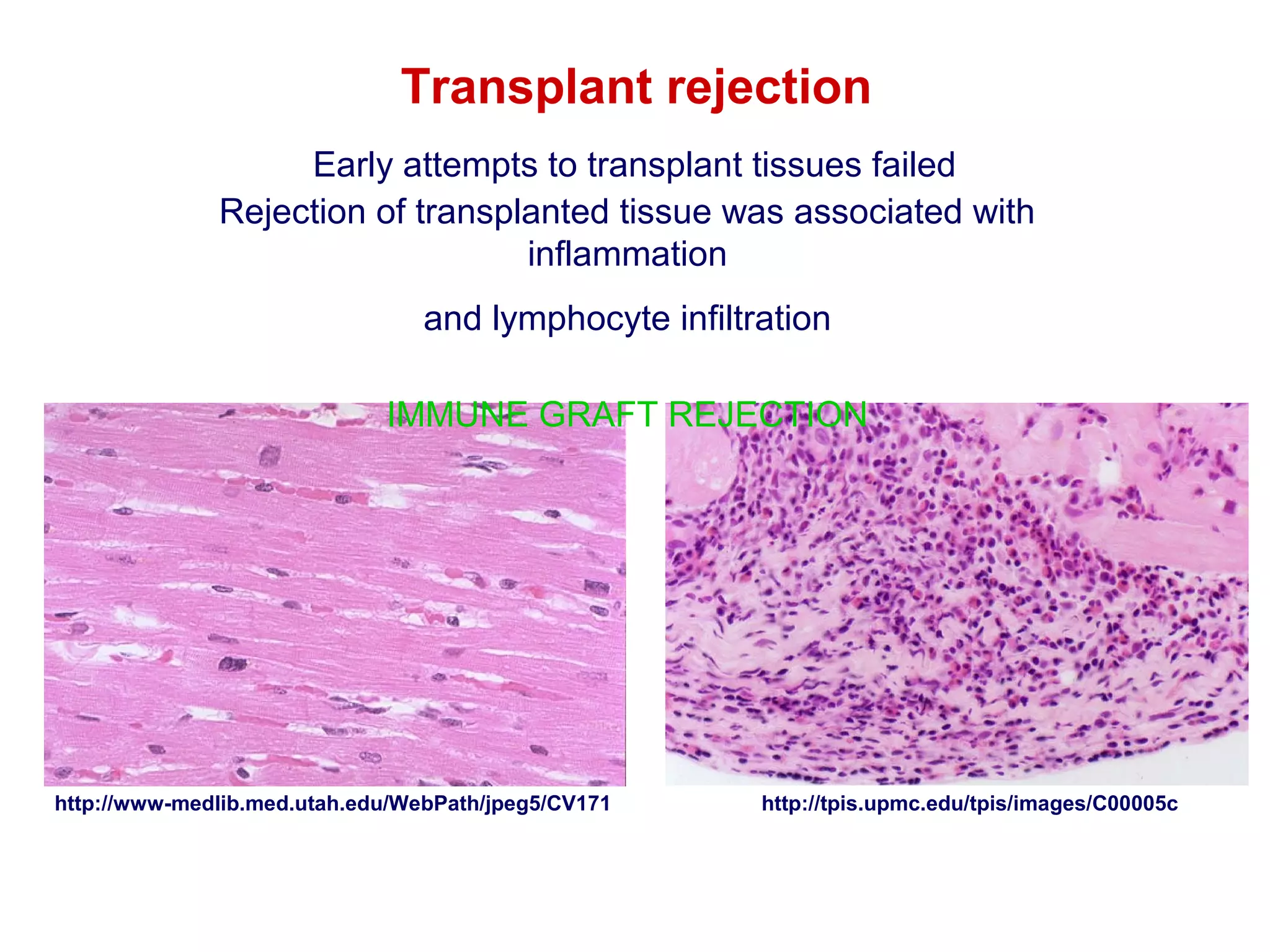
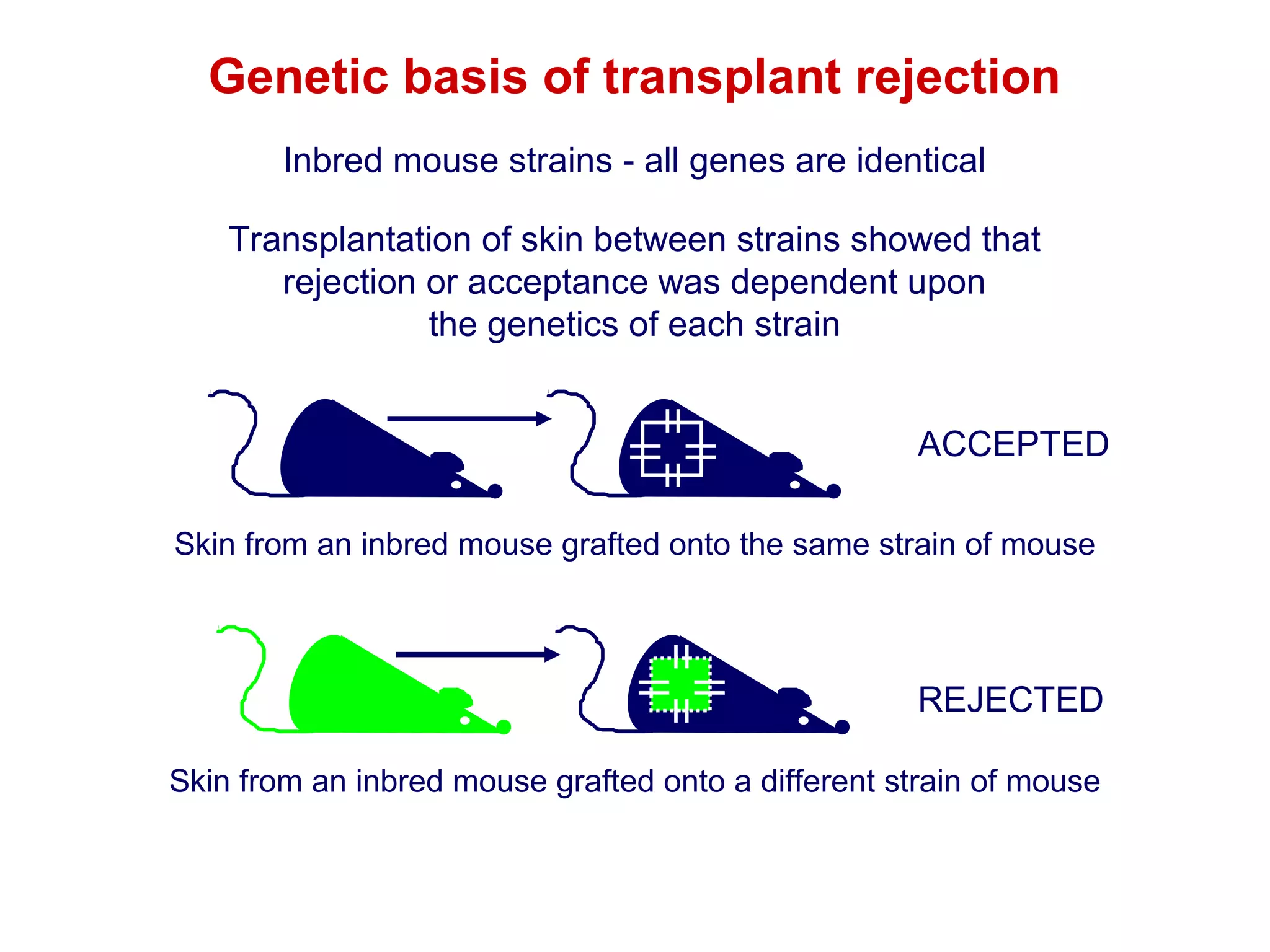
