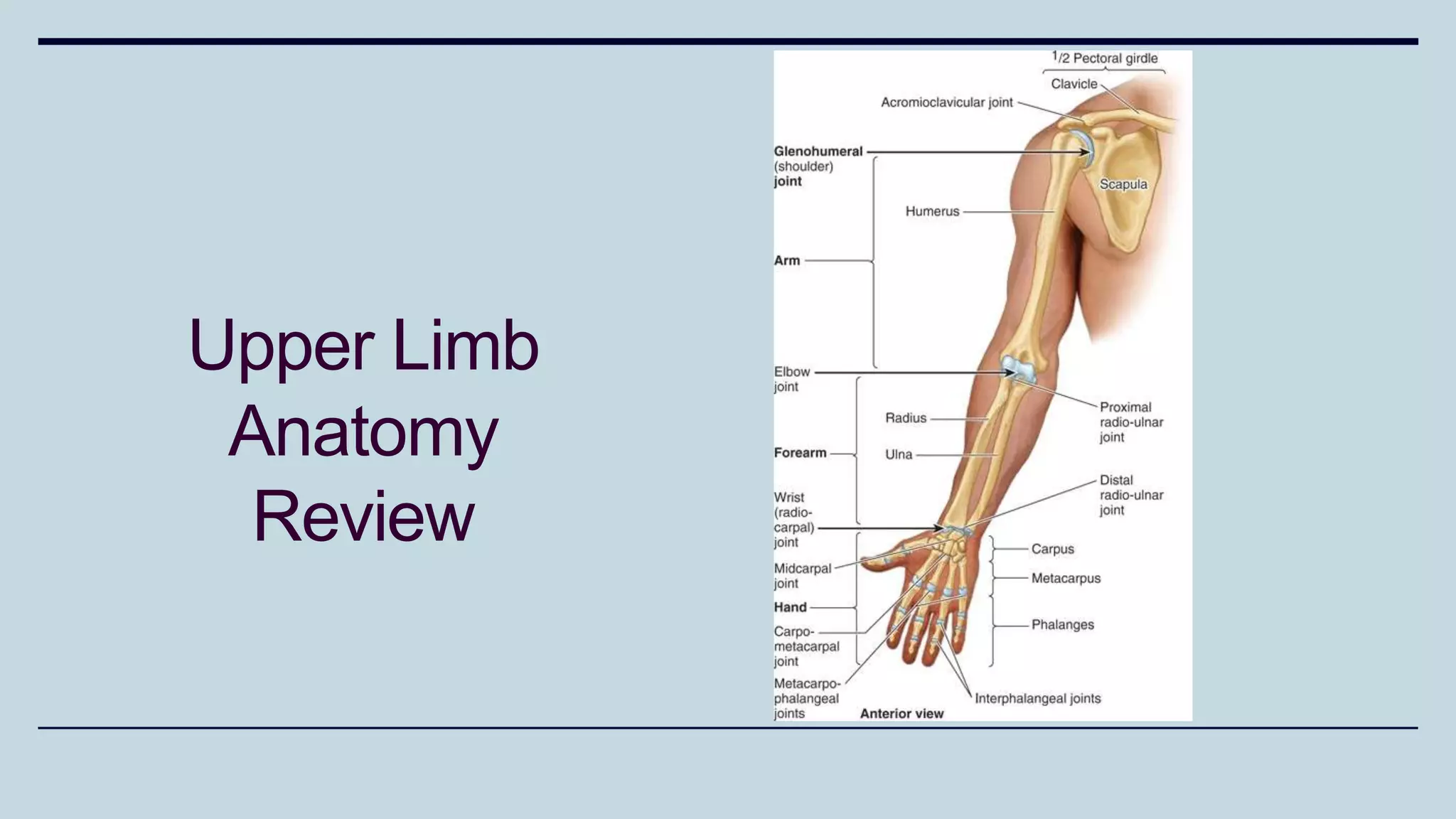
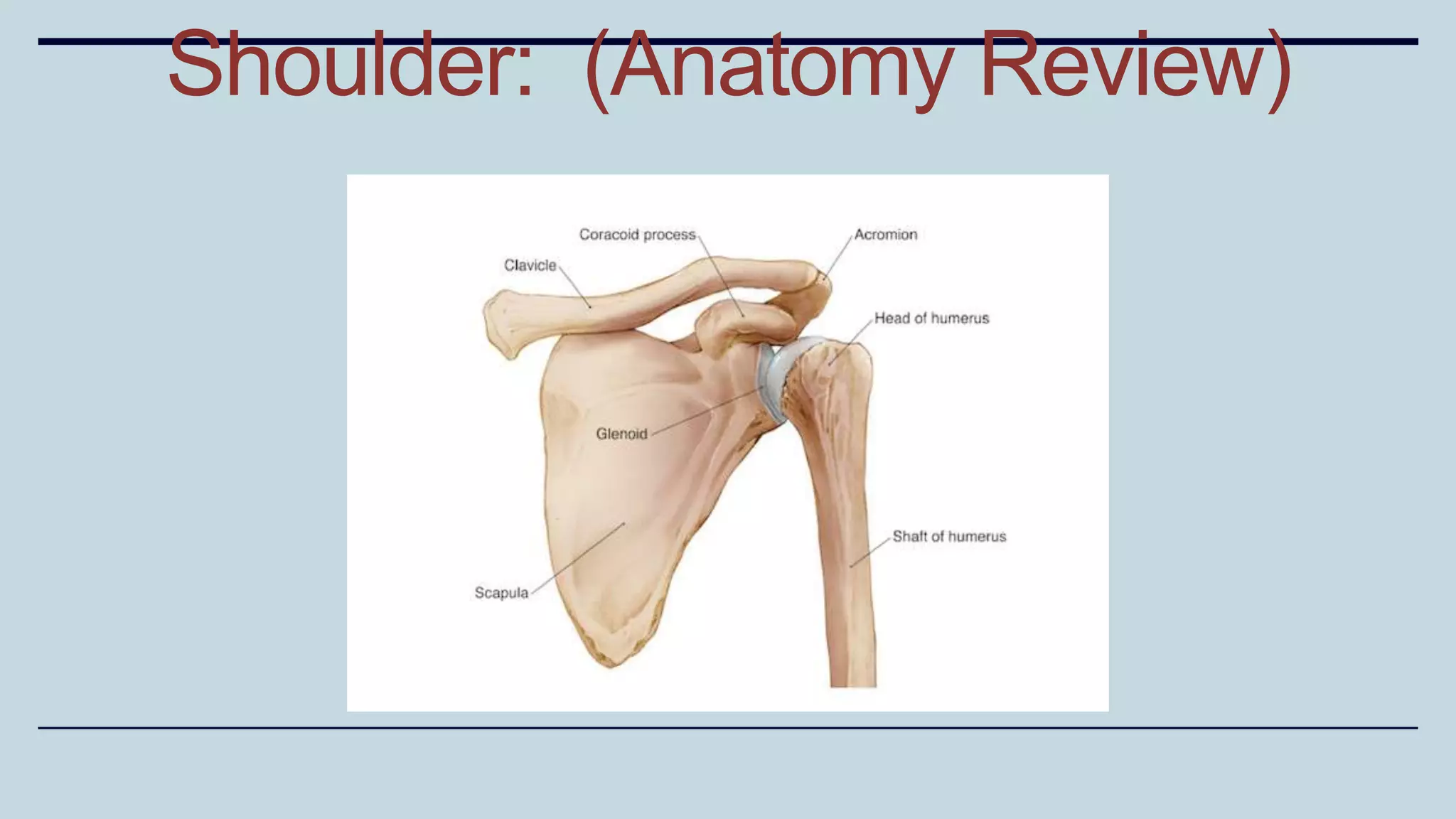
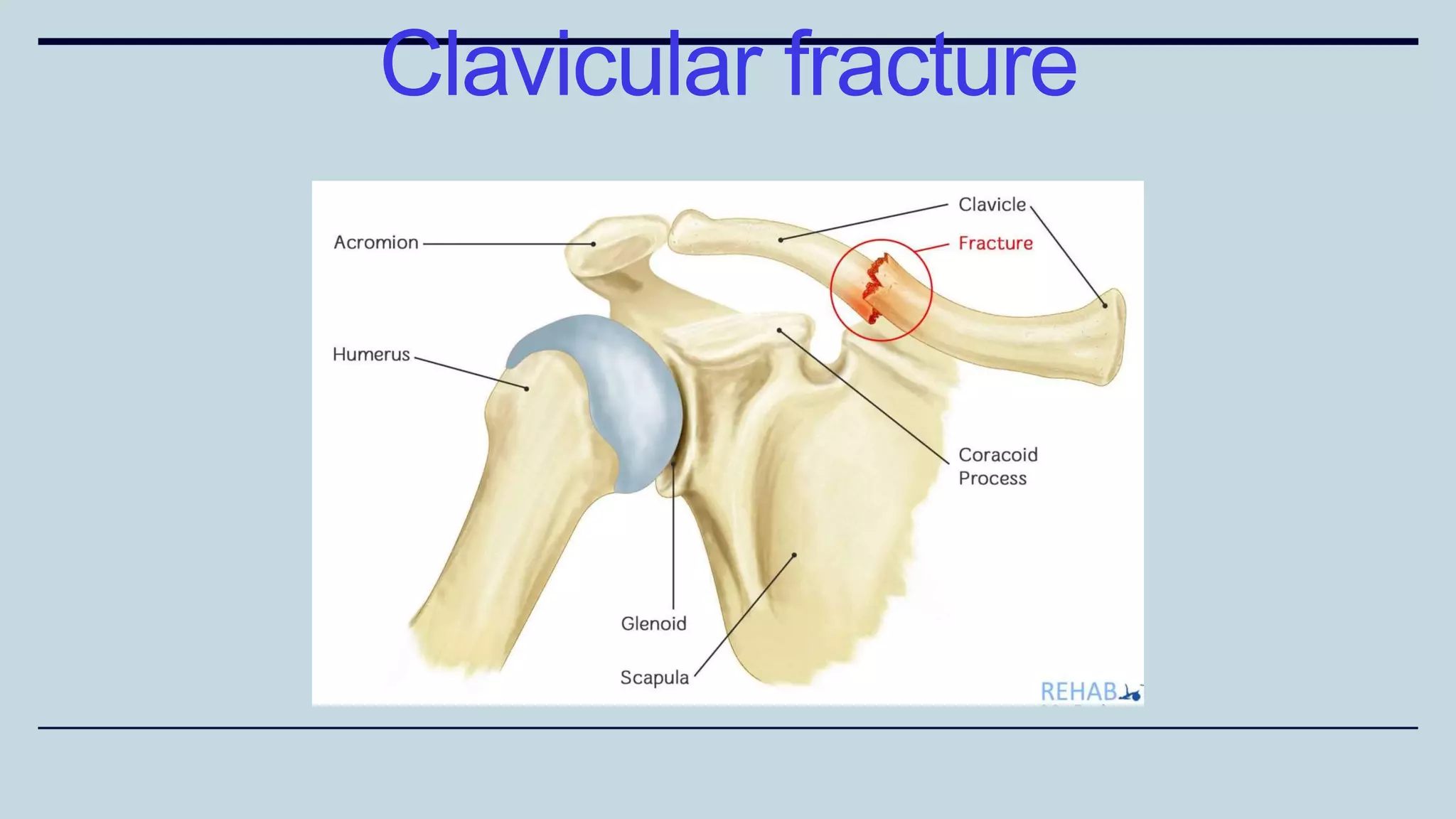
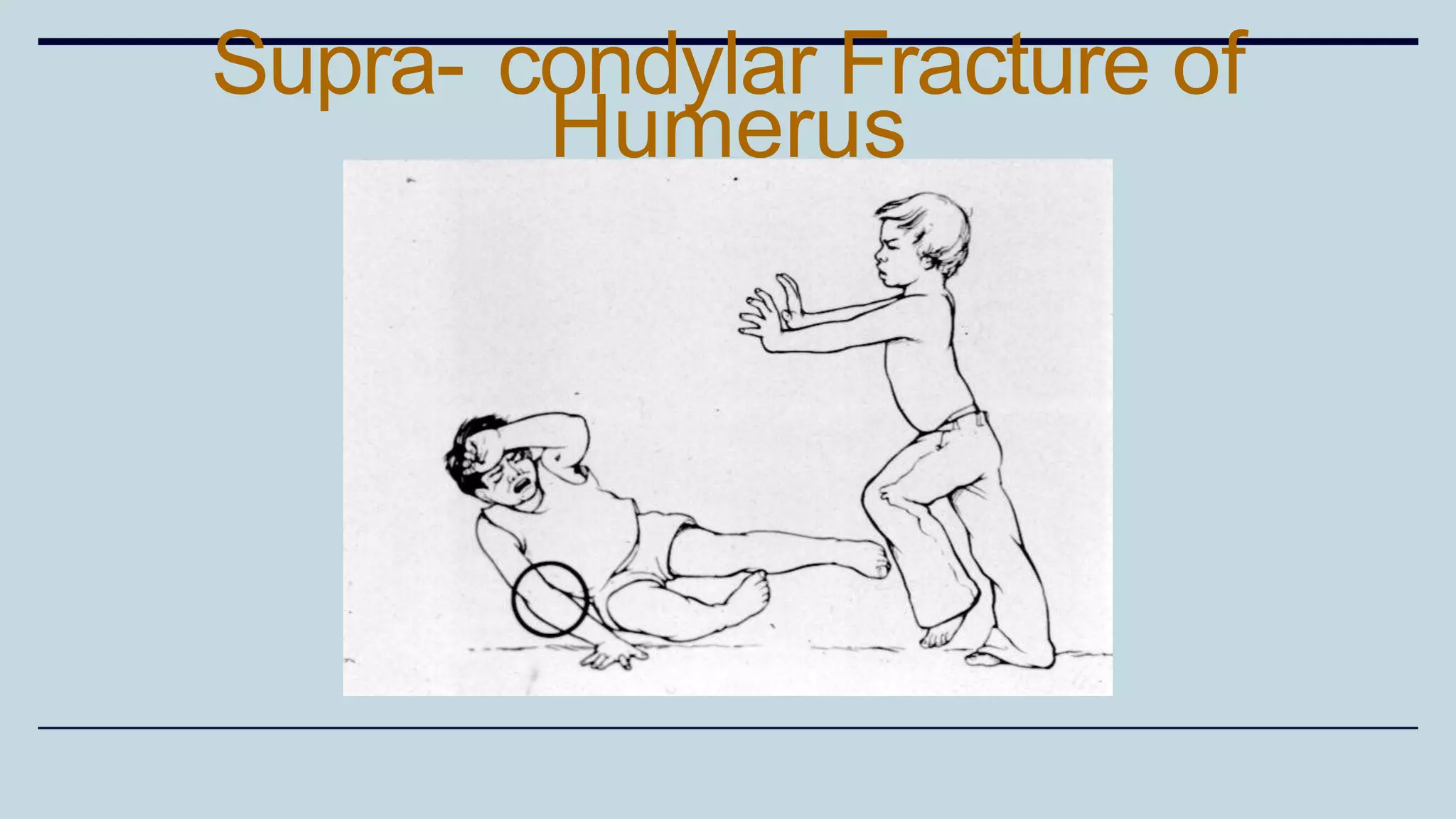
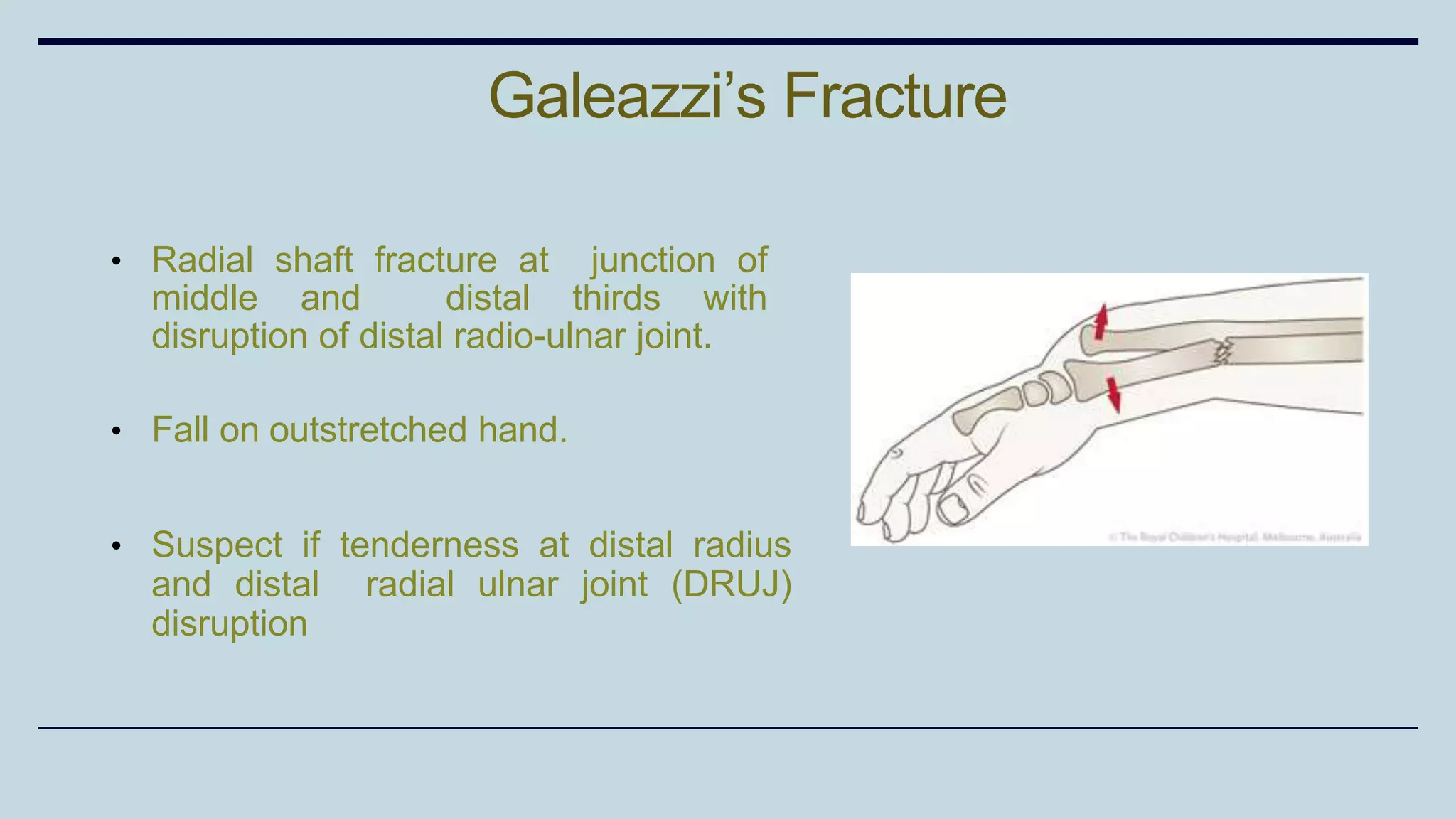
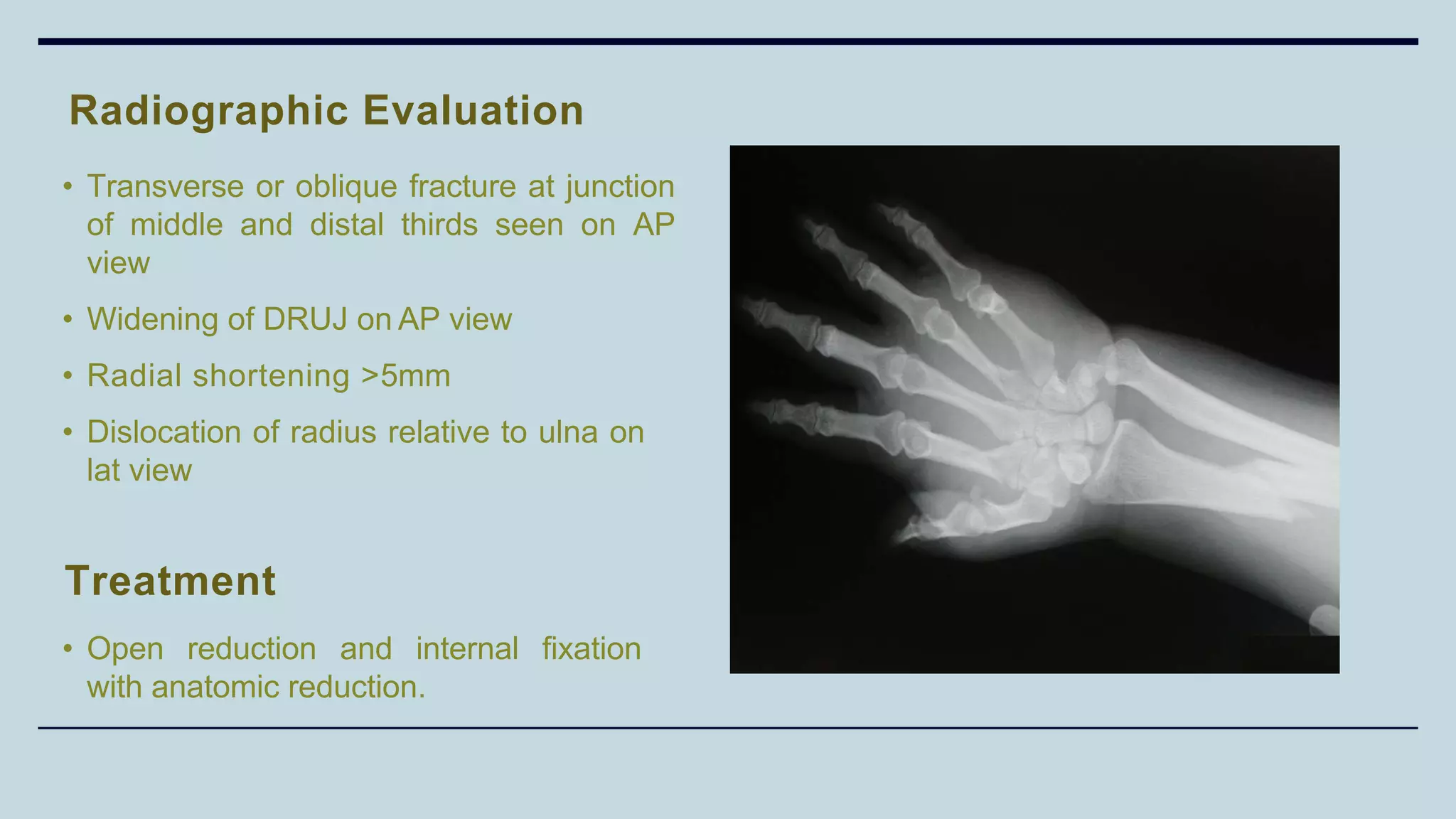
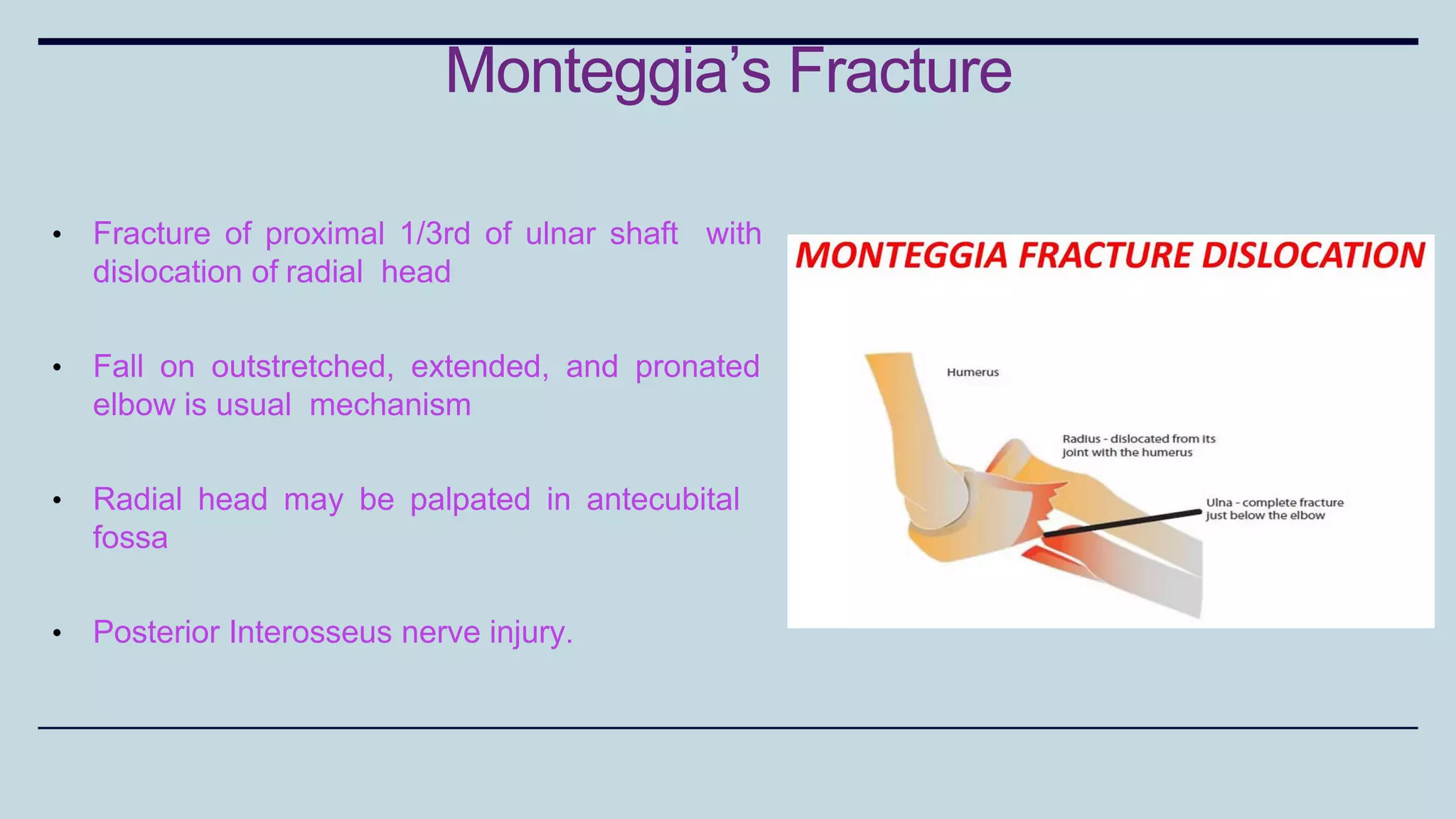
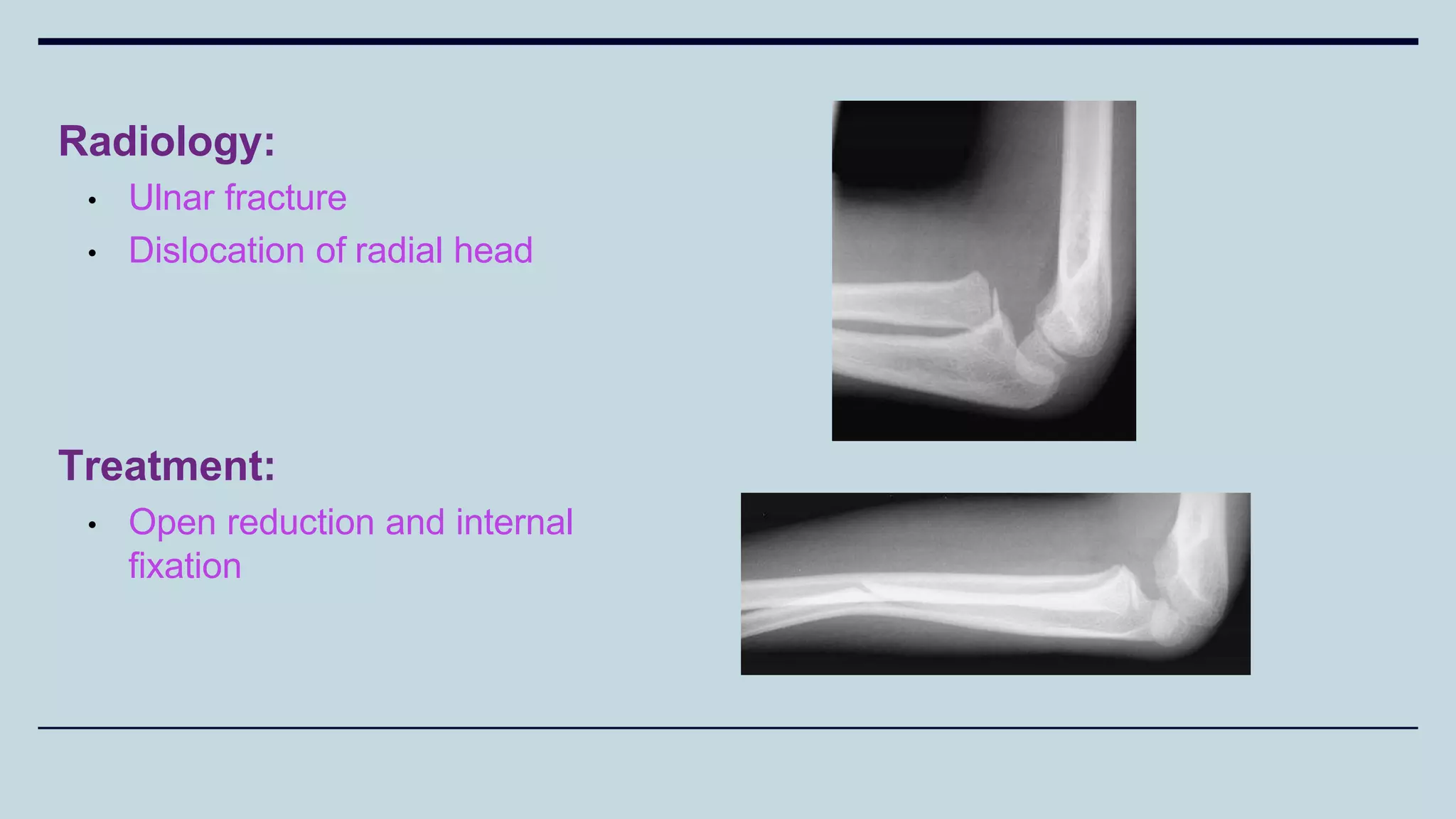
