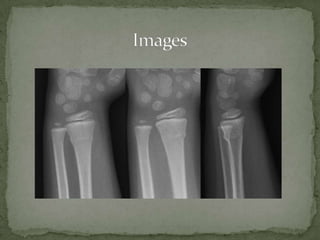
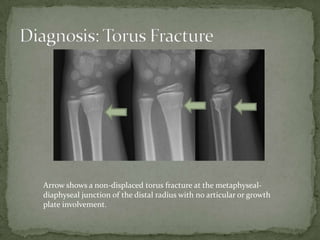


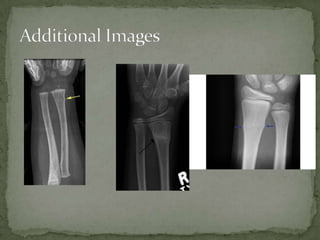

A 7-year-old boy presented with right arm pain after falling on an outstretched arm while playing. Examination revealed tenderness over the distal forearm with full range of motion of the fingers and intact neurovascular status. X-ray showed a non-displaced torus fracture of the distal radius. Treatment consists of splinting and a short arm cast for 3 weeks for comfort and prevention of further injury, with no reduction needed. Torus fractures are unique to children and occur when pediatric bone buckles rather than fully fracturing under axial loads.