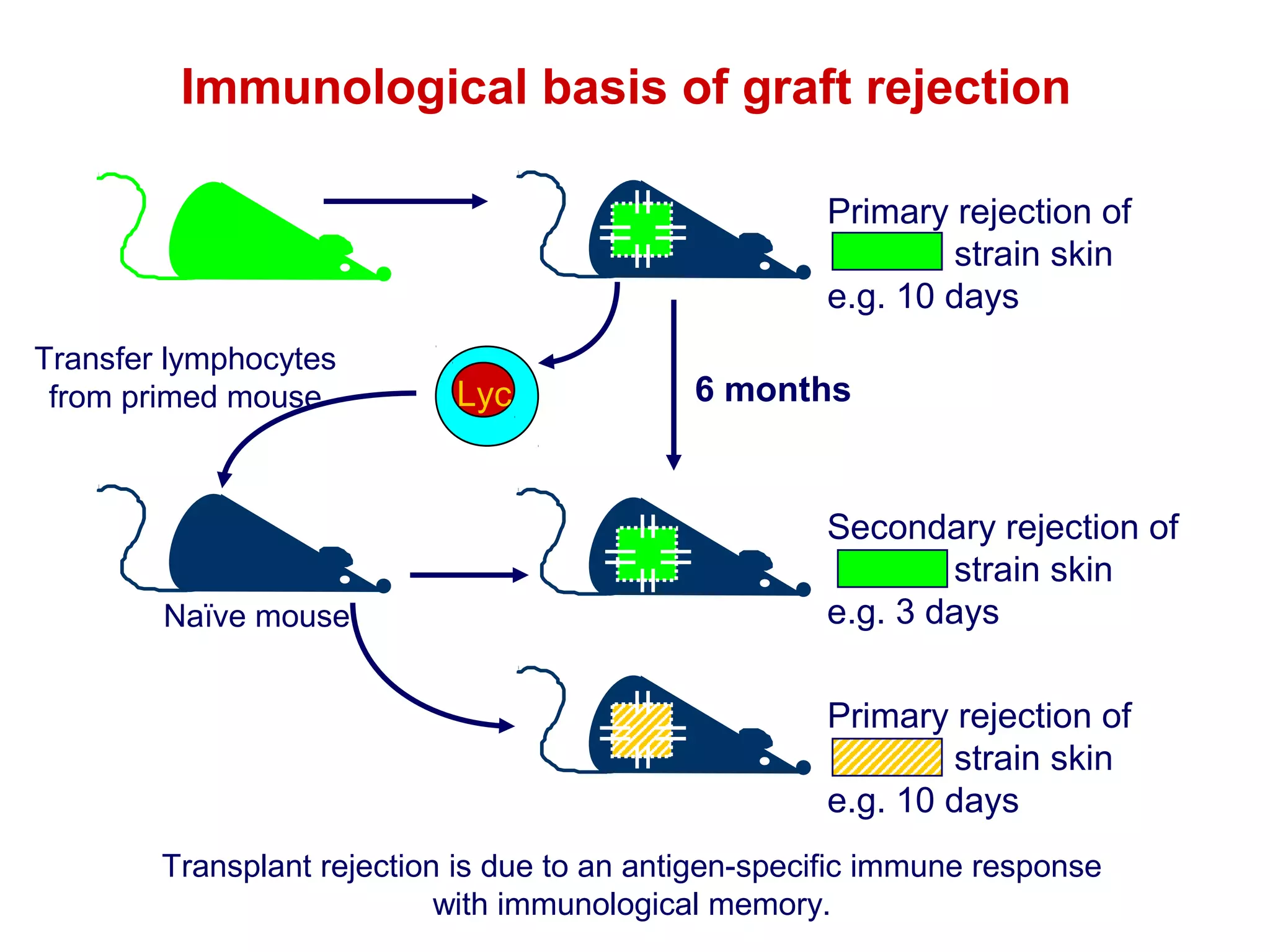