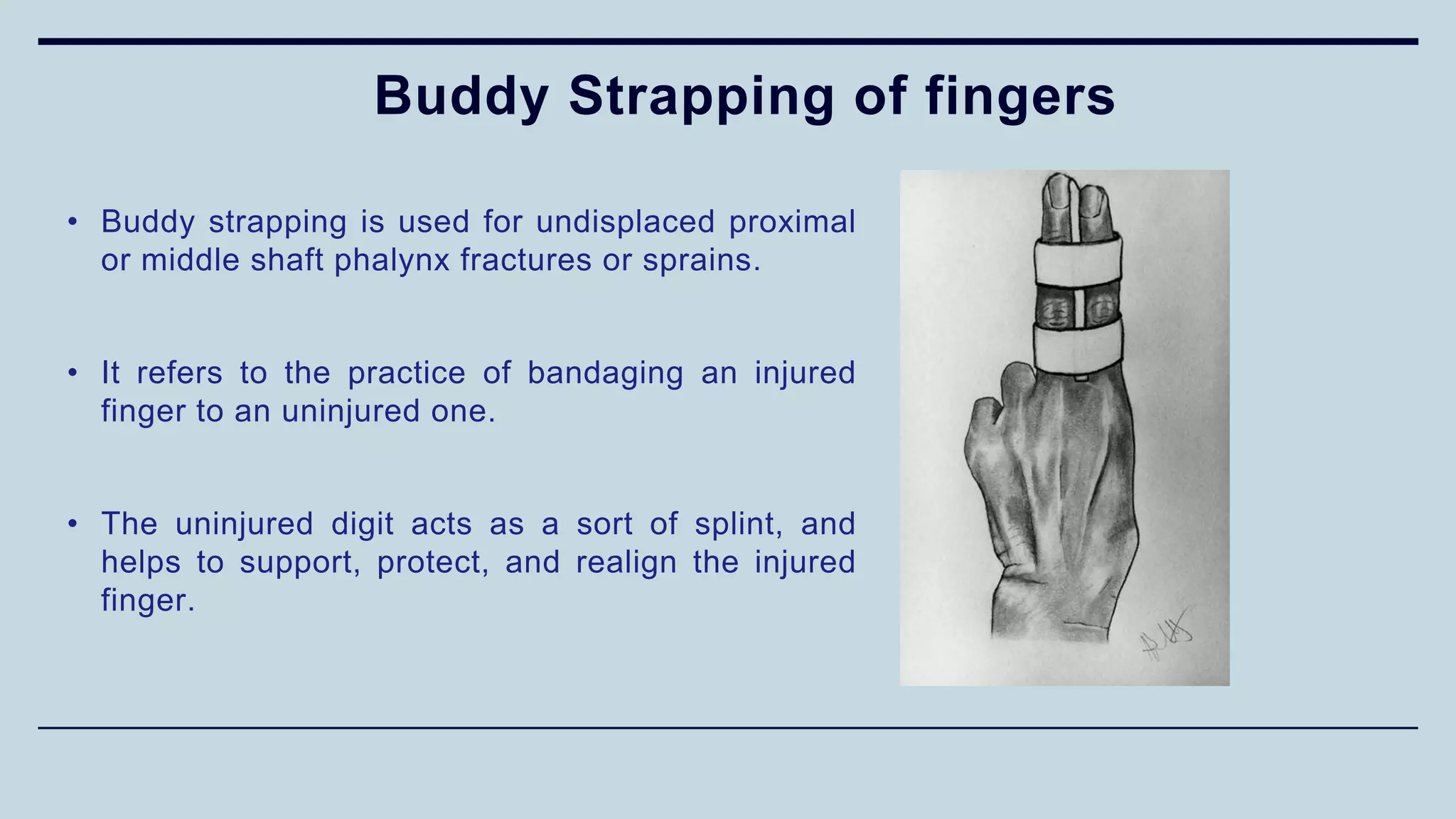
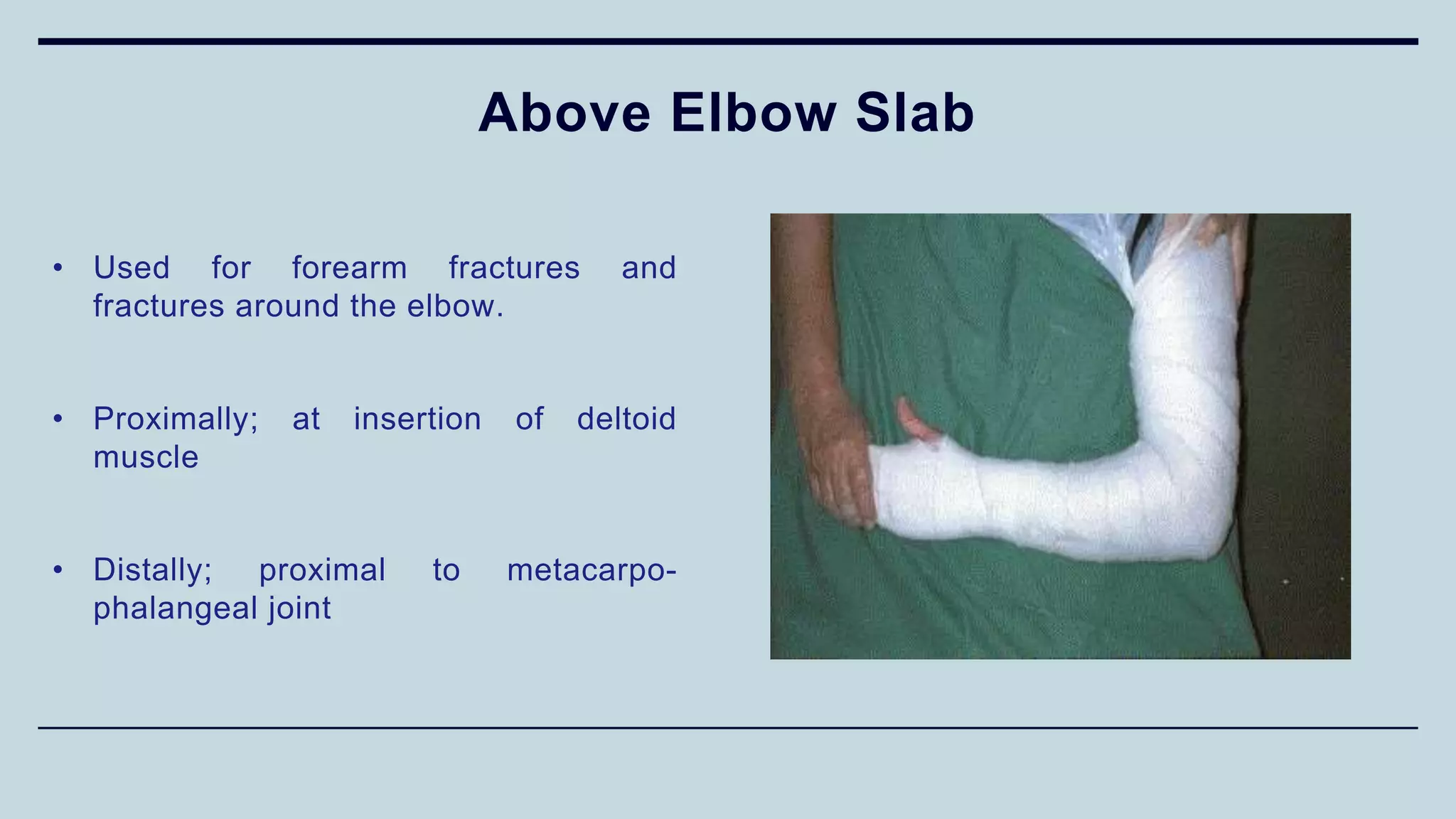
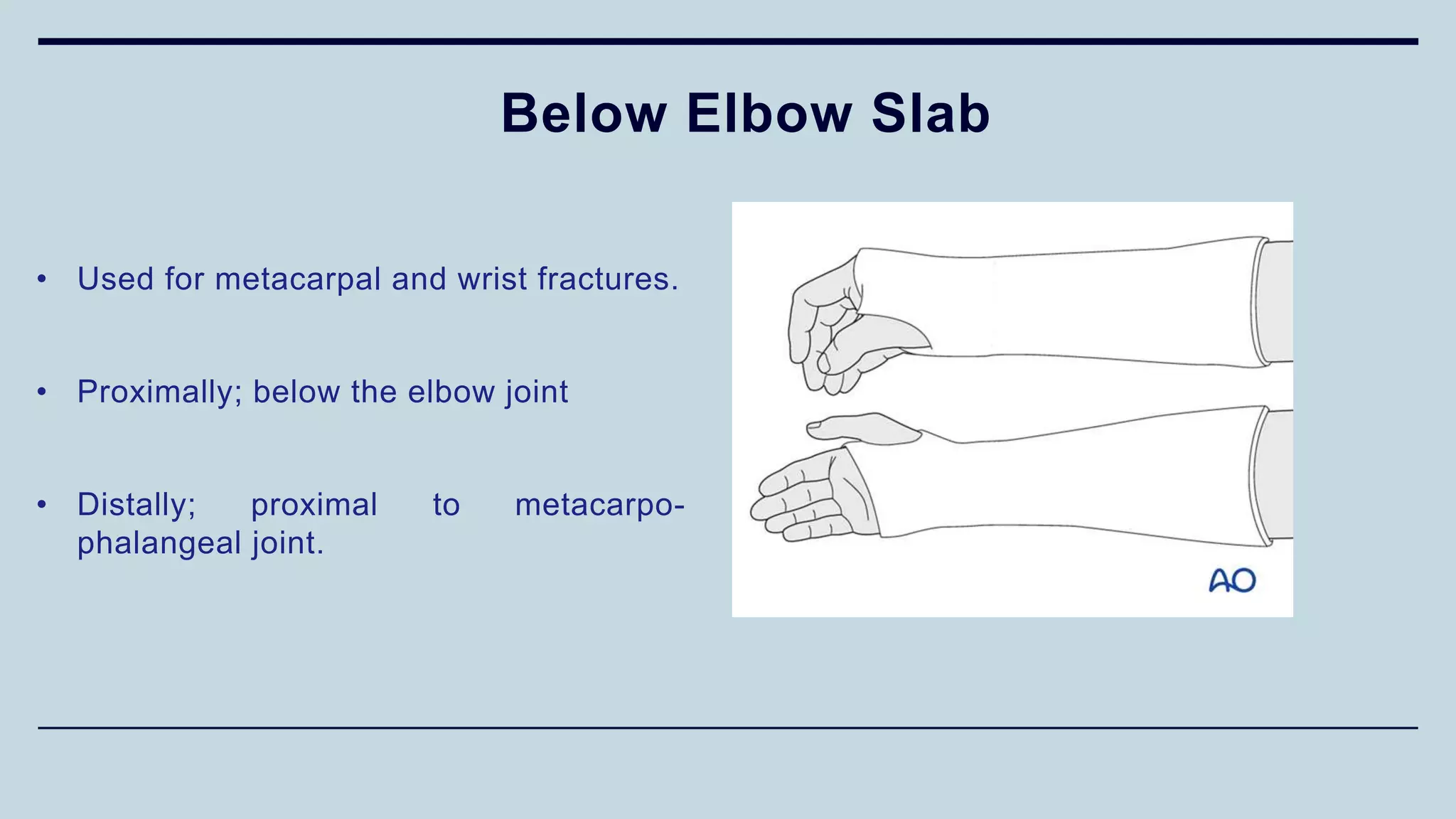
1) The document discusses various types of upper limb trauma including fractures and dislocations of the shoulder, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand.
