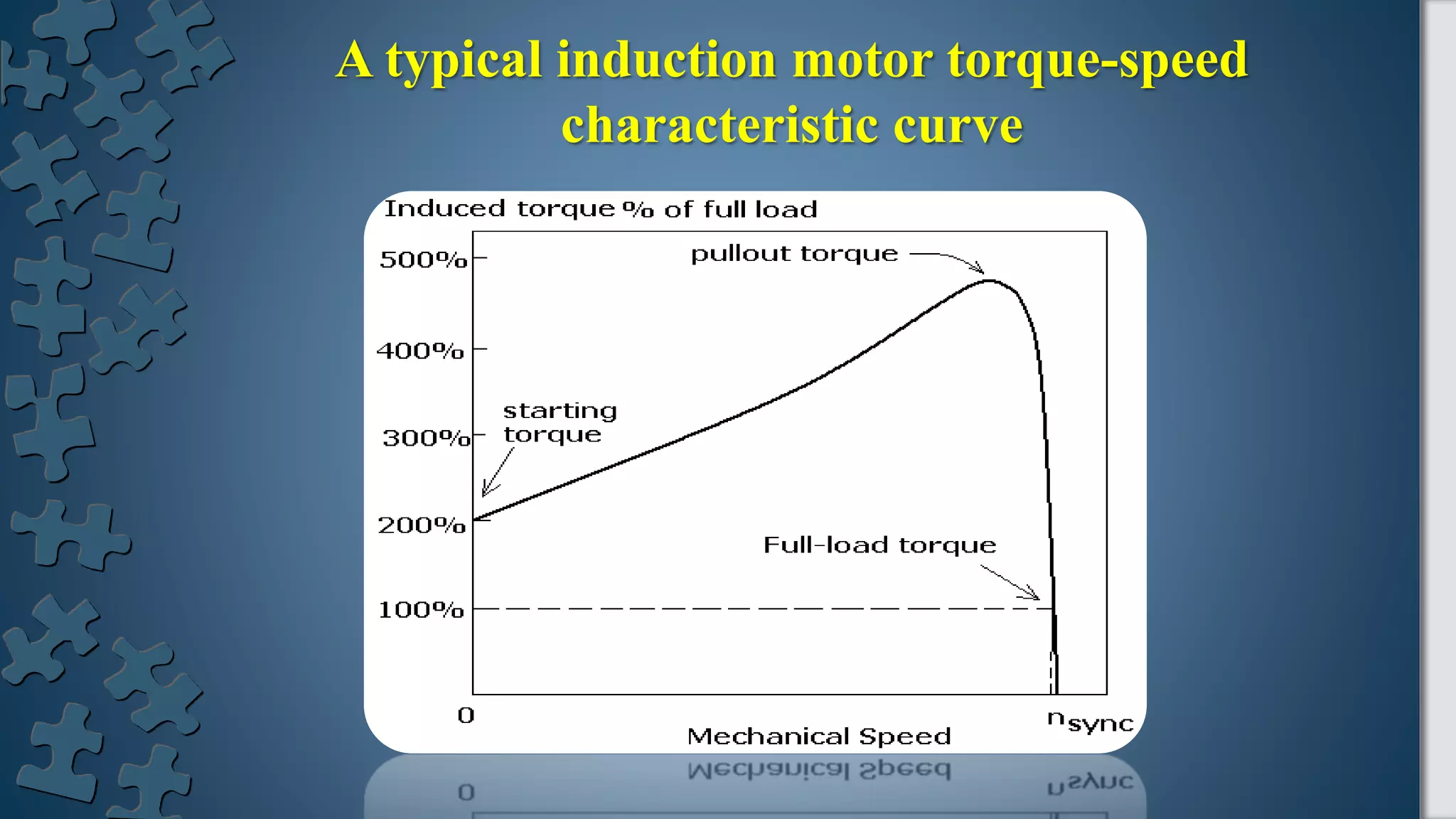
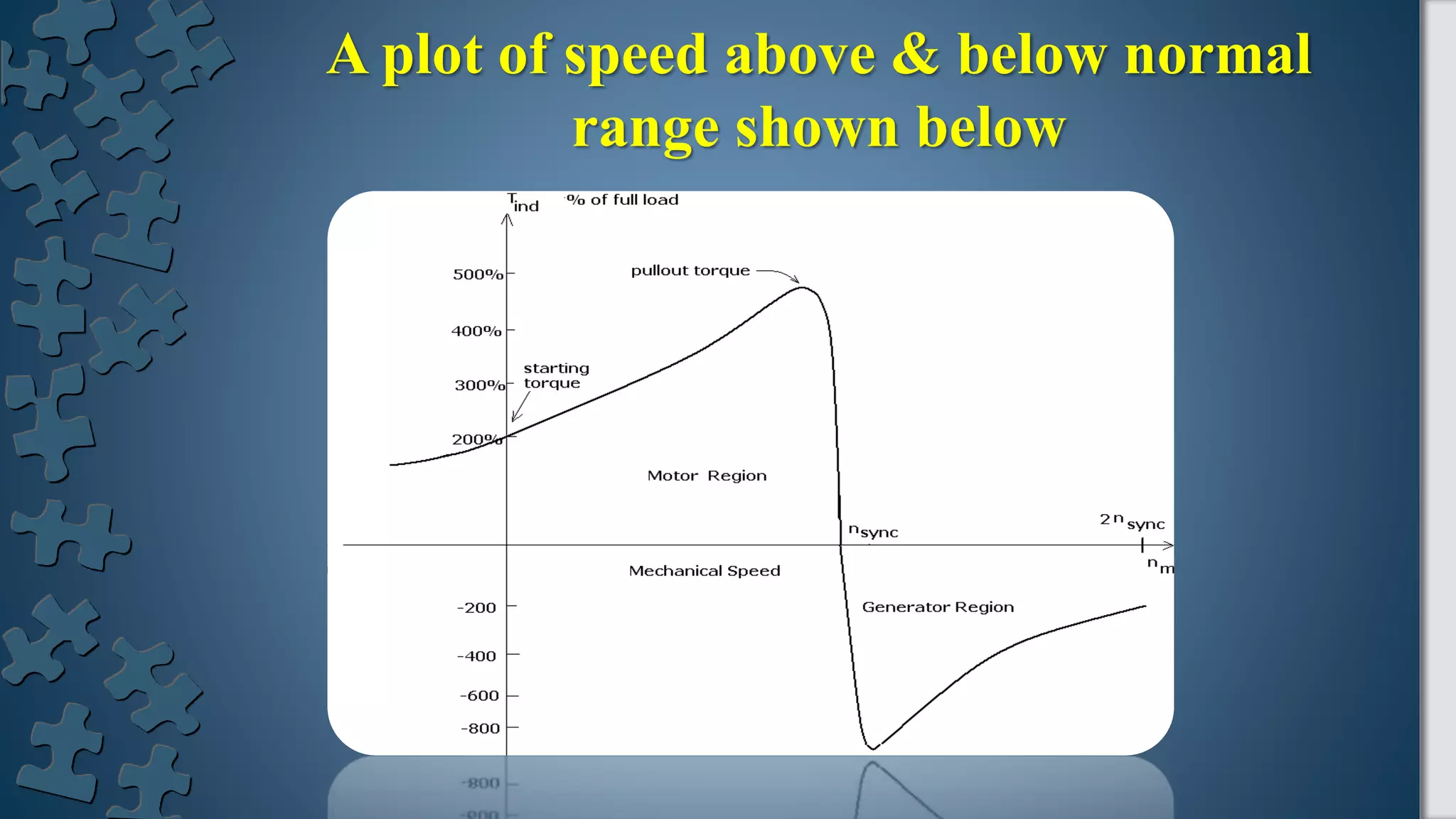
This presentation discusses the torque-speed curve of an induction motor. It explains that torque is the tendency of a force to cause rotational motion and that motors convert electrical energy into rotational mechanical energy. It then discusses how the torque-speed curve provides important information, including that torque is zero at synchronous speed and increases linearly between no load and full load. It shows a typical torque-speed characteristics curve and that peak power occurs at a different speed than maximum torque. The presentation concludes with a graph showing induced torque and power converted versus motor speed.