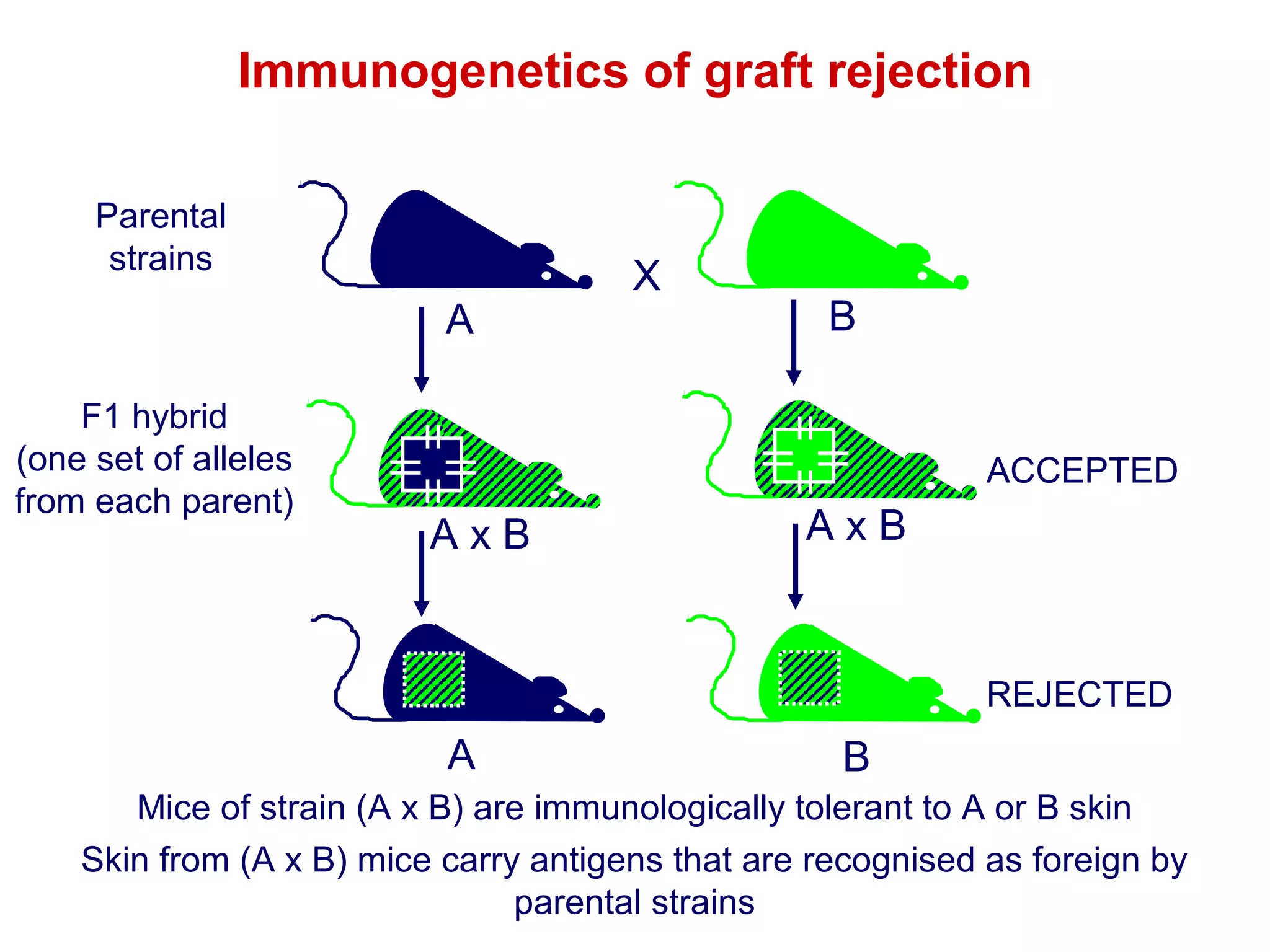
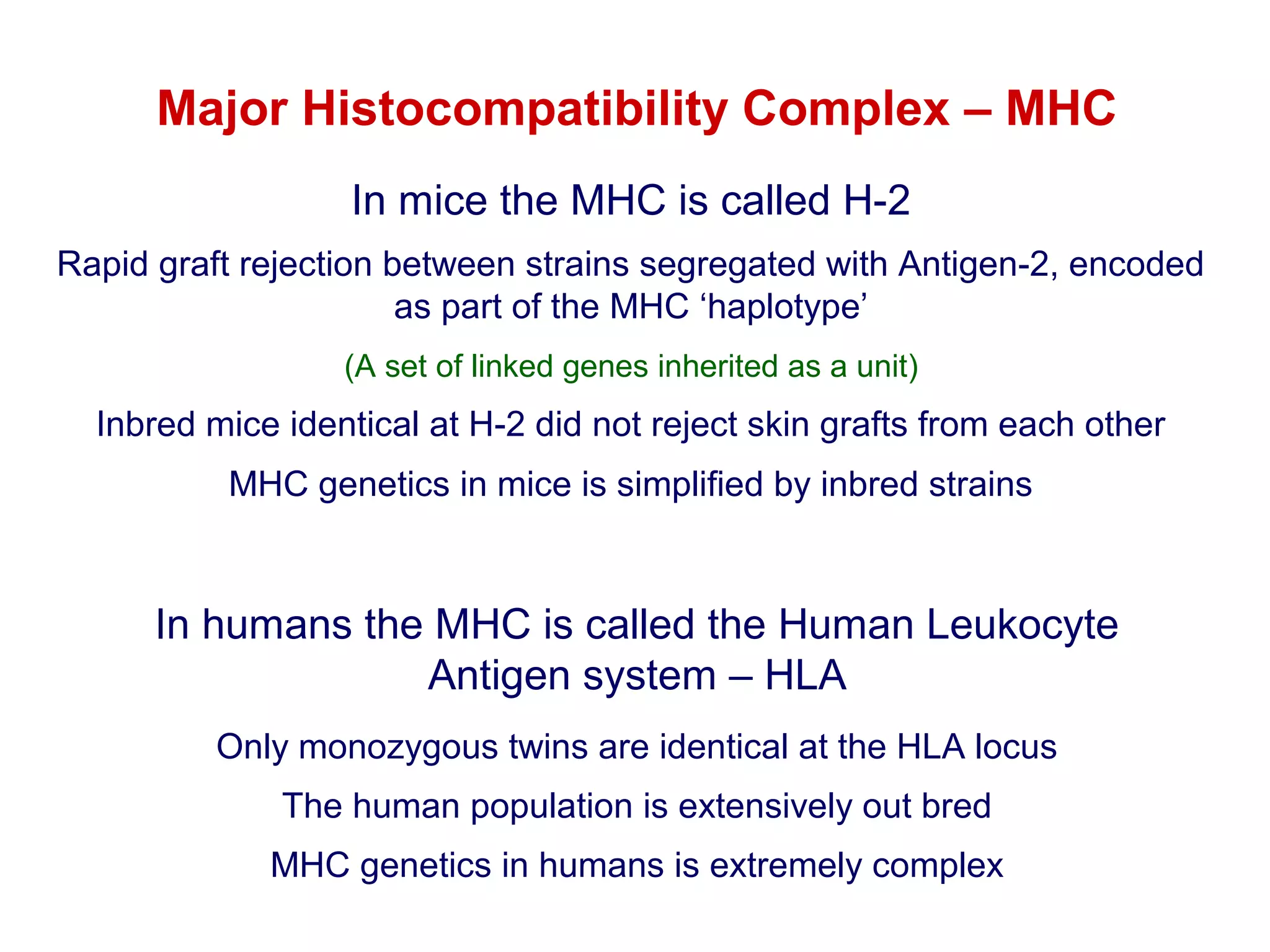