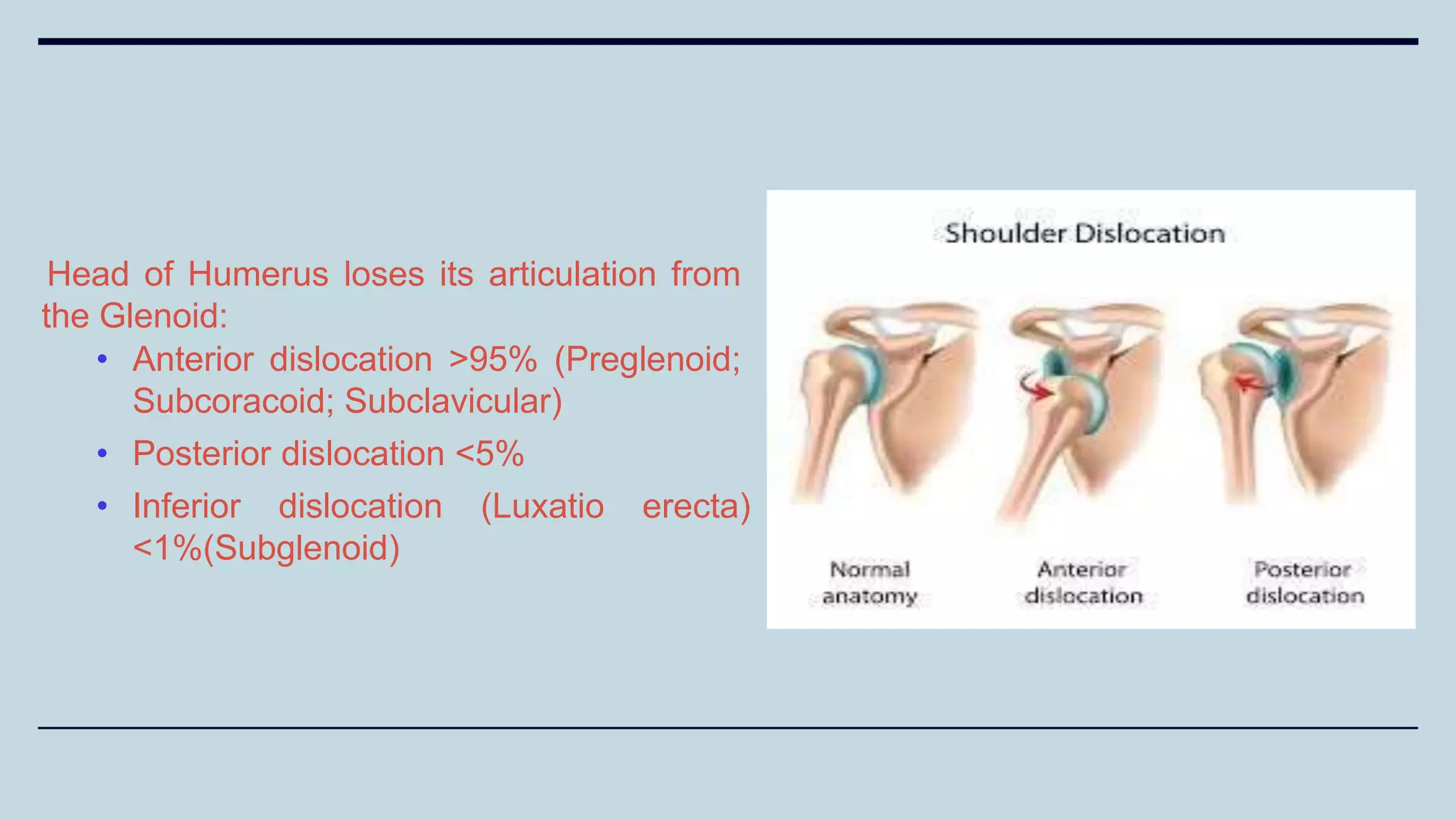
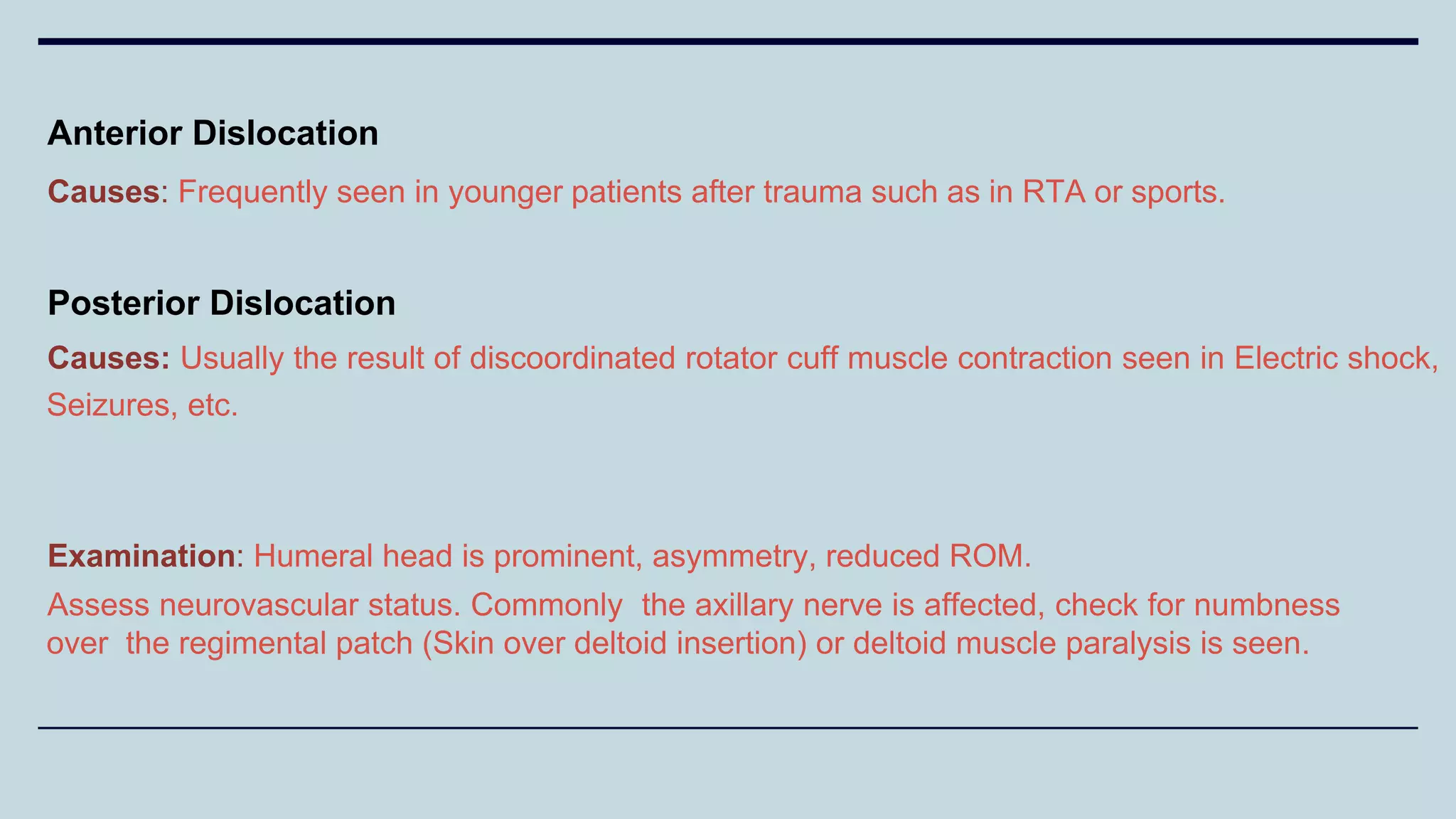
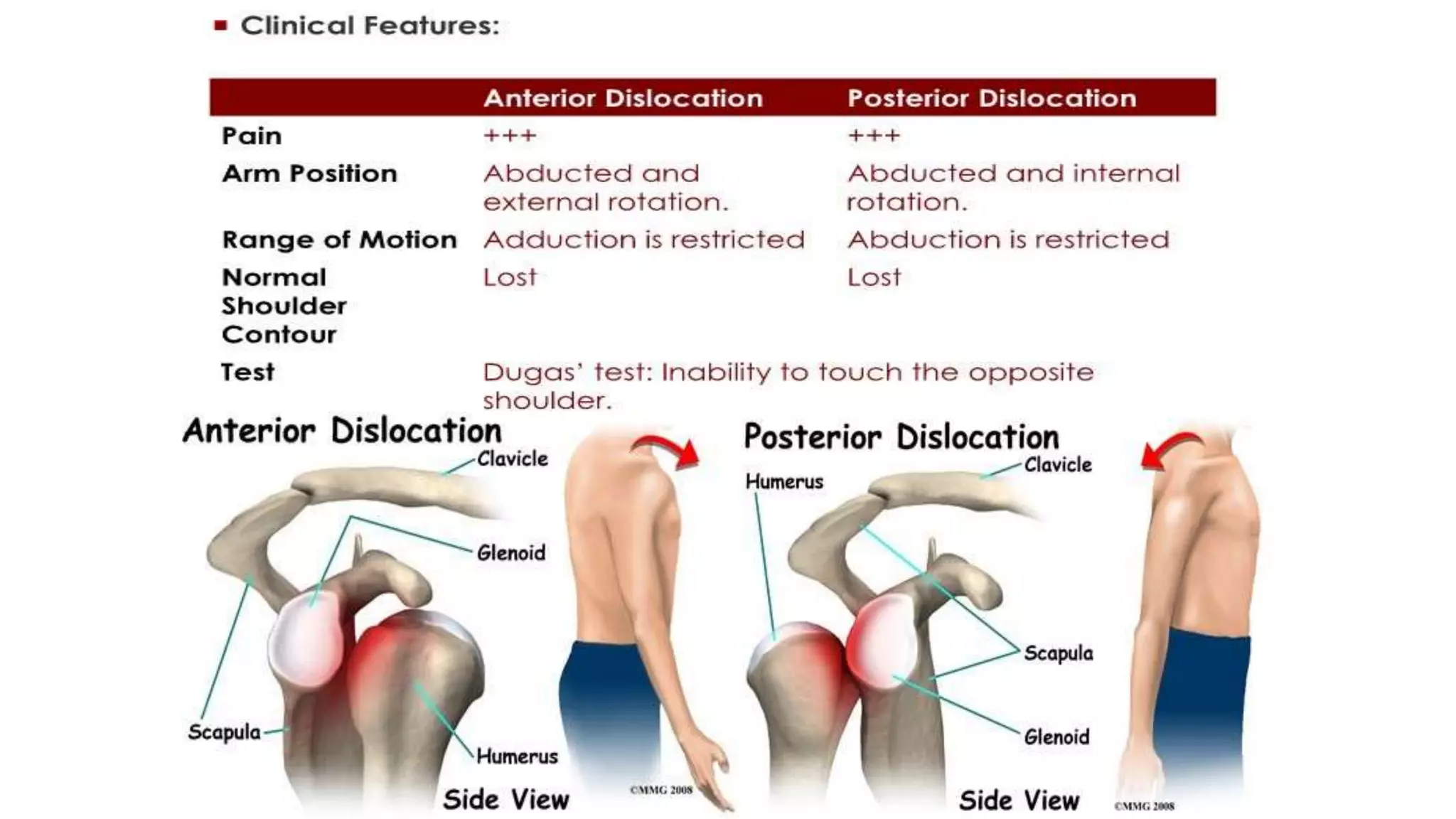
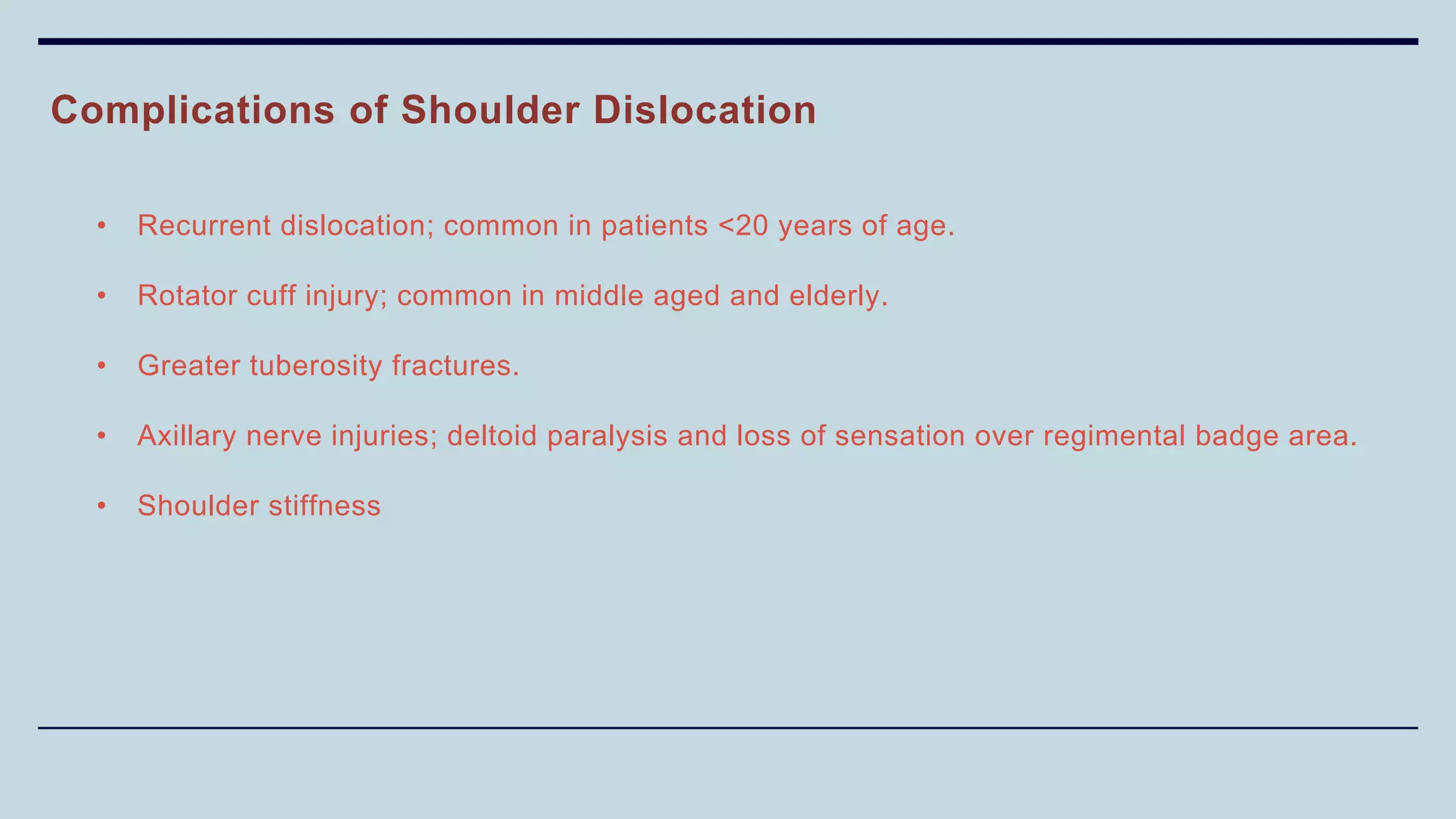
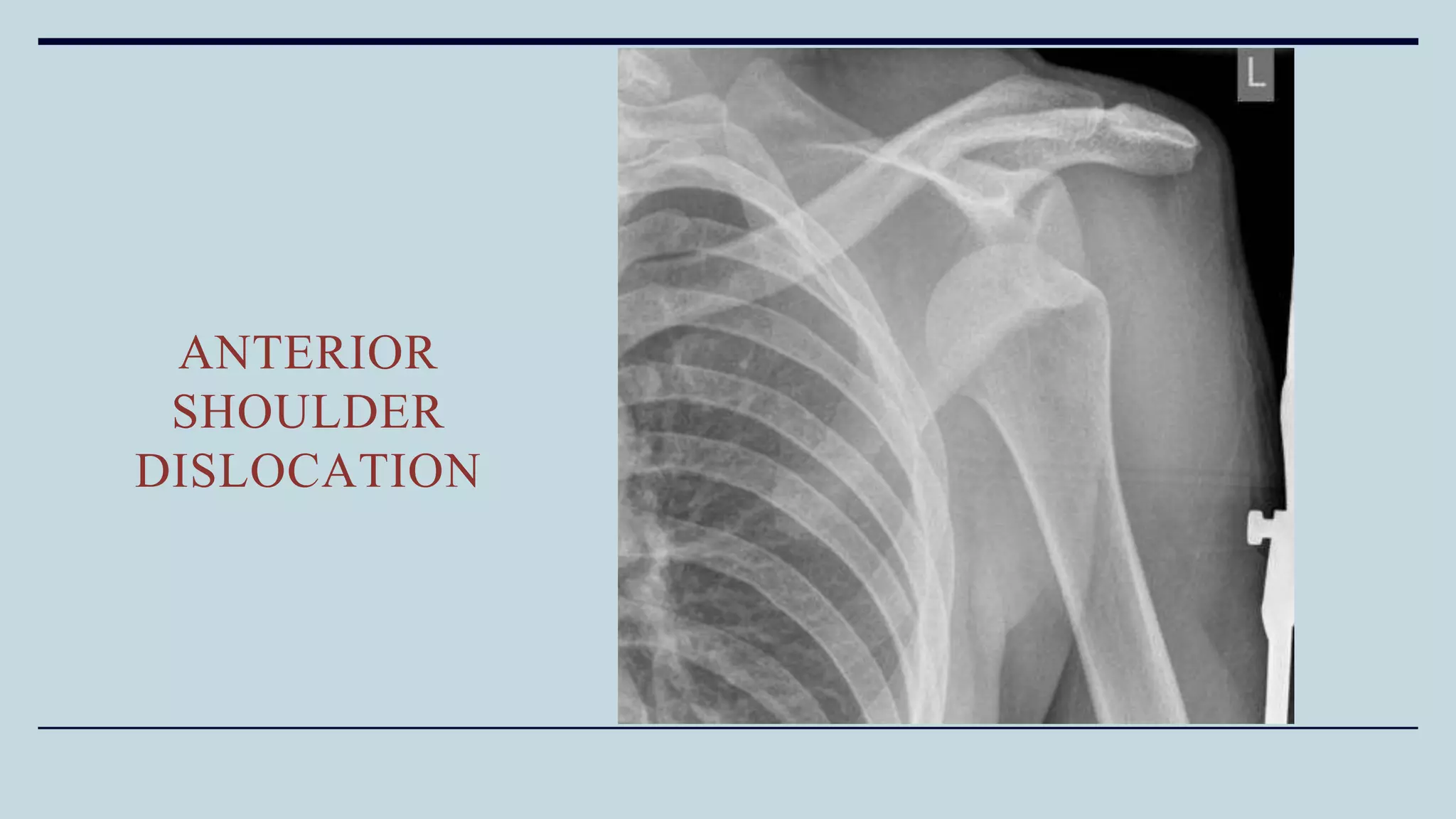
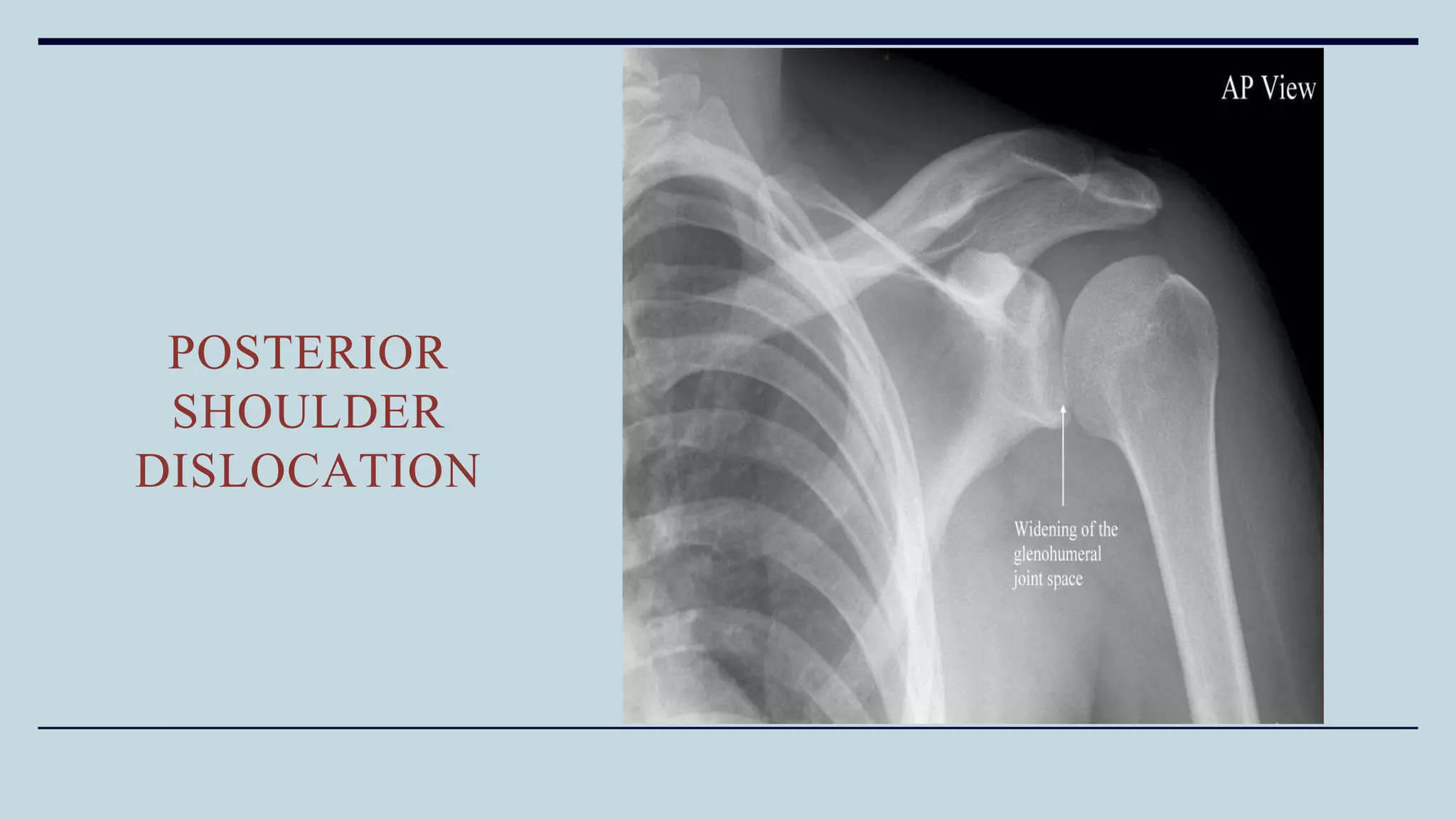
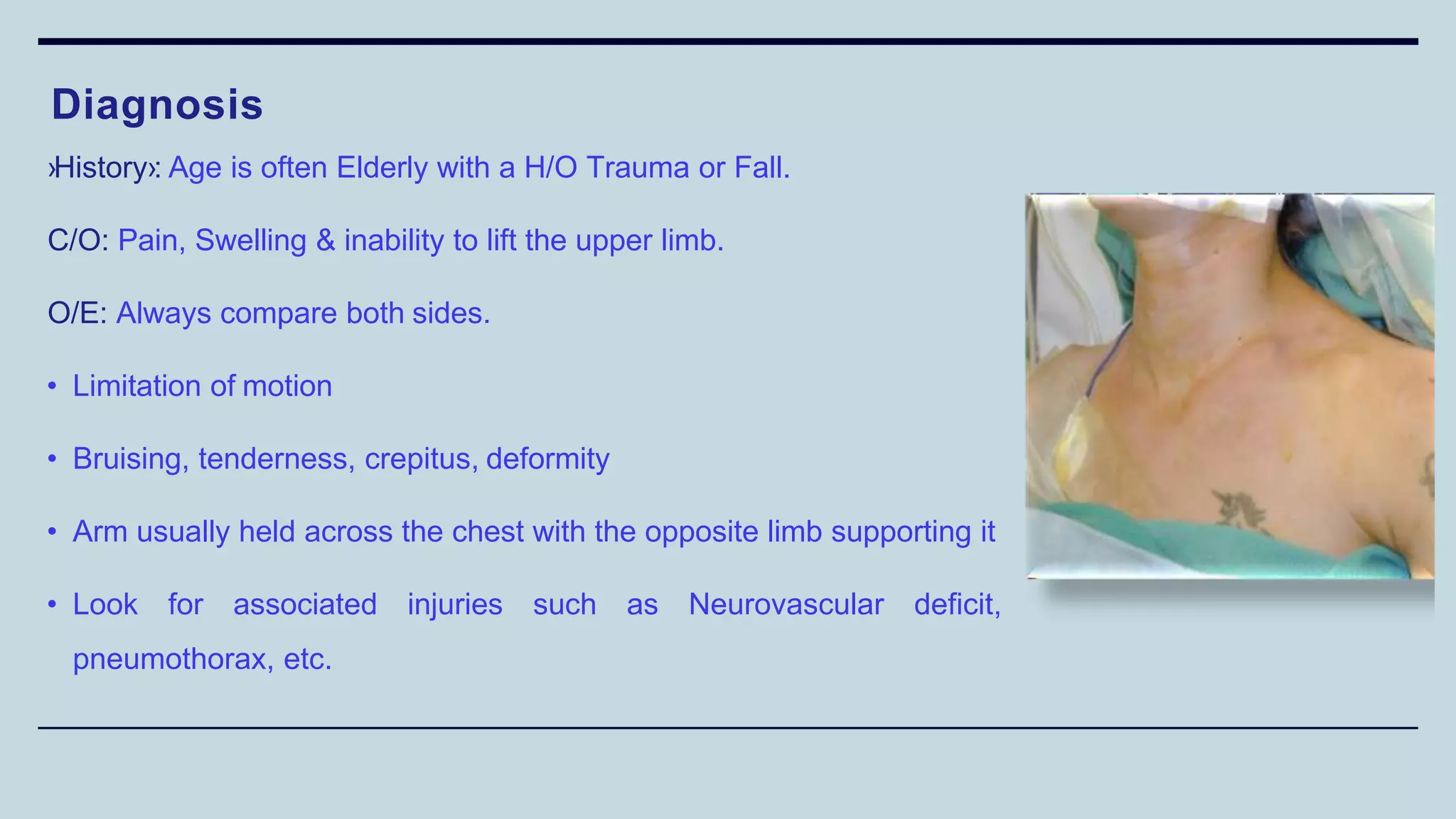
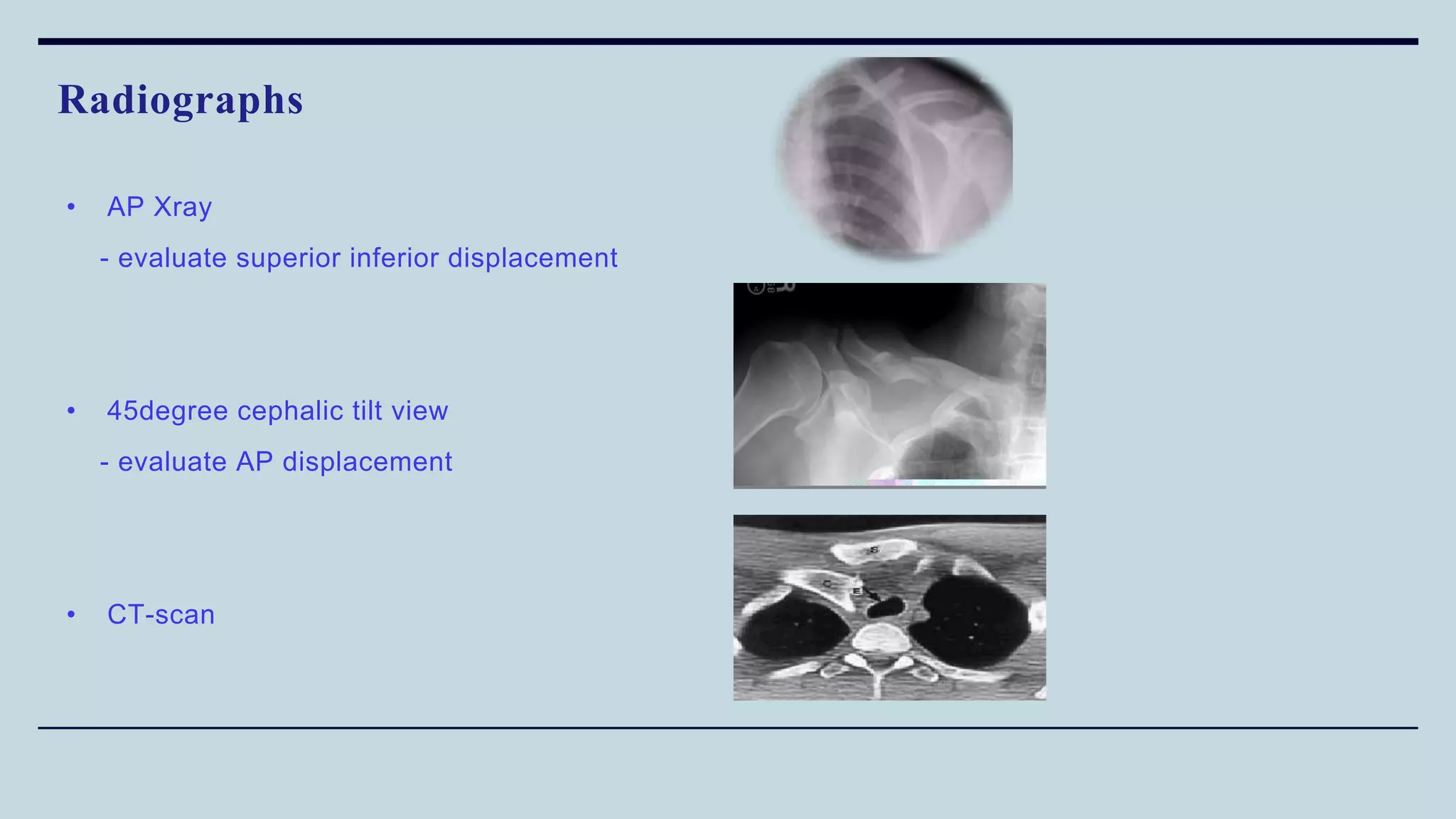
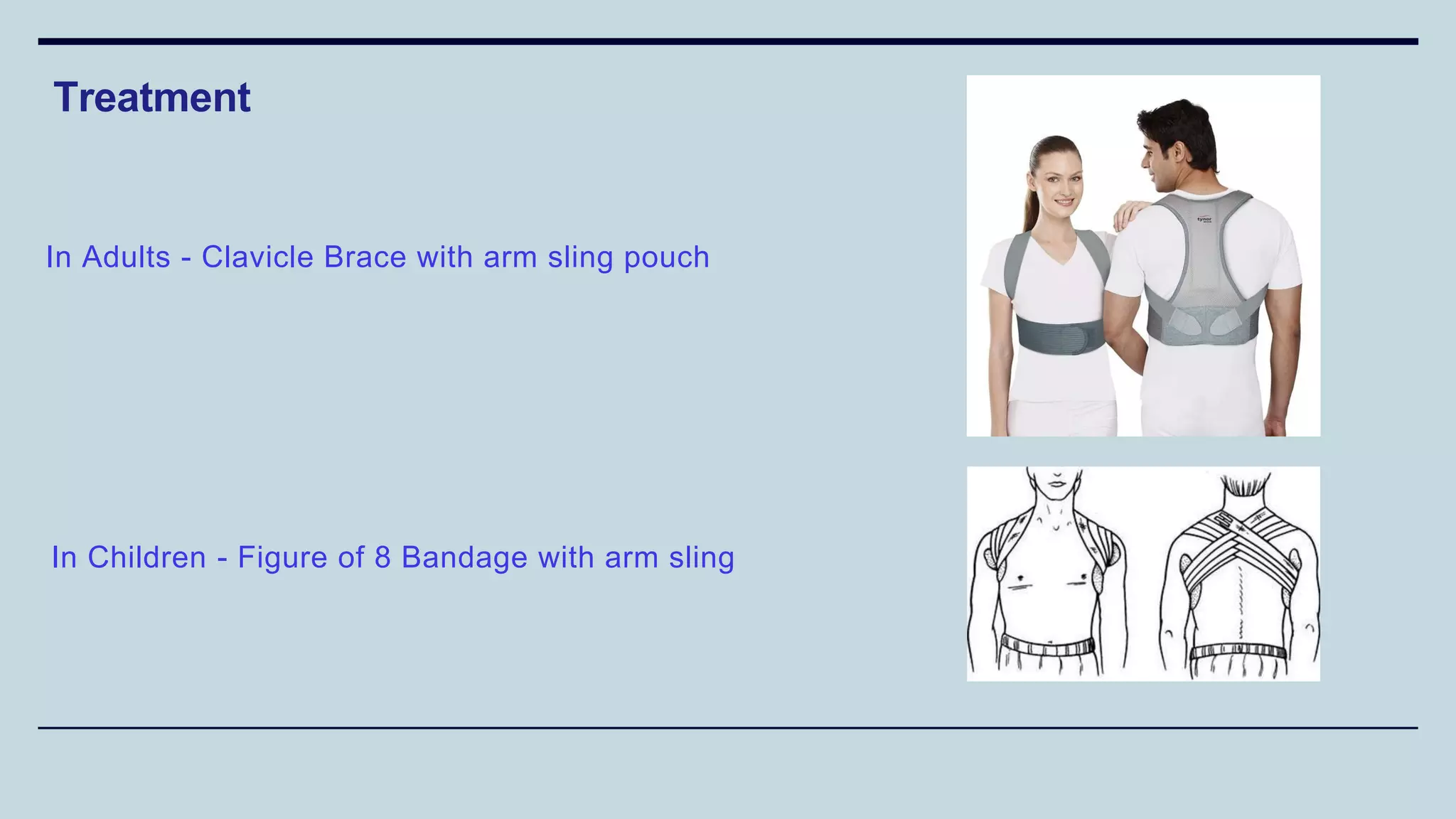
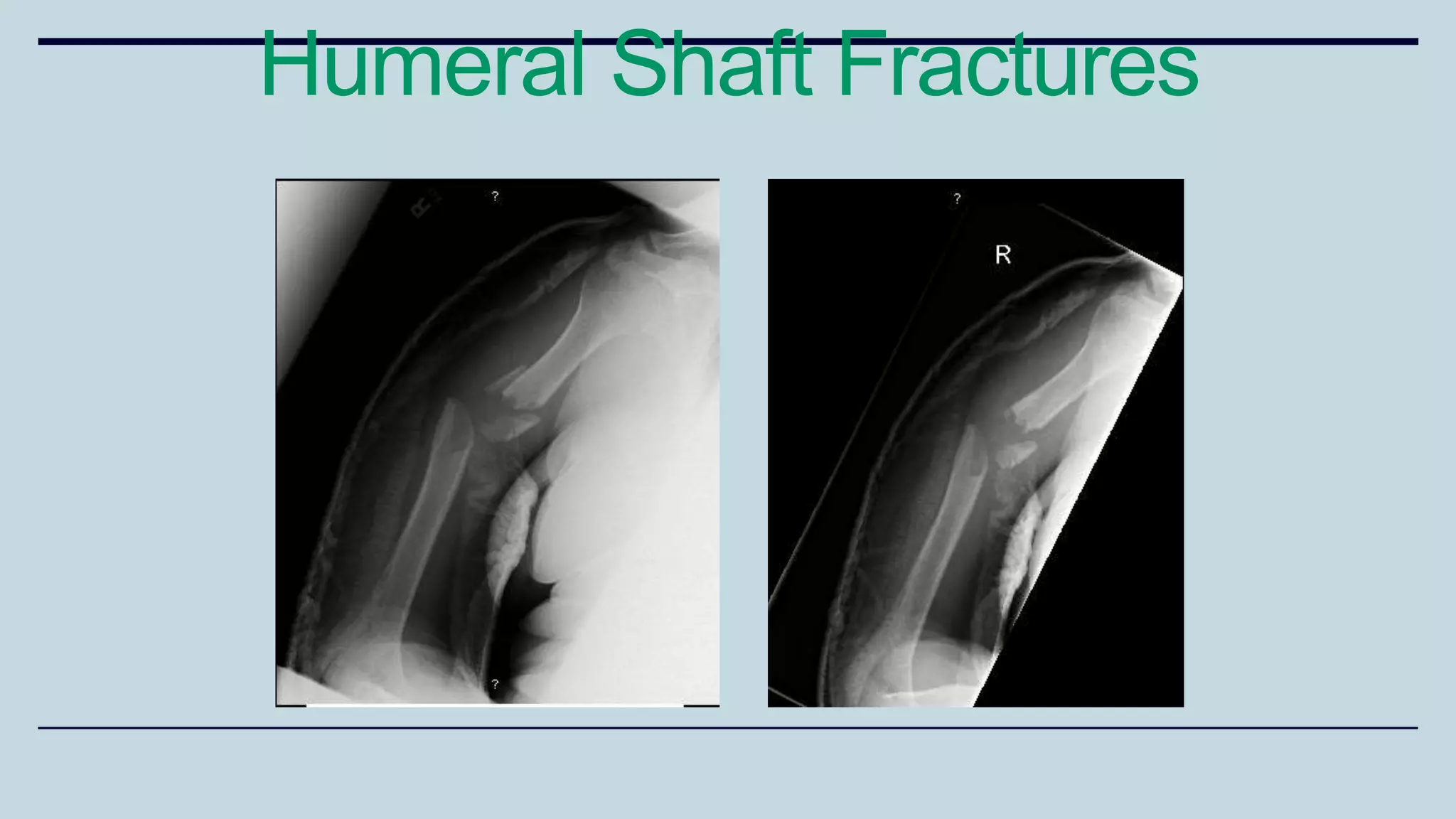
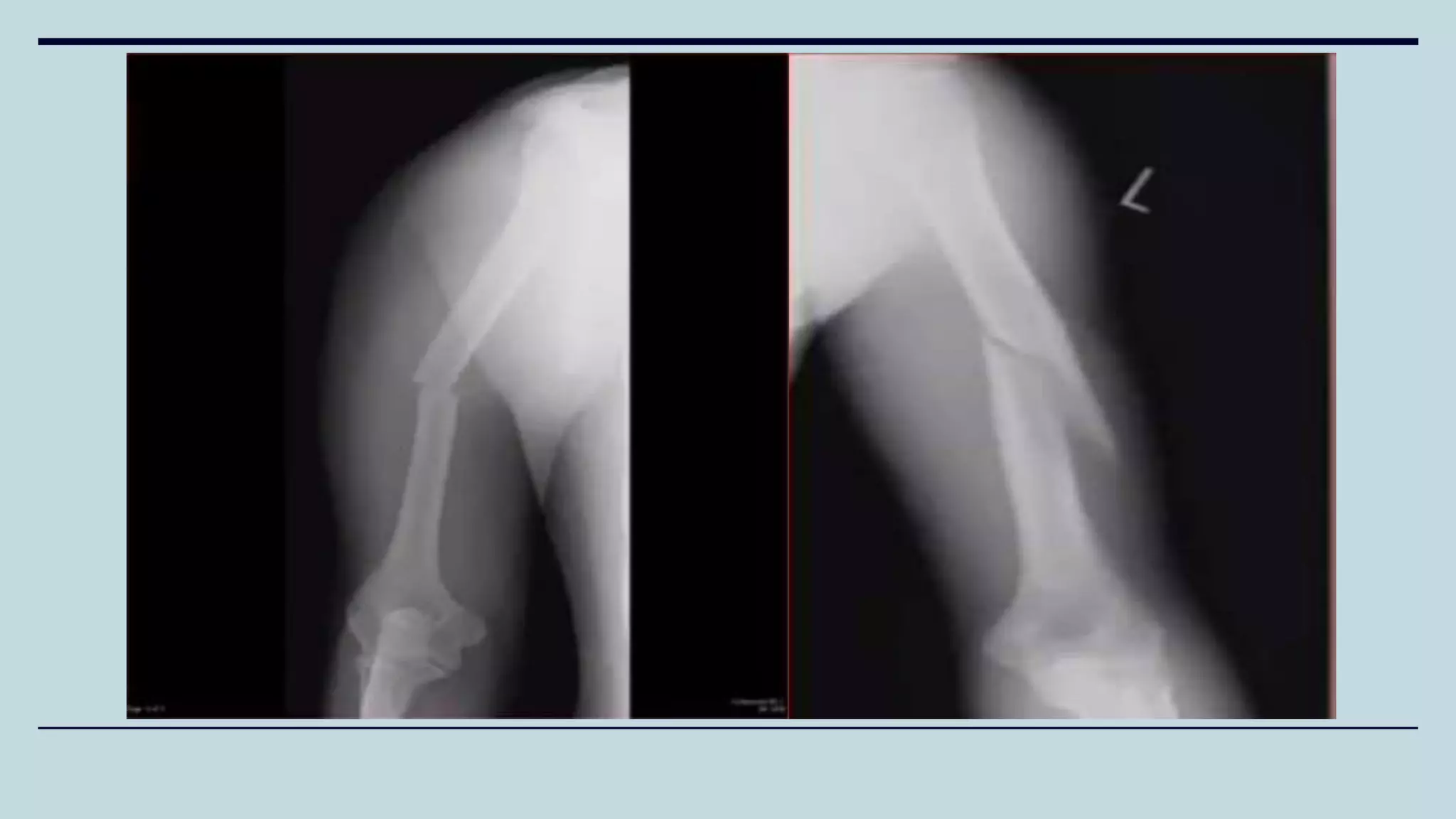
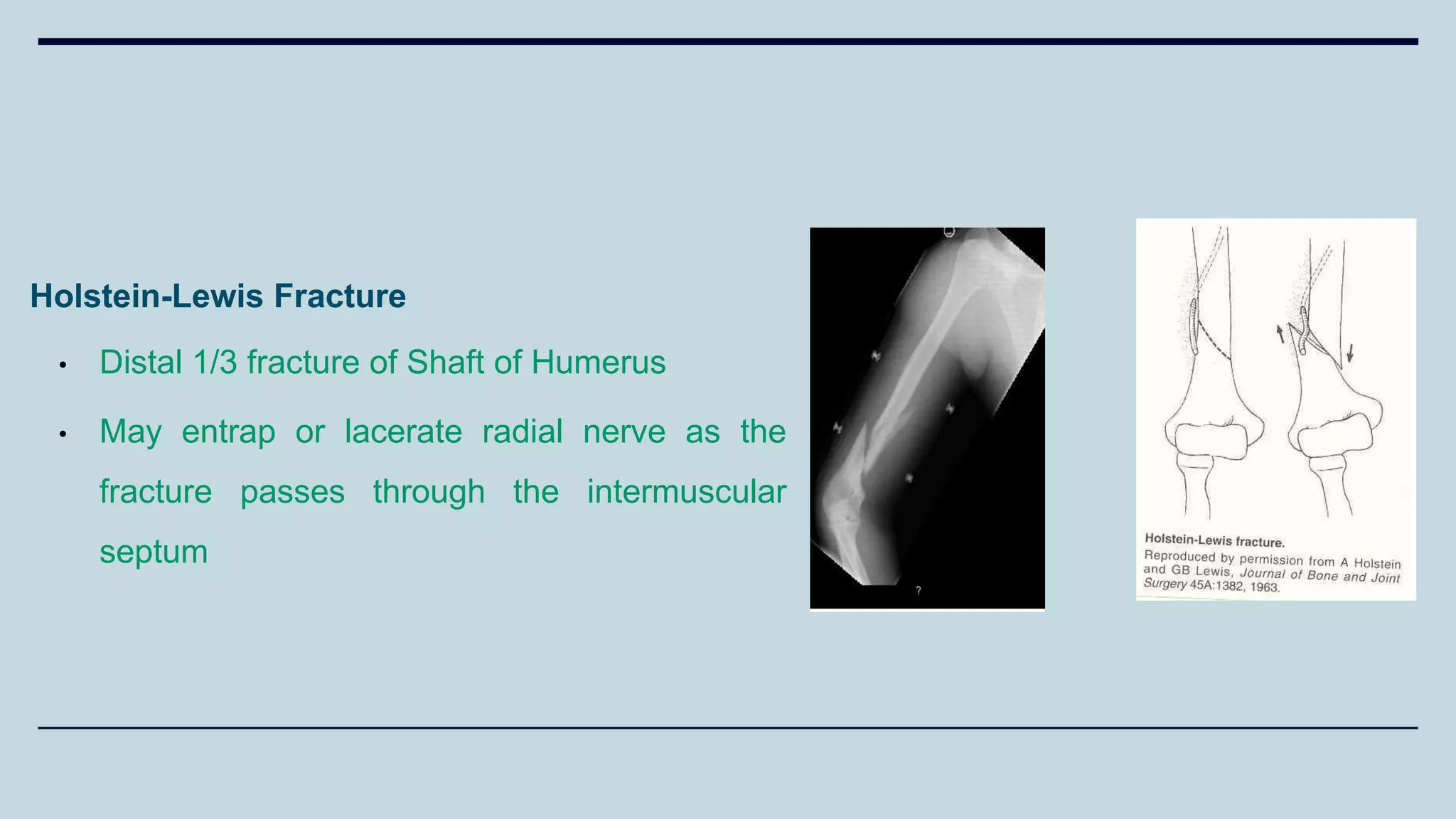
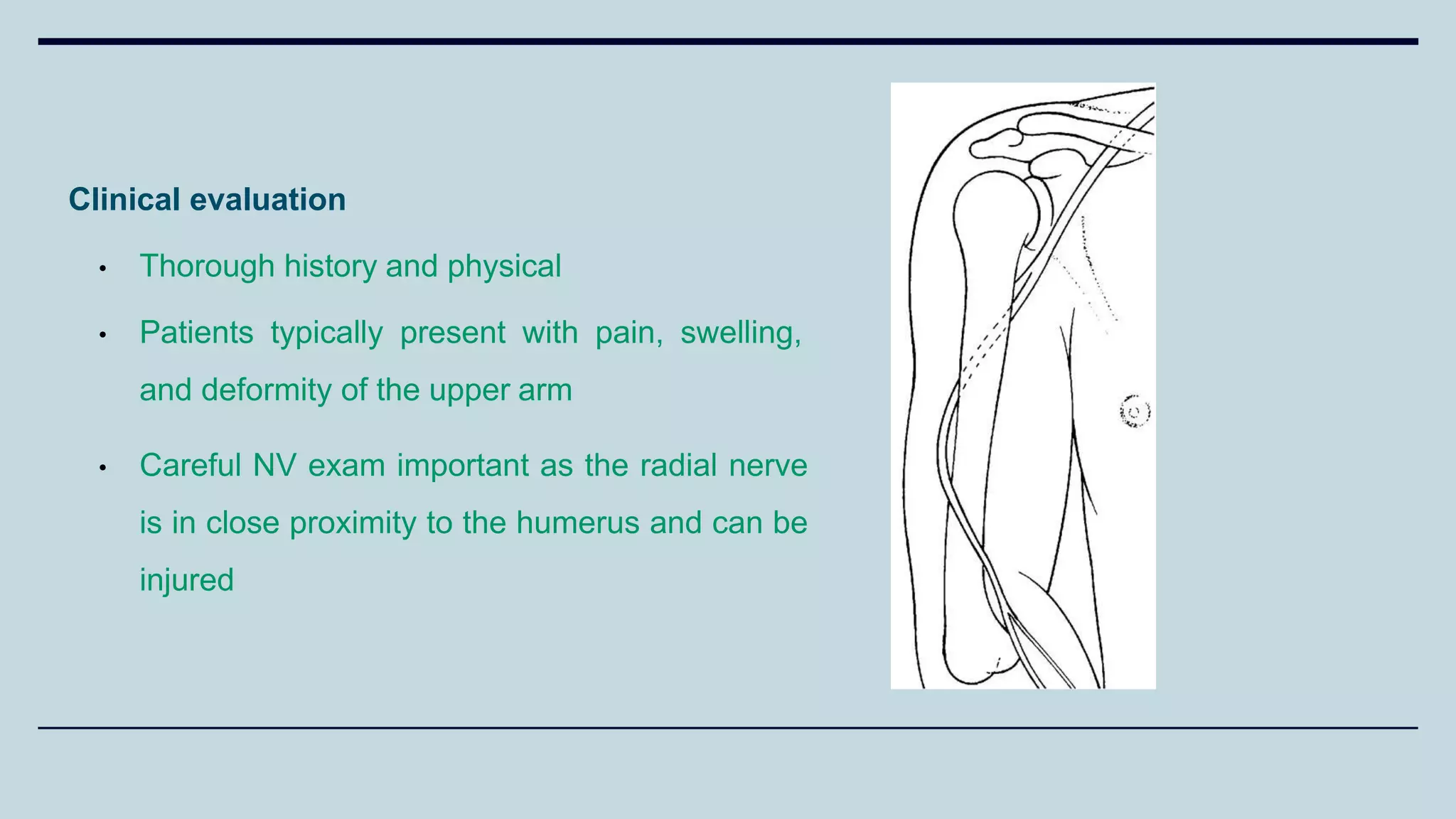
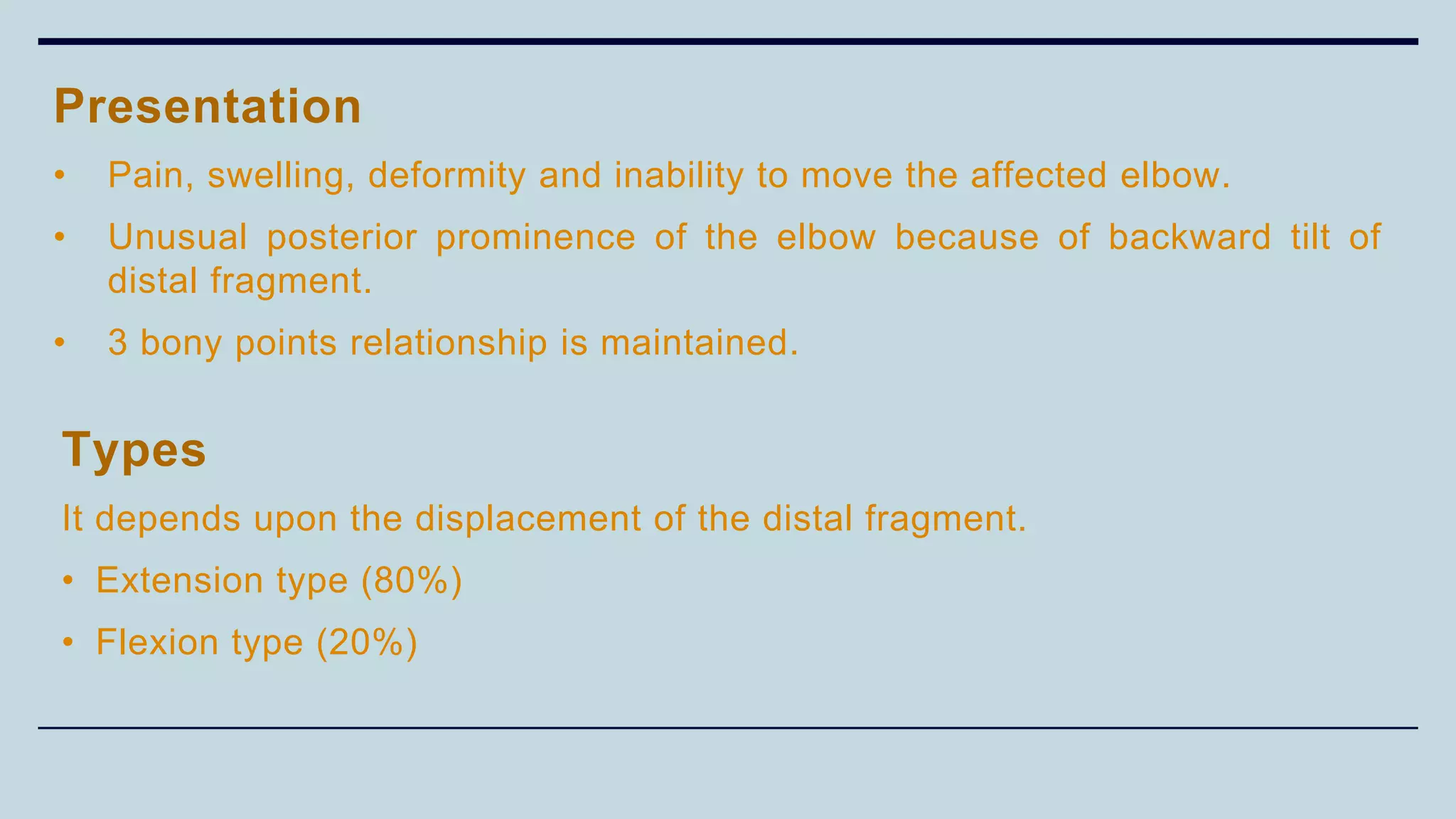
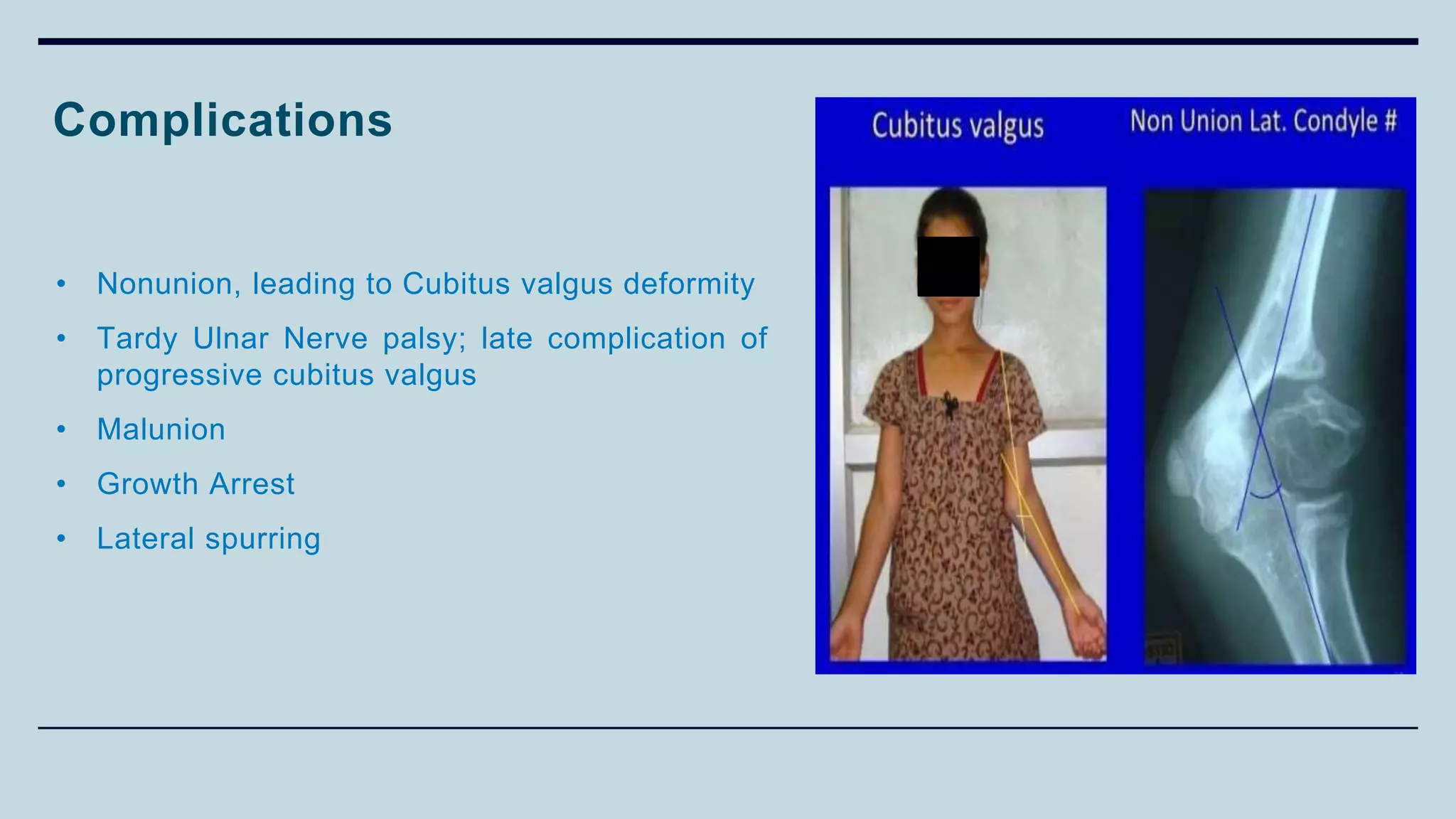
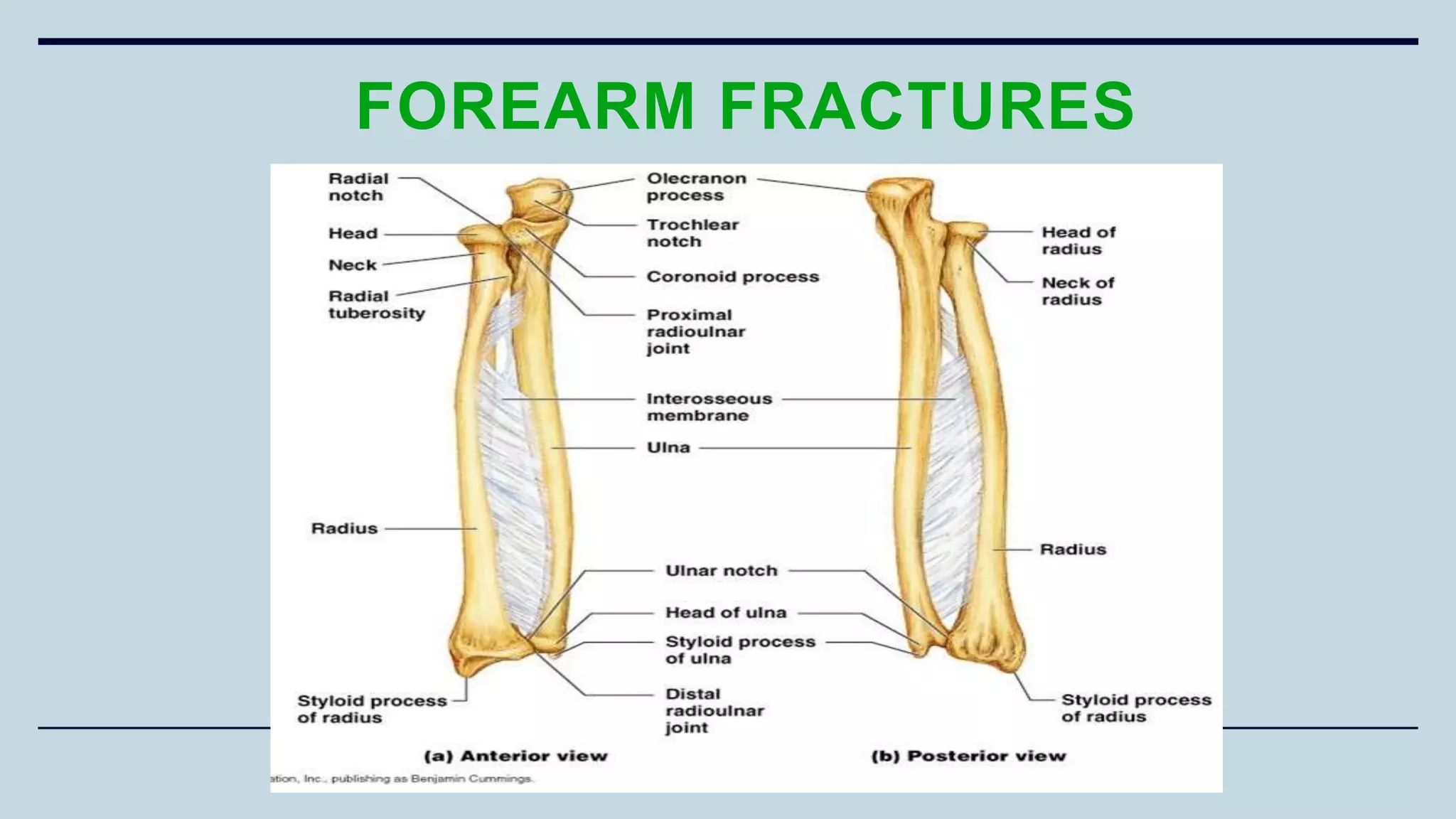