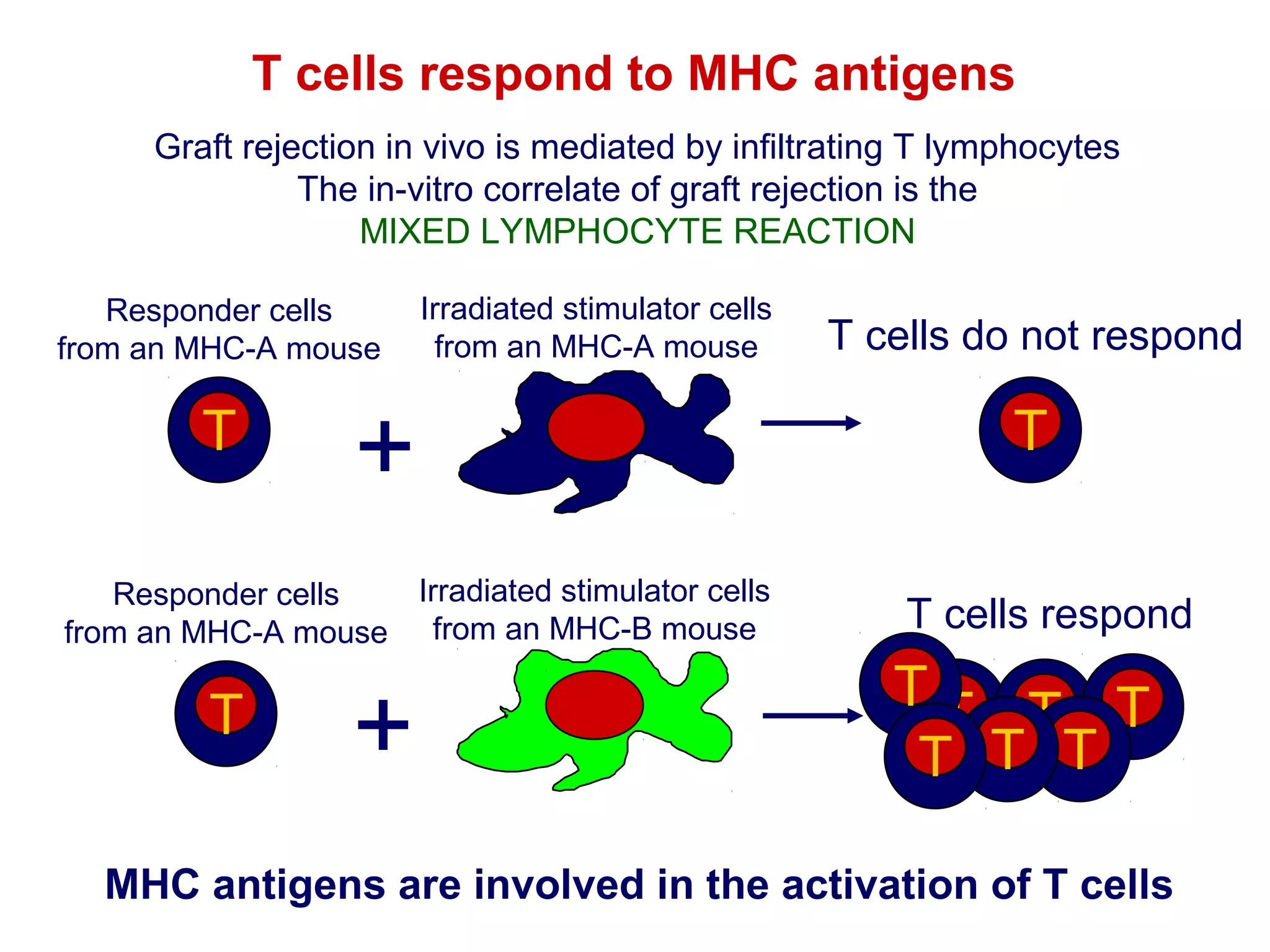