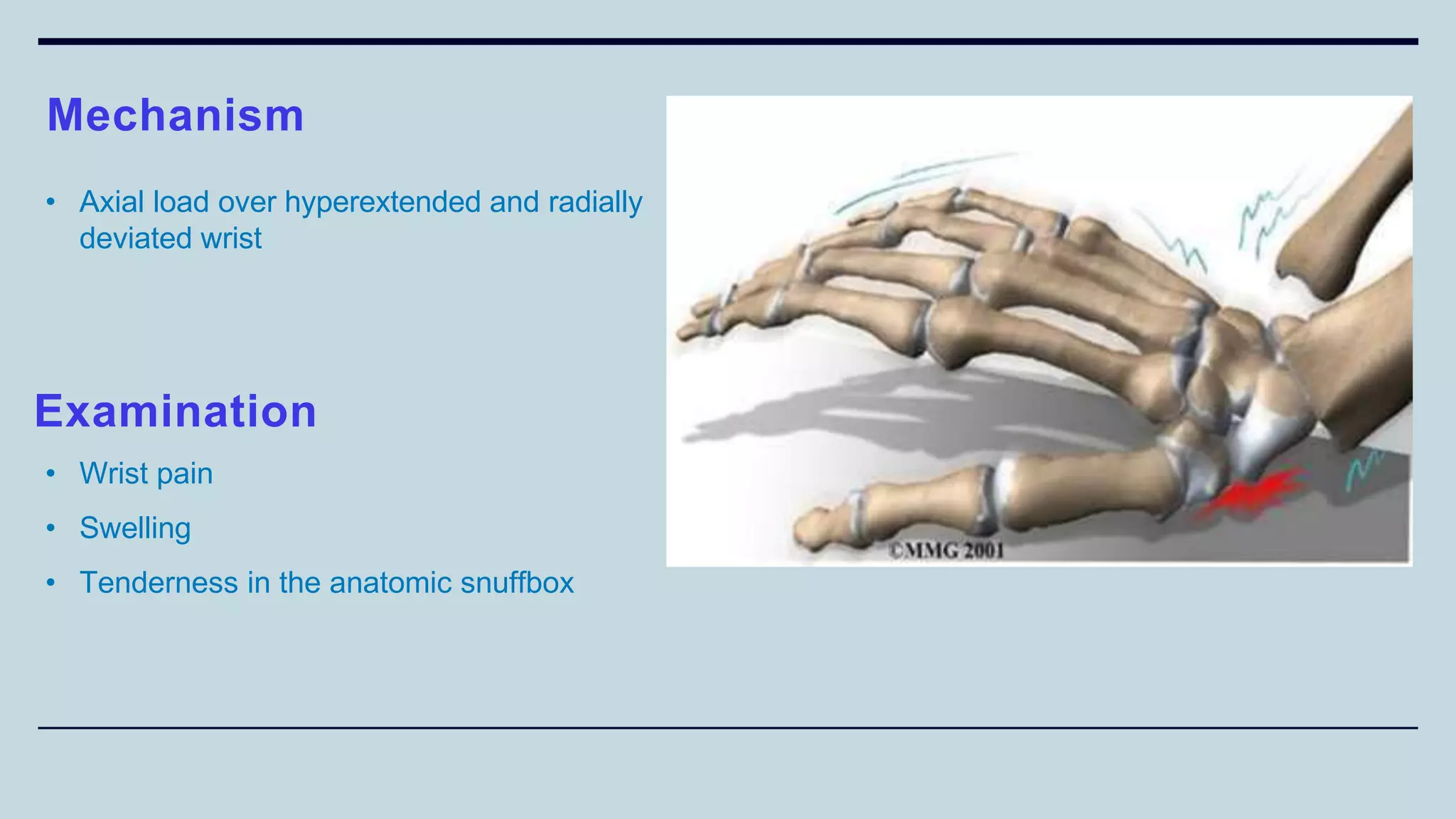
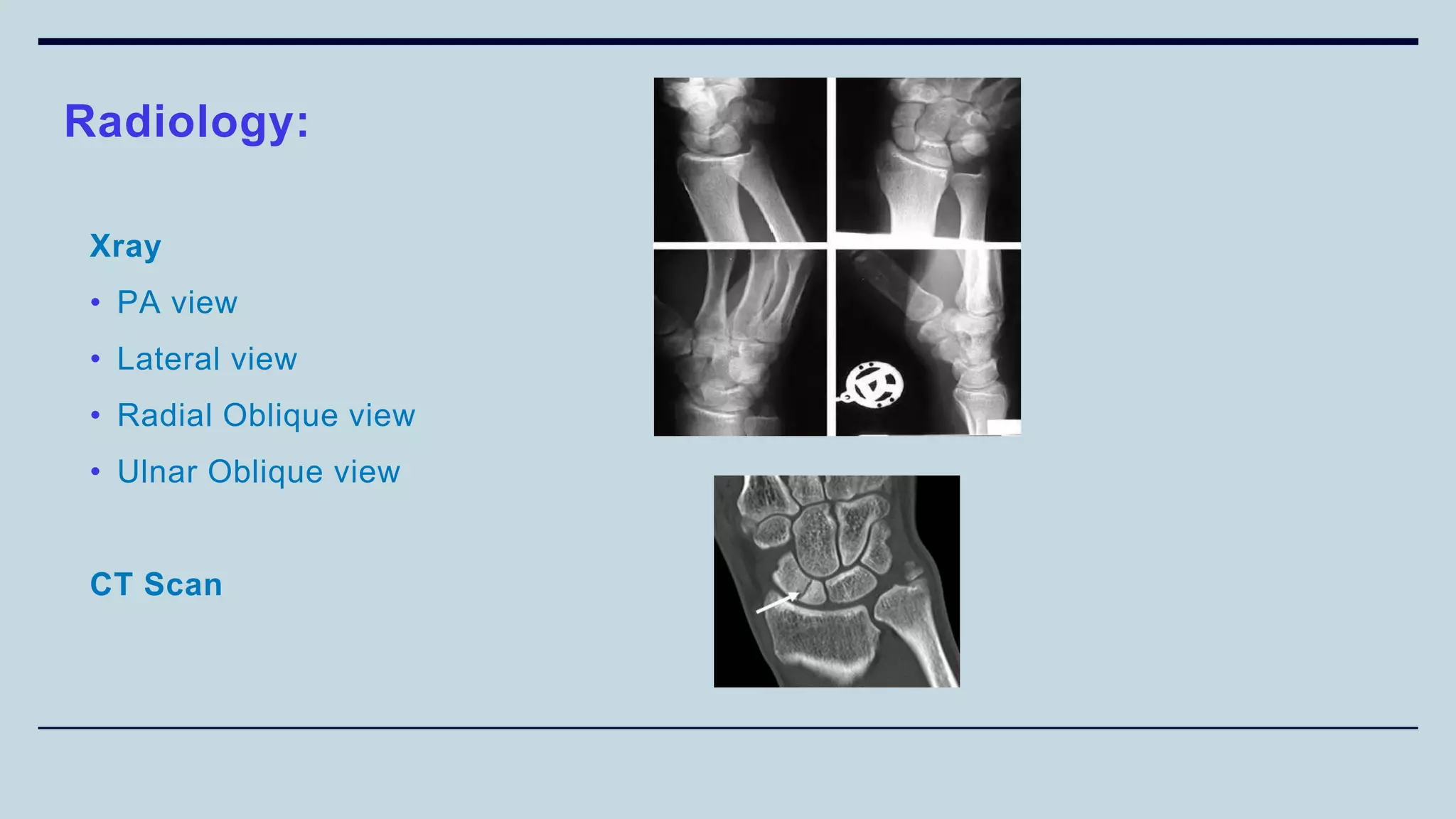
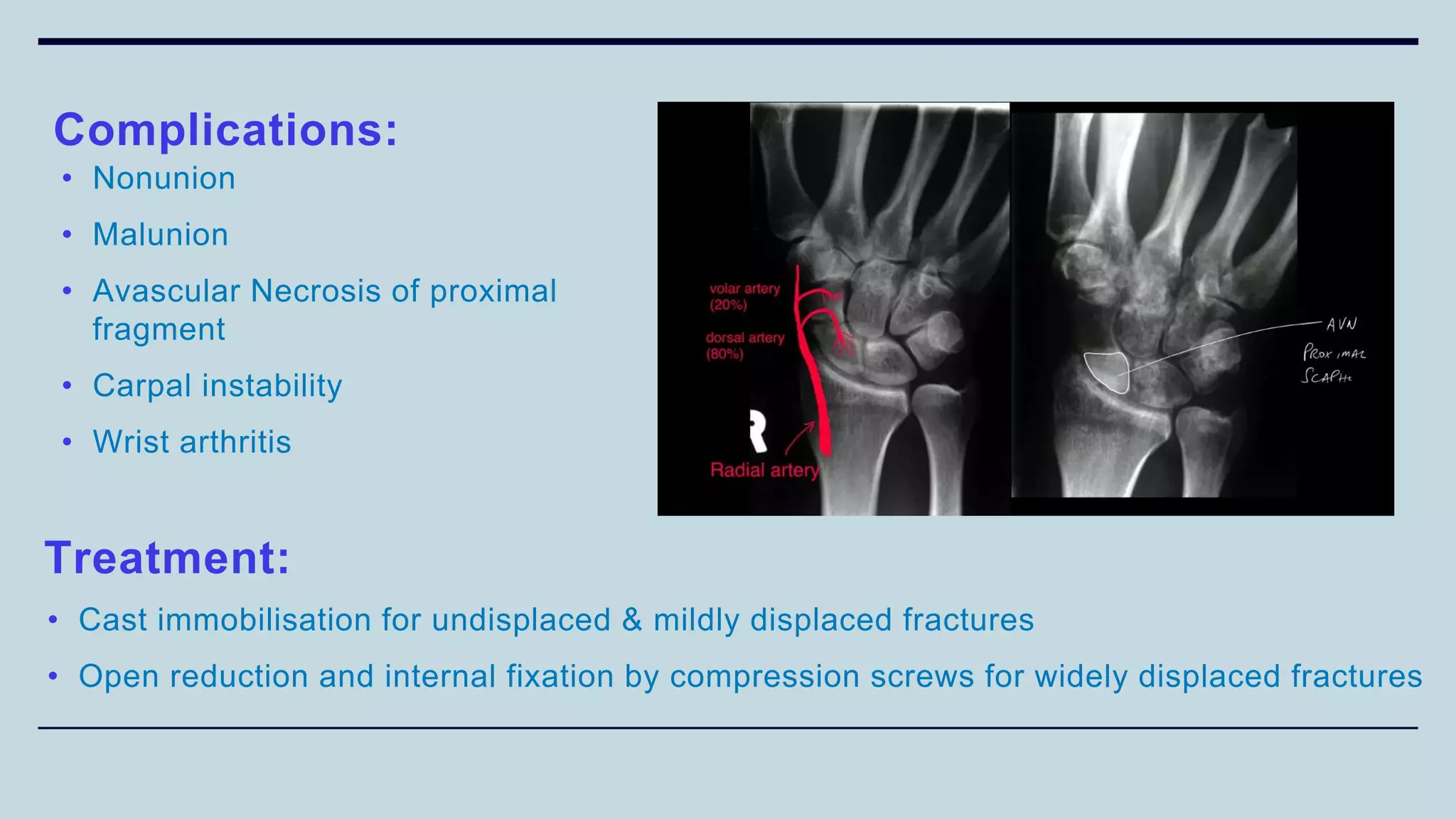
2) Signs and symptoms, mechanisms of injury, clinical evaluation including relevant tests and imaging, complications and treatment options are described for conditions like shoulder dislocation, humeral fractures, supracondylar humerus fractures, forearm fractures and wrist fractures.
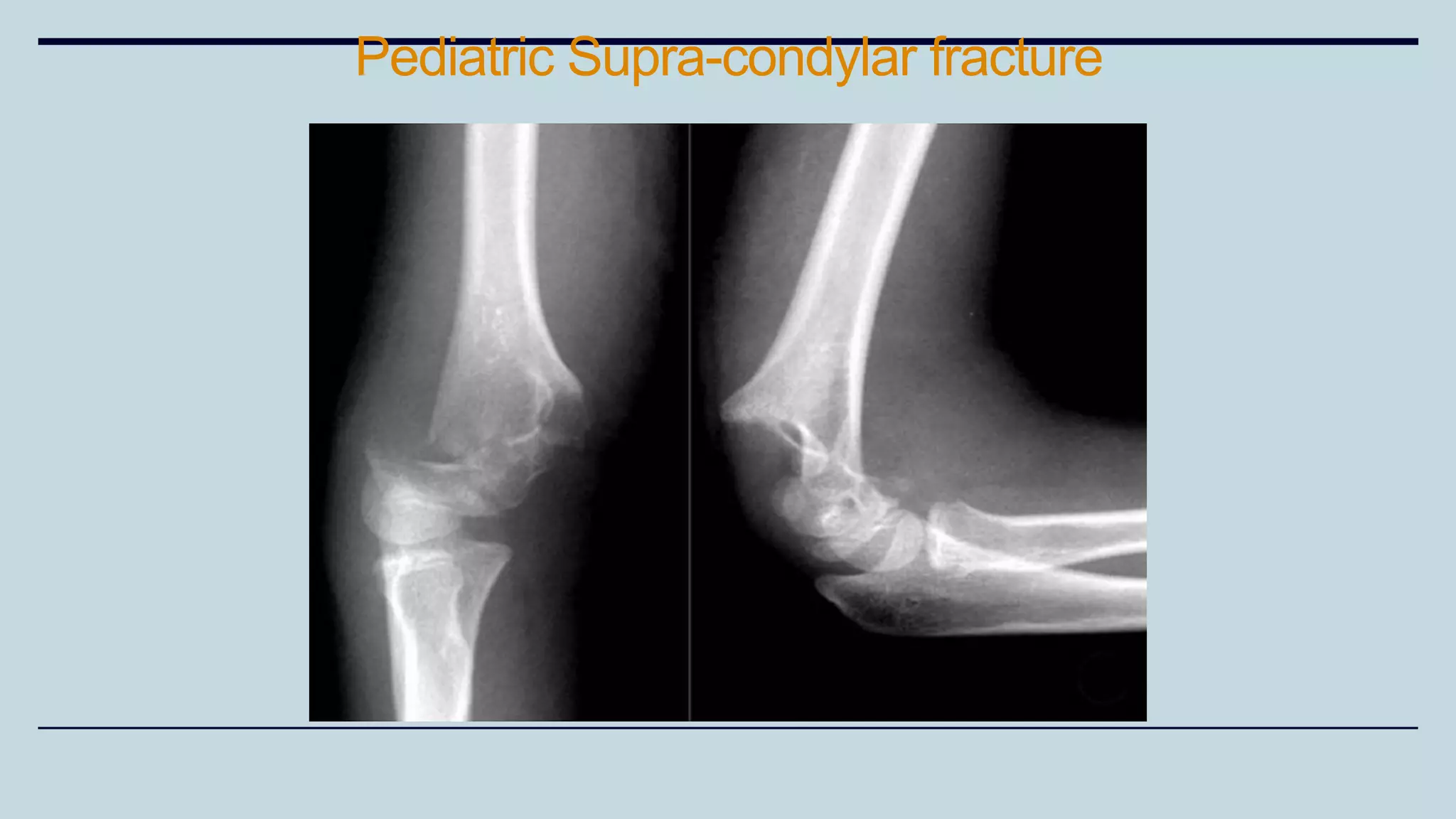
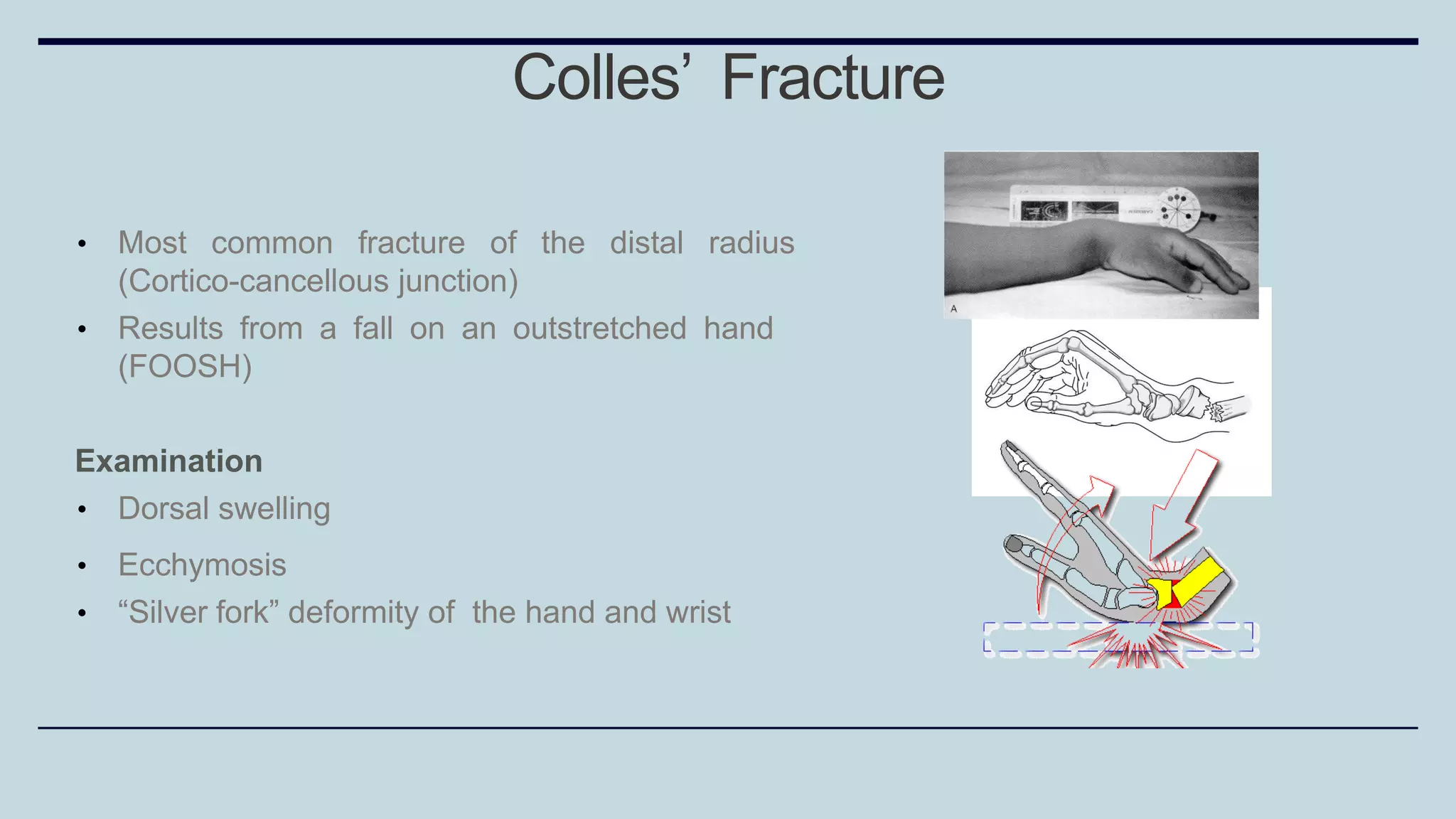
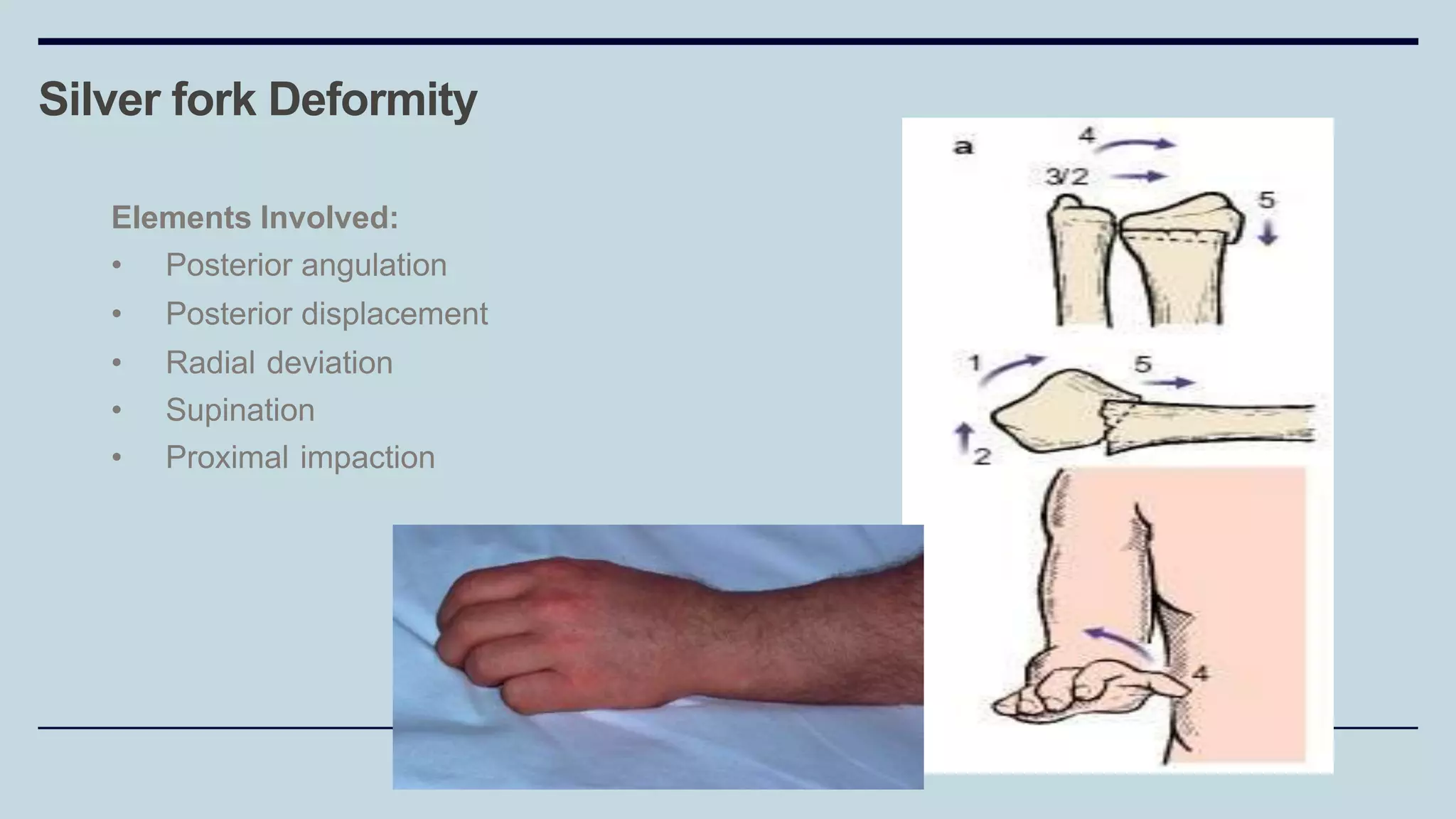
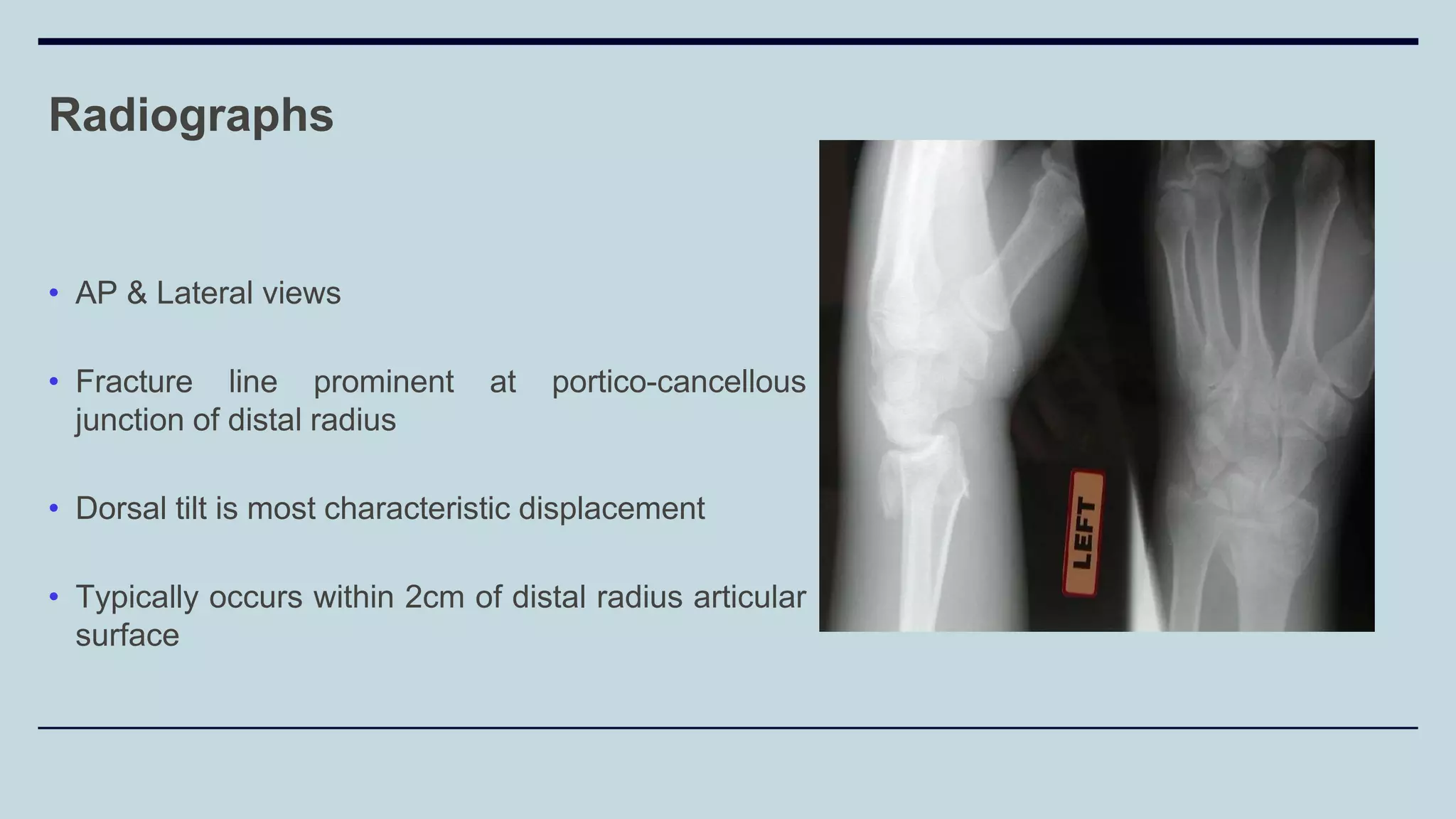
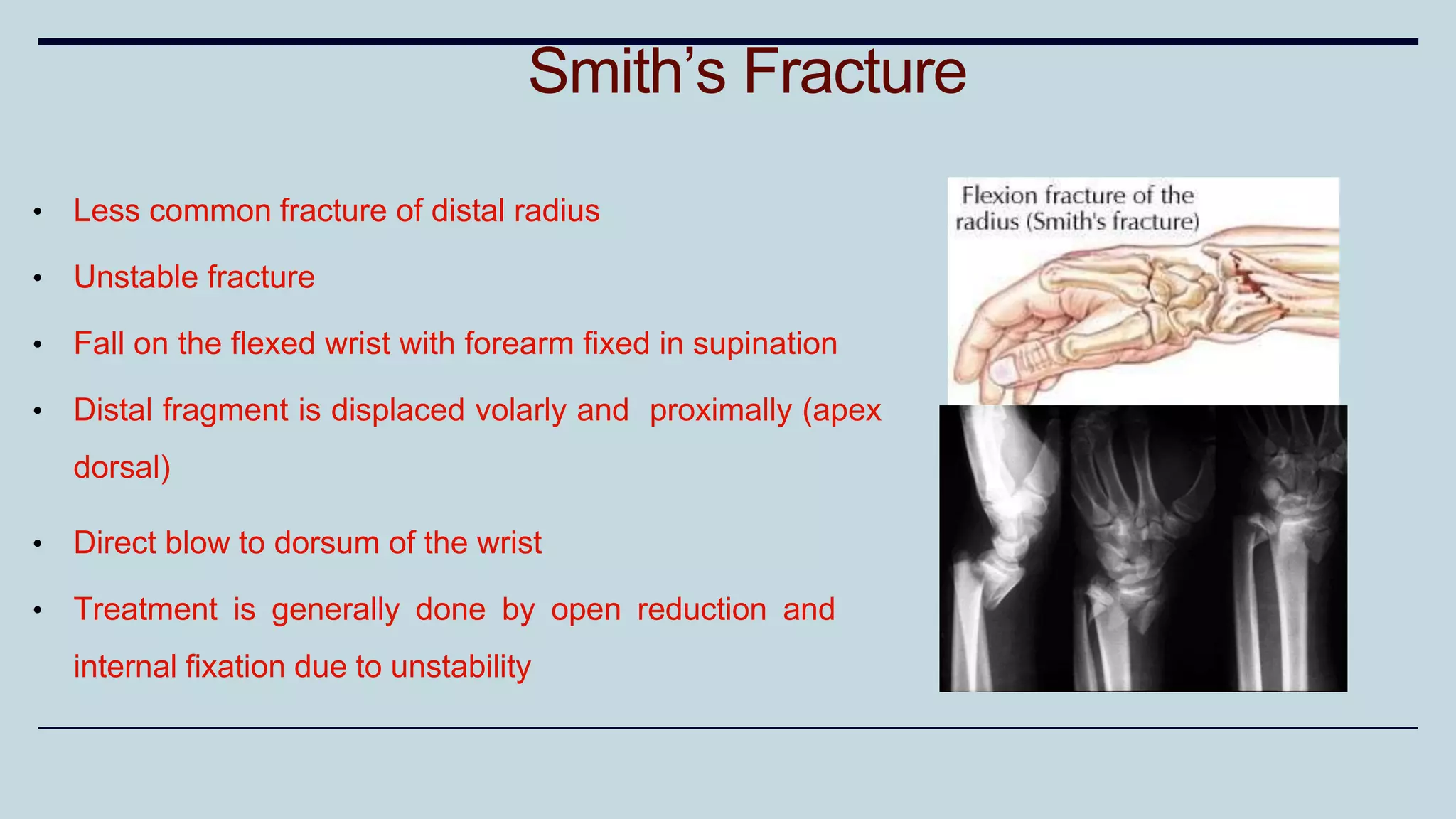
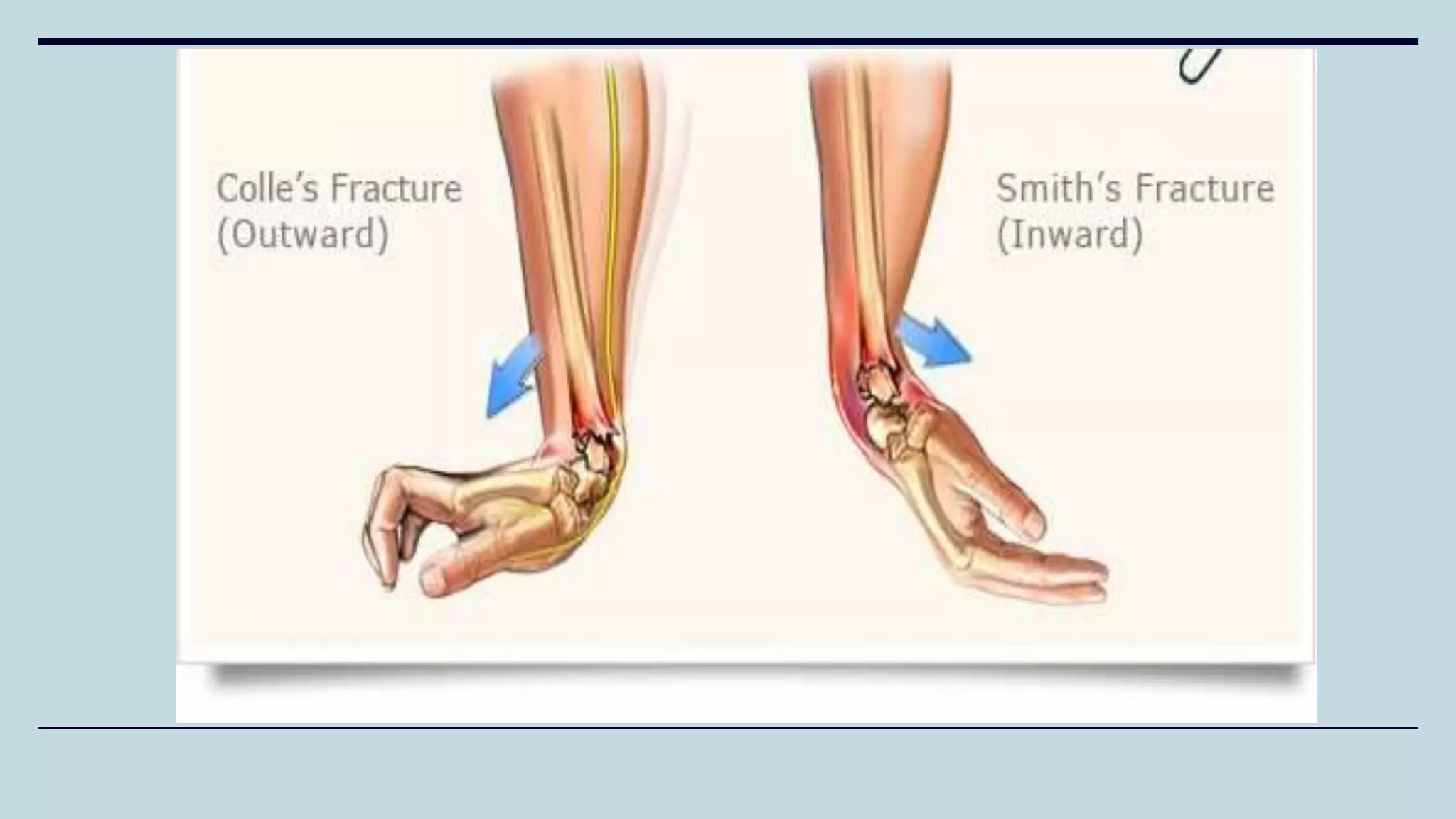
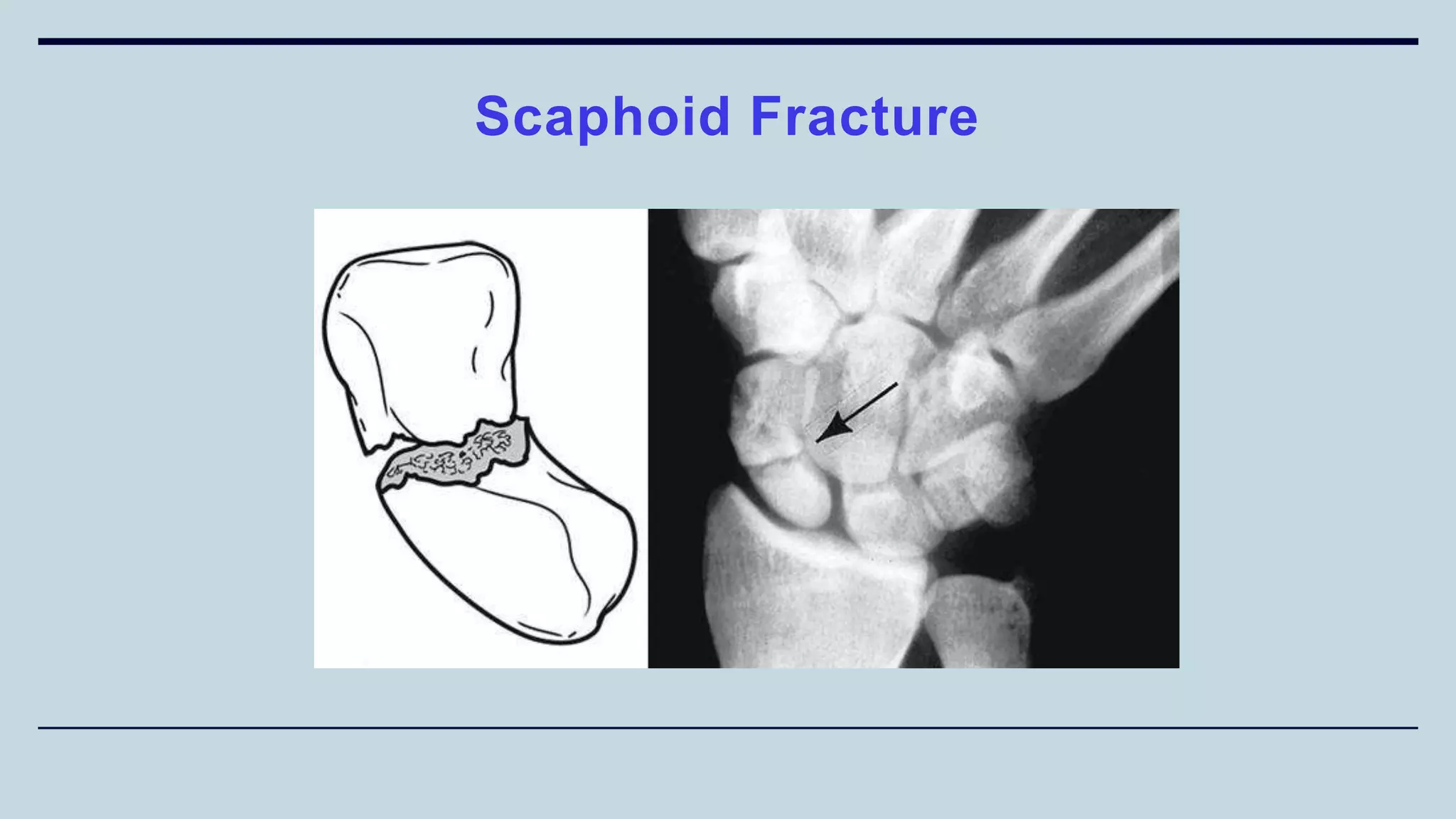