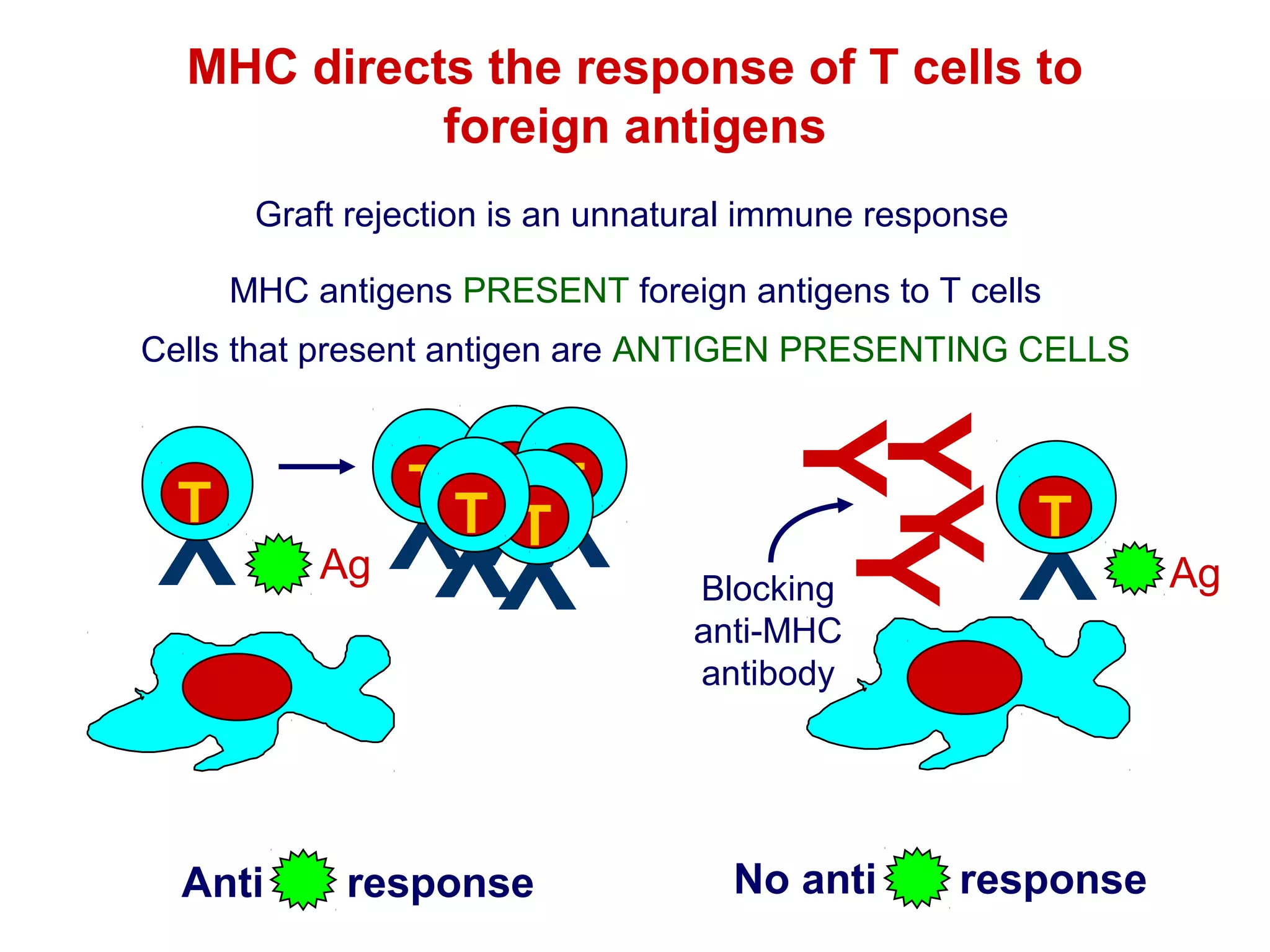
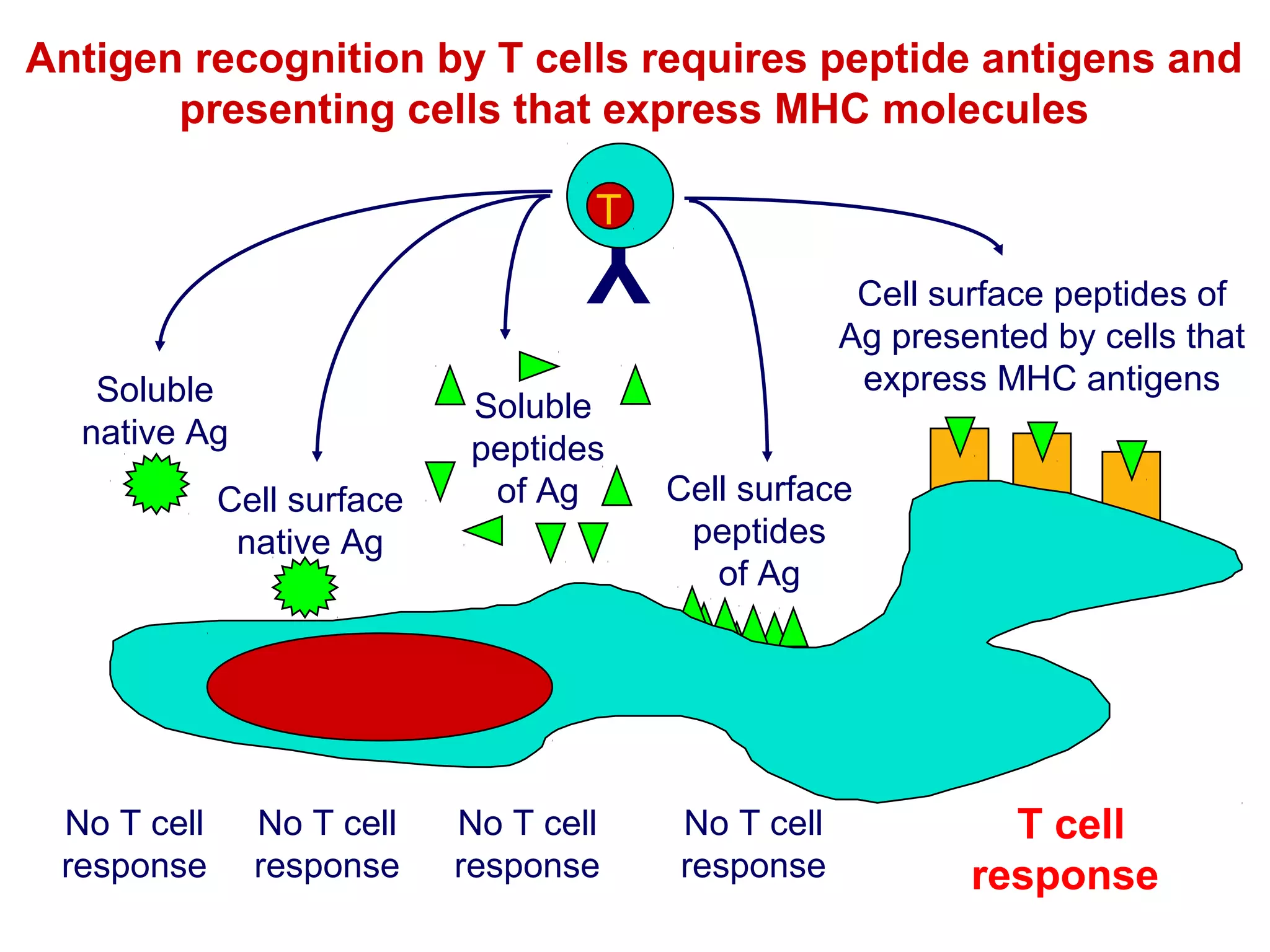
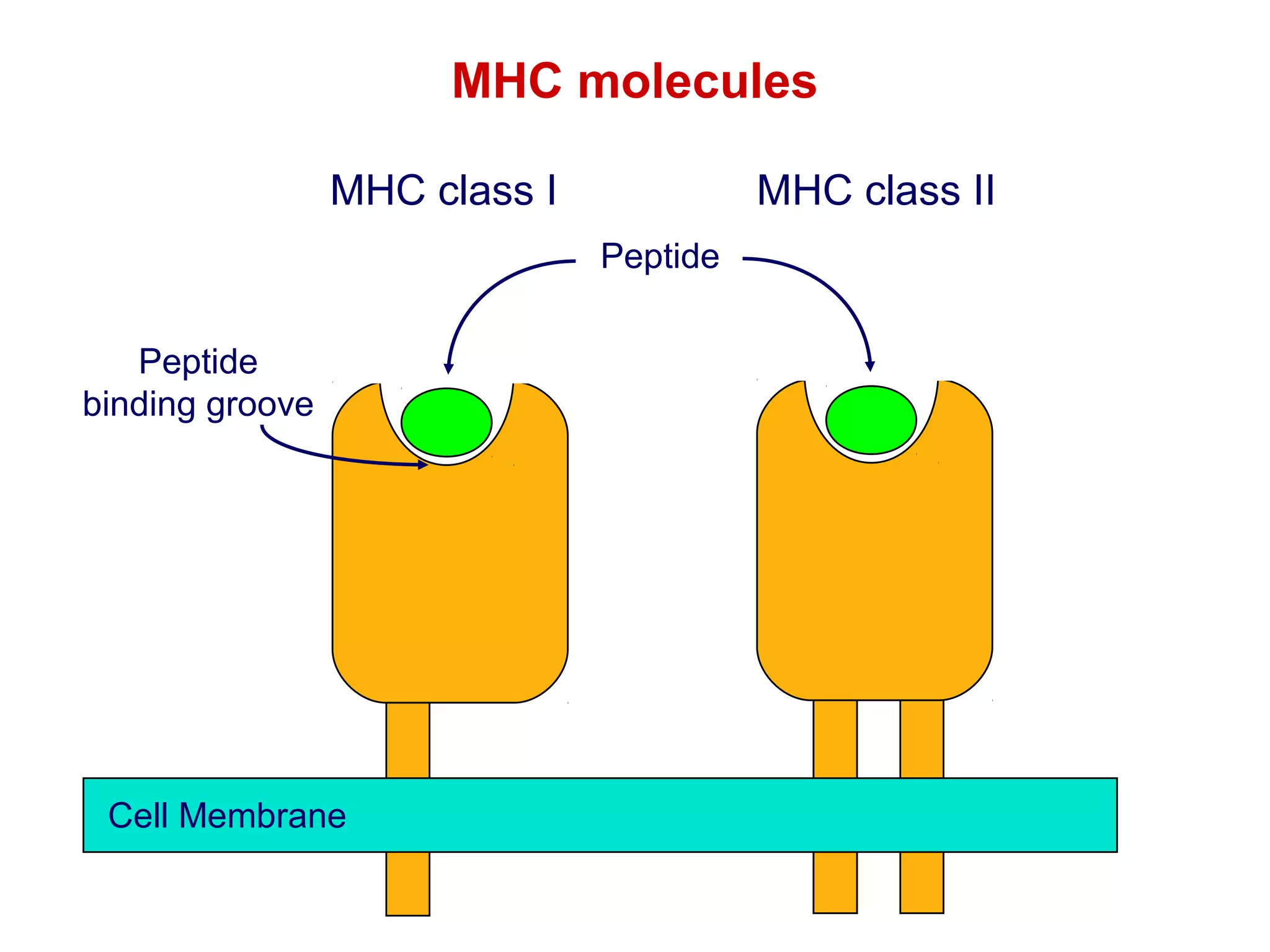
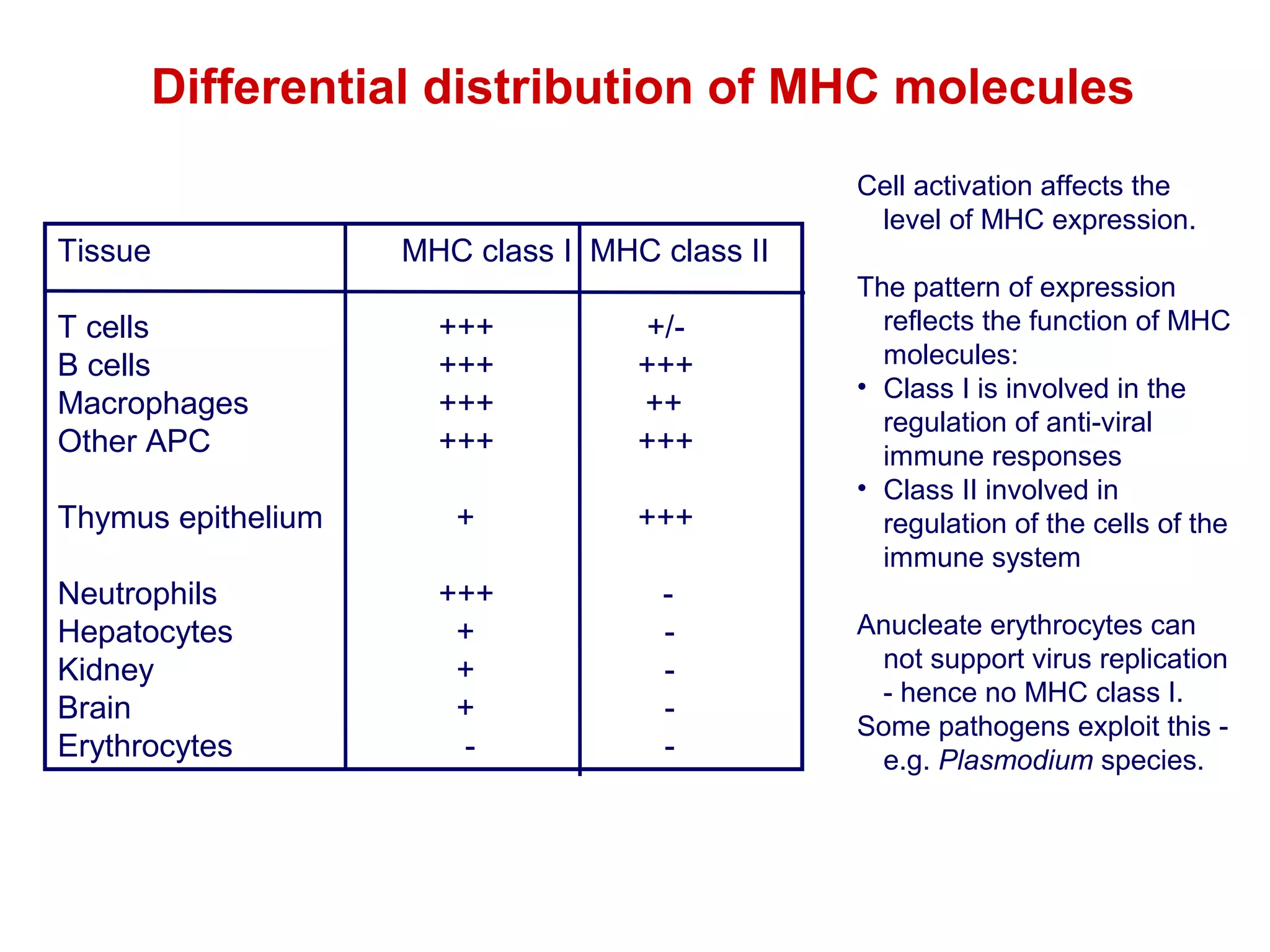
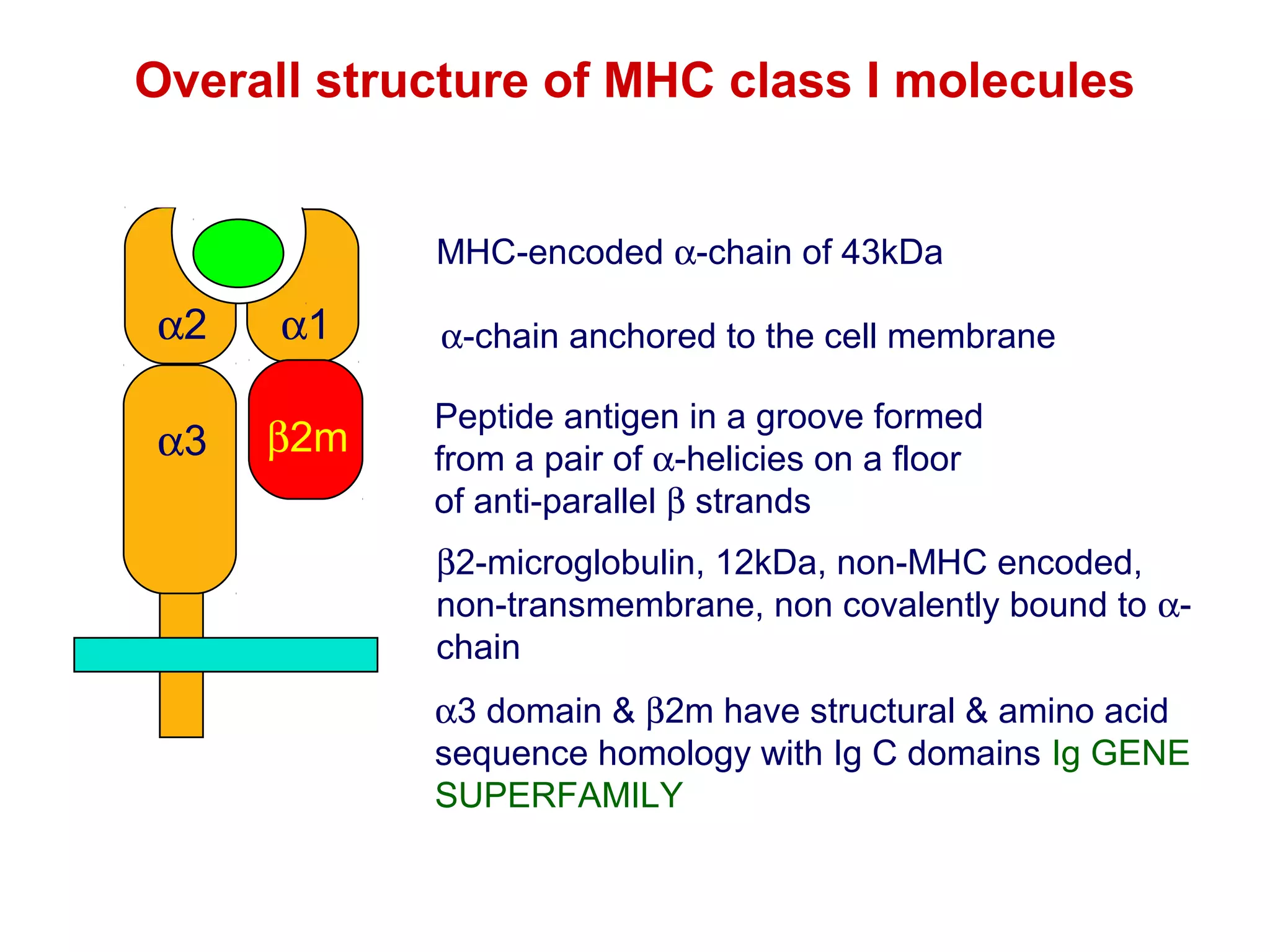
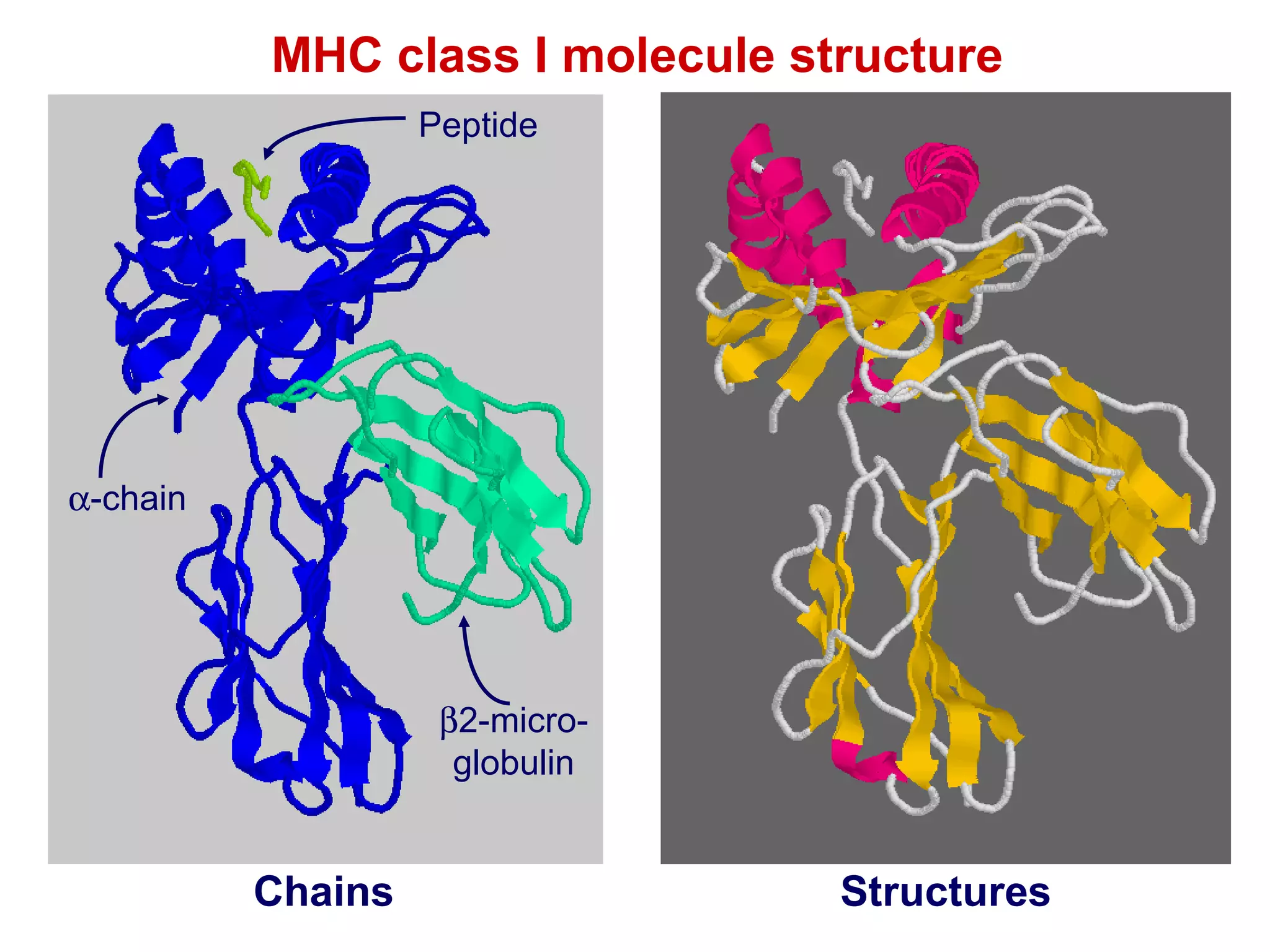
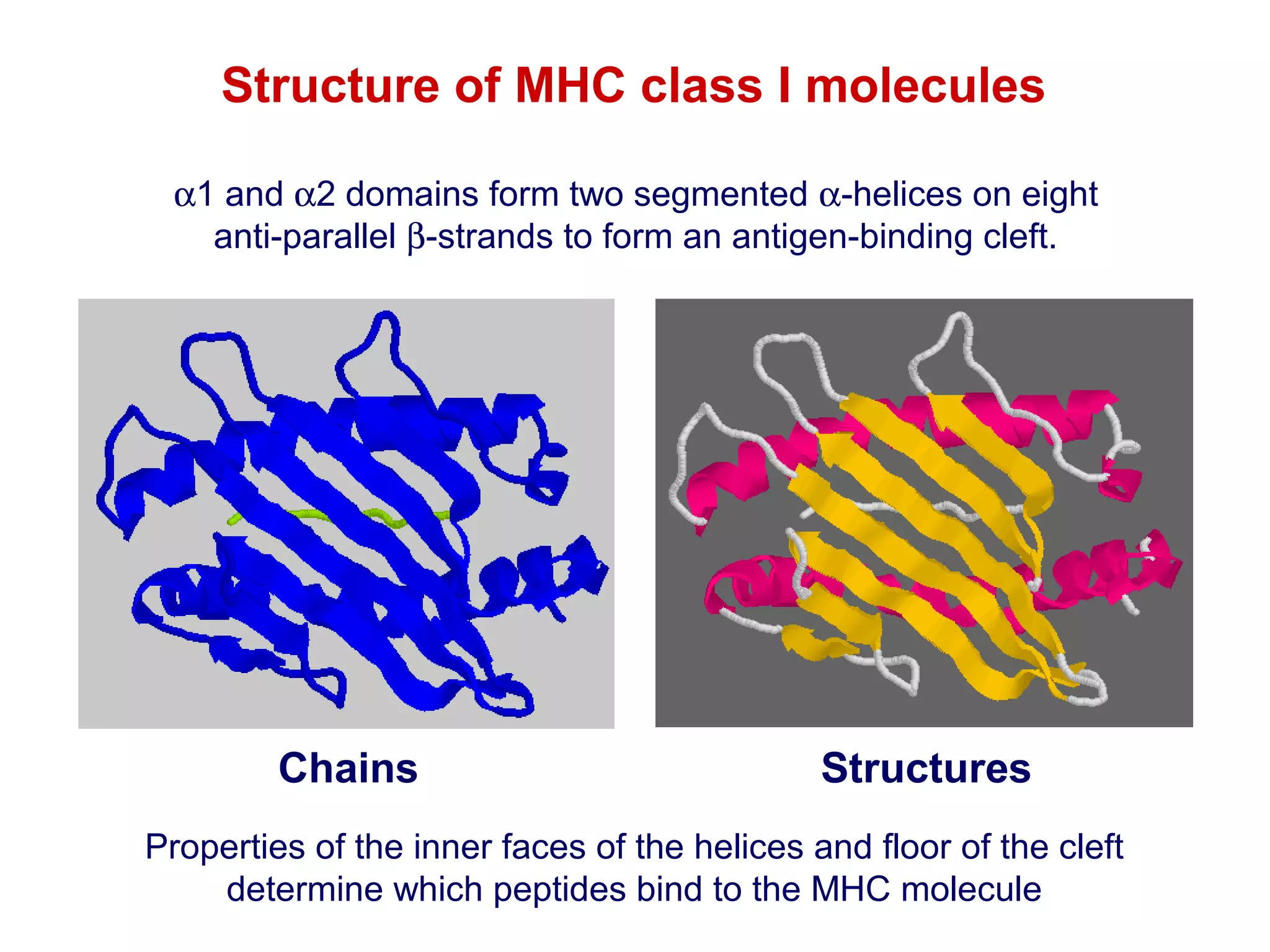