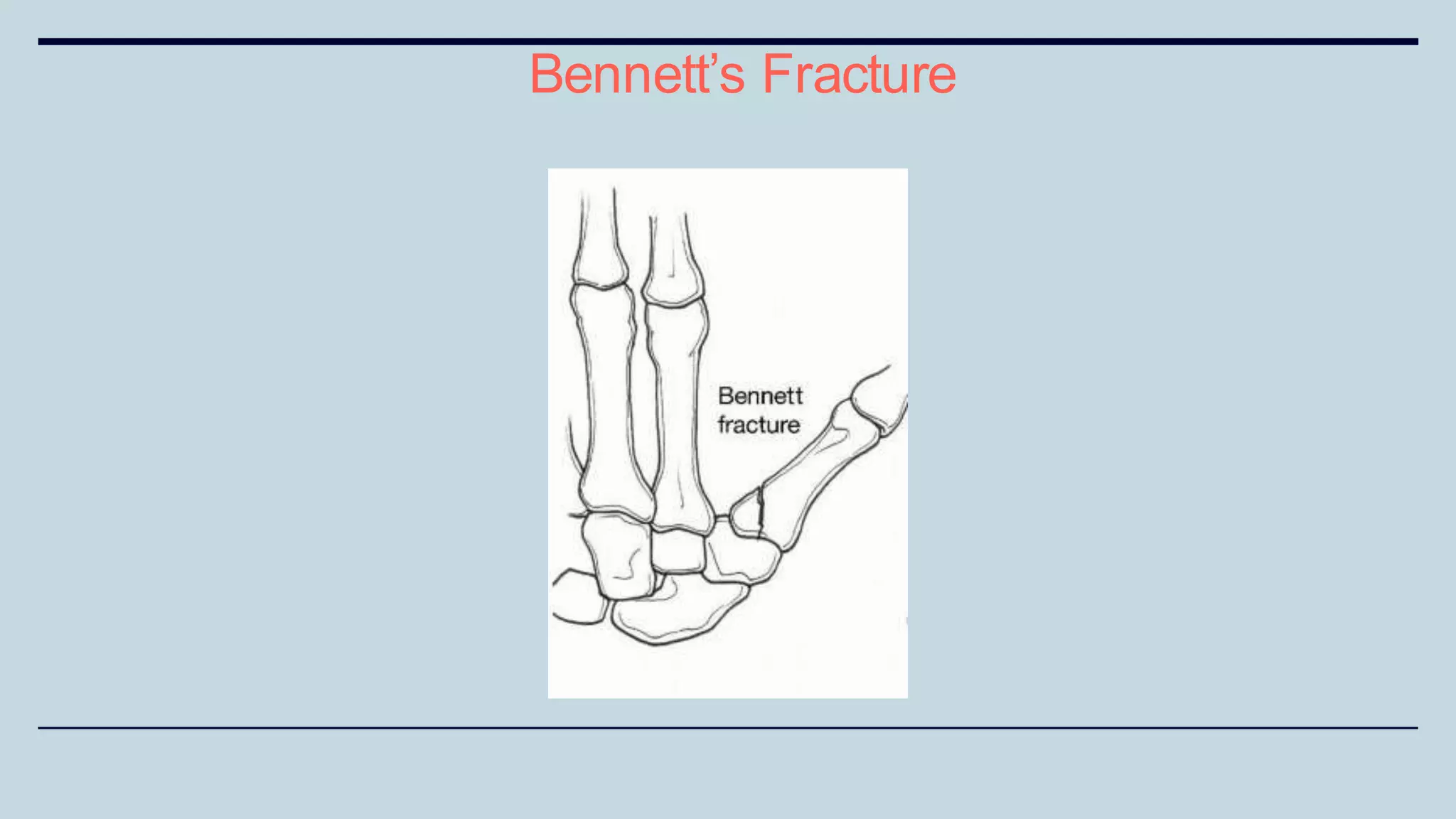
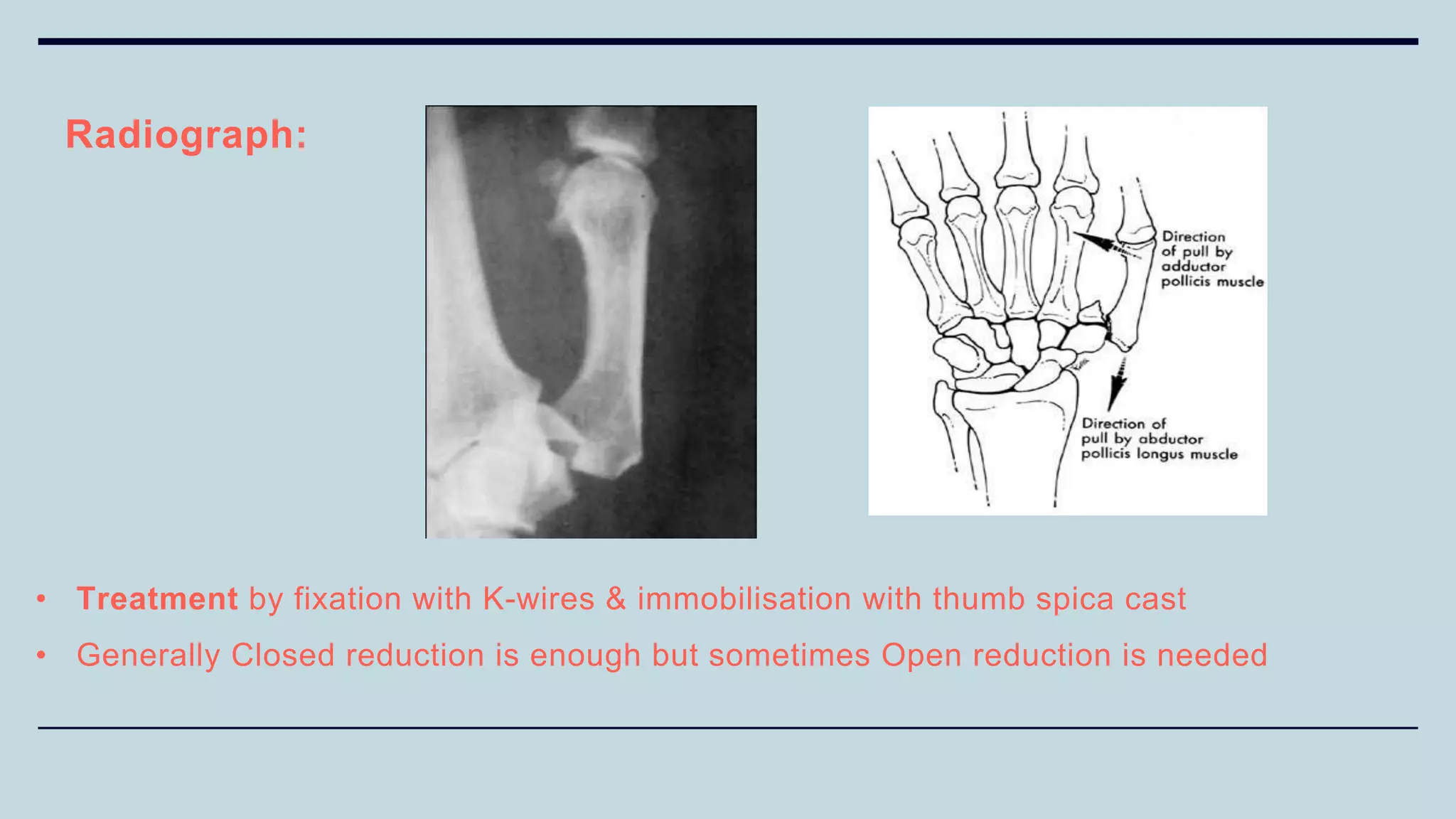
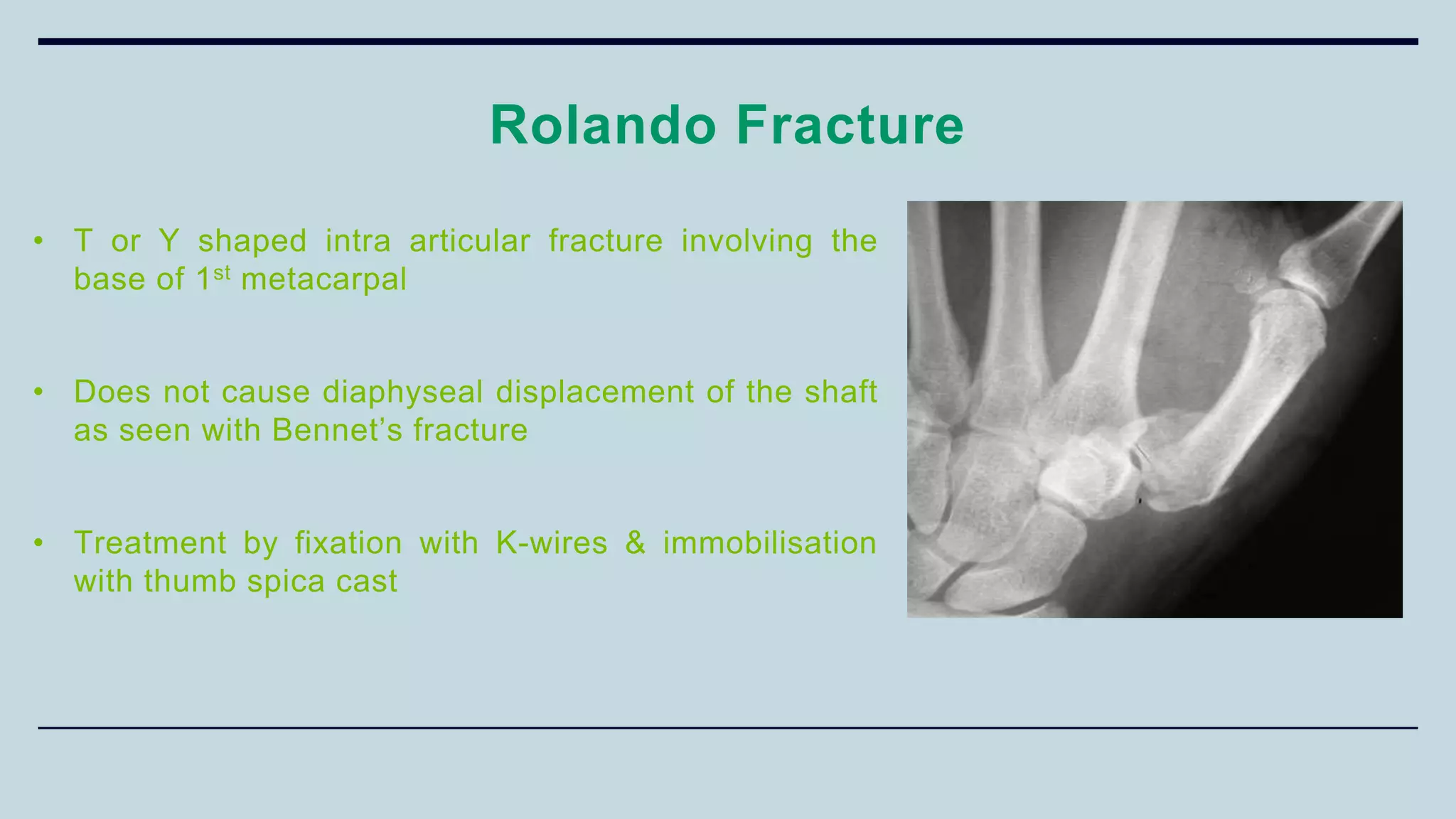
3) Common fractures discussed include Colles fracture of distal radius, supracondylar humerus fractures in children, lateral condyle humerus fracture and Bennett's and Rolando fractures of the thumb.
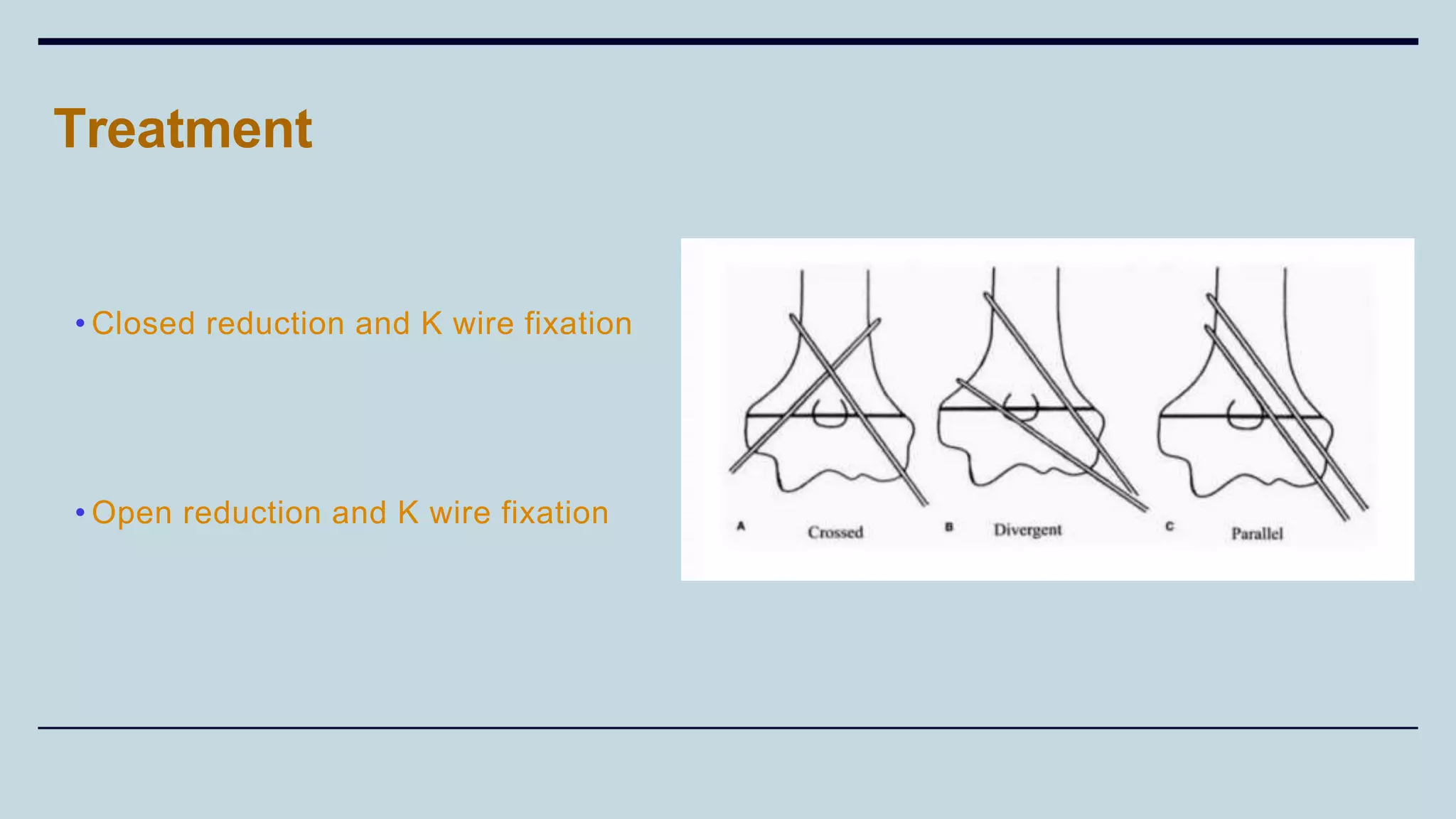
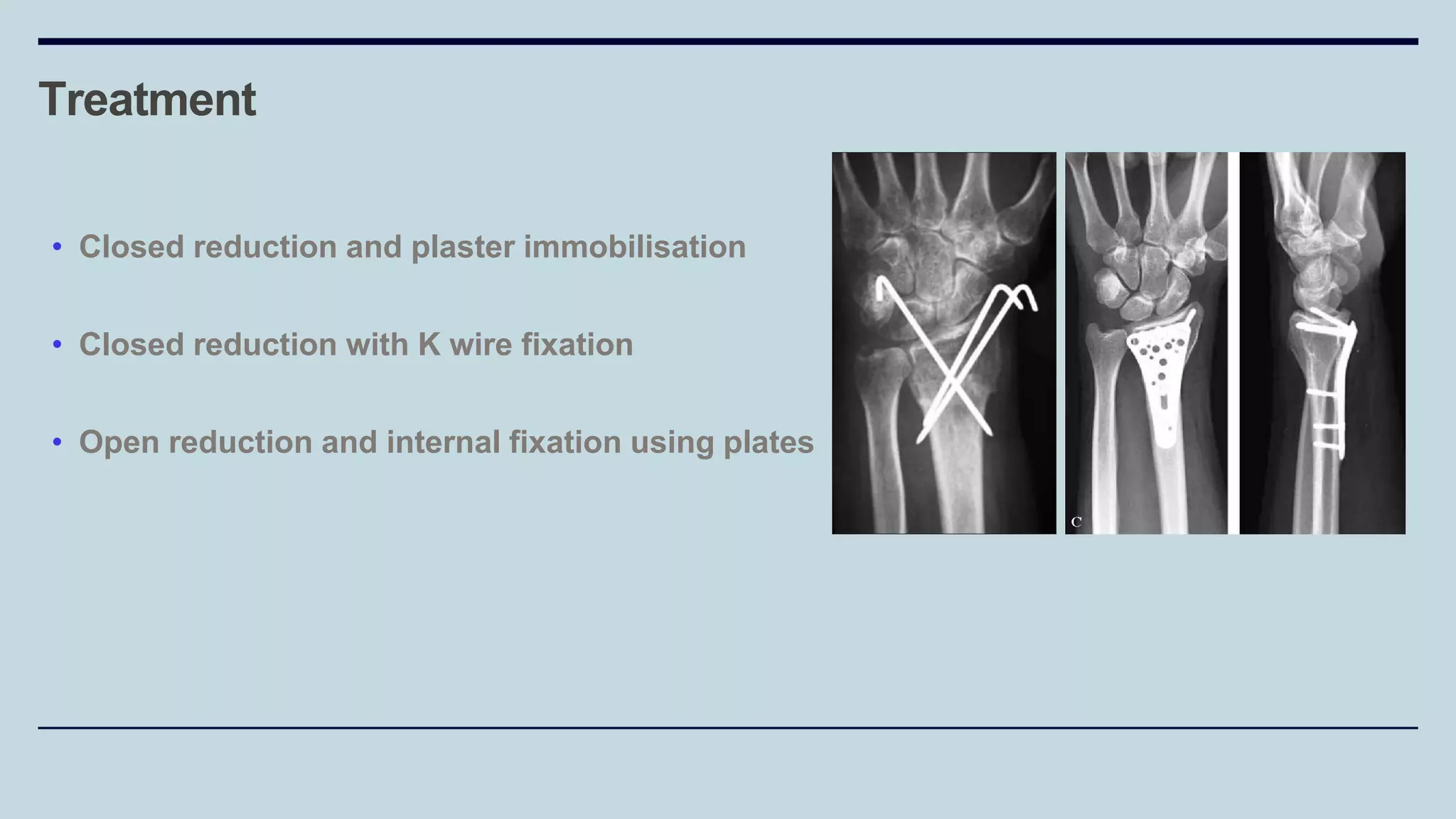
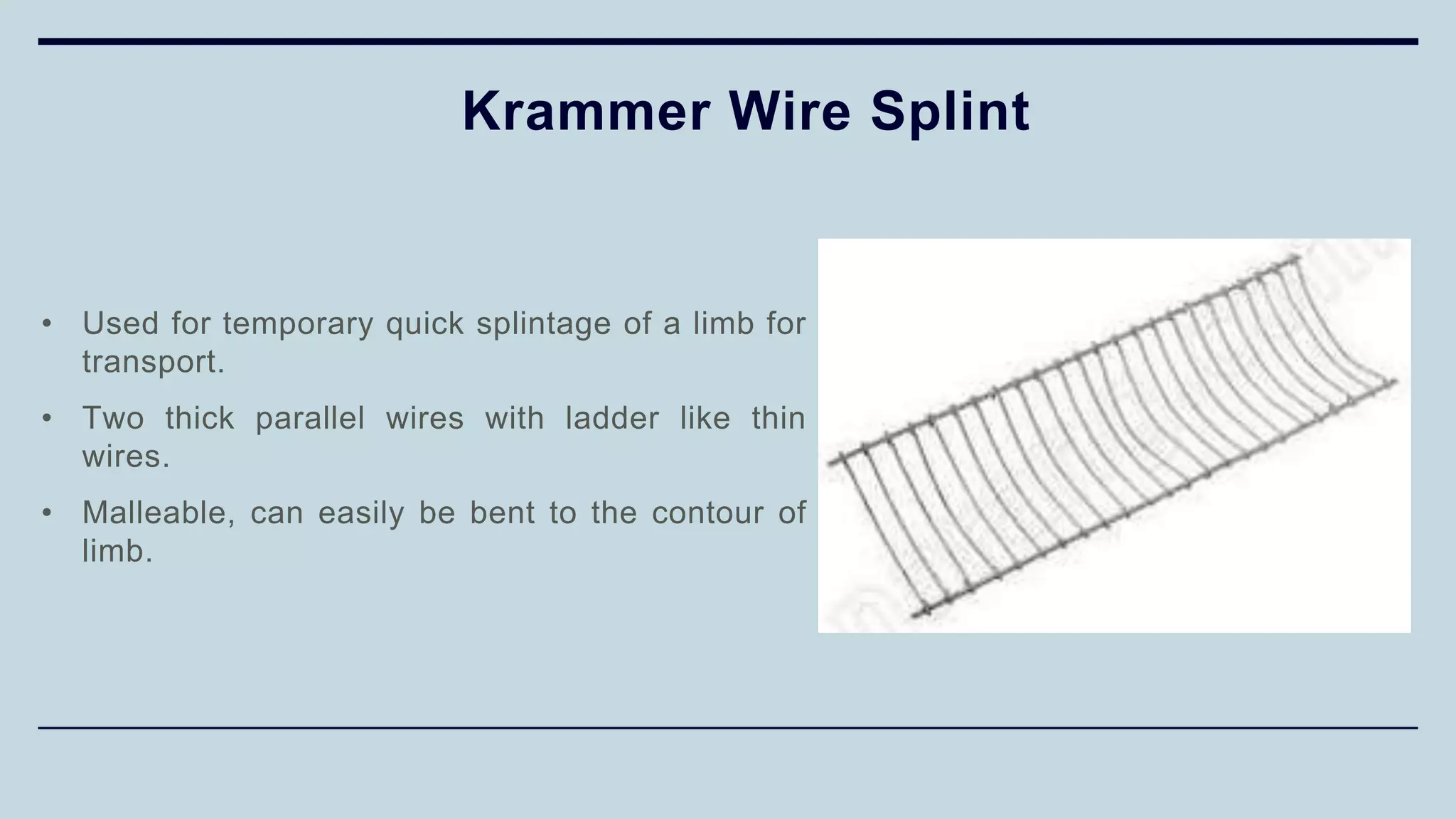
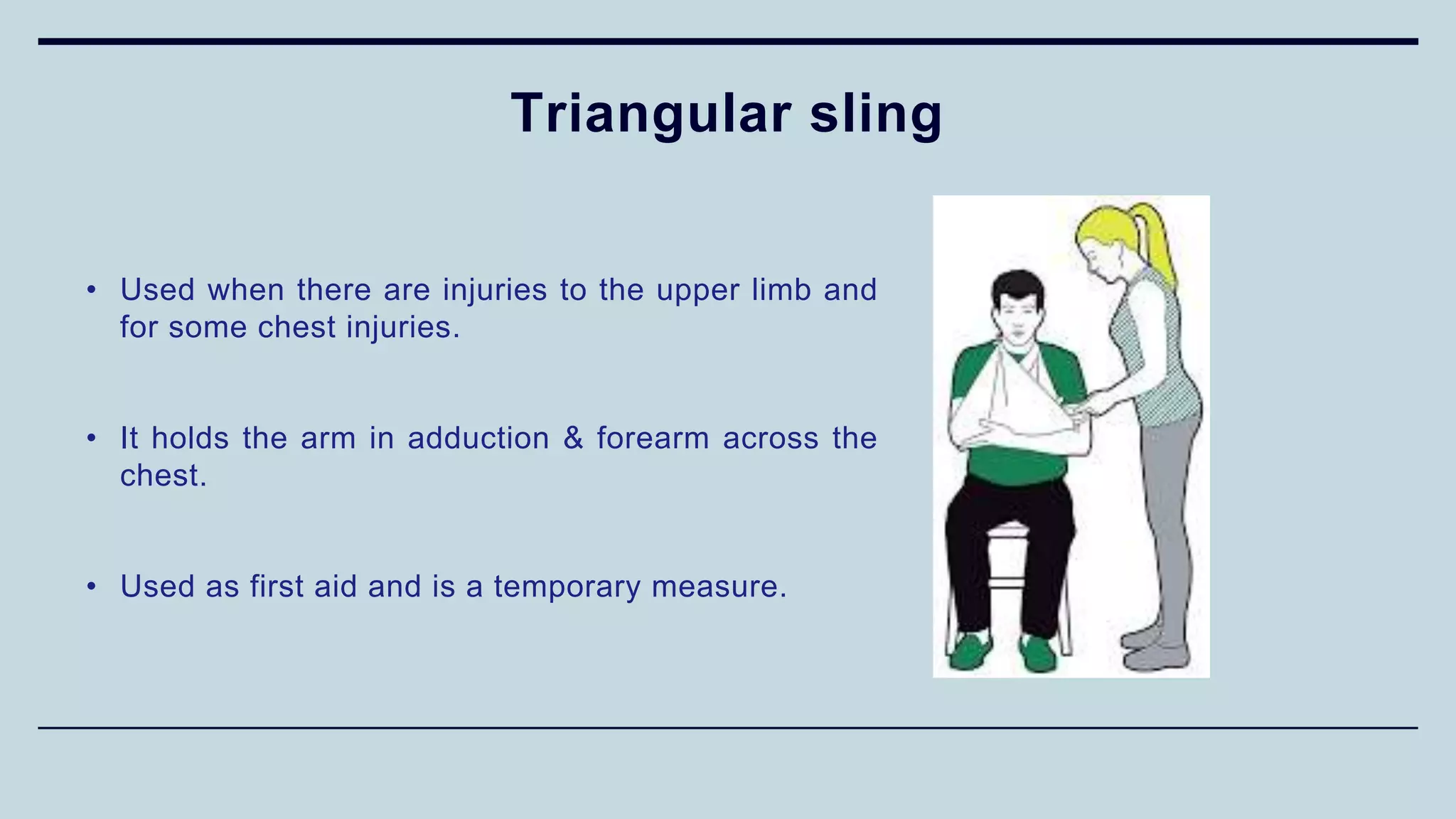
4) Different types of splints used for immobilization like K wire splint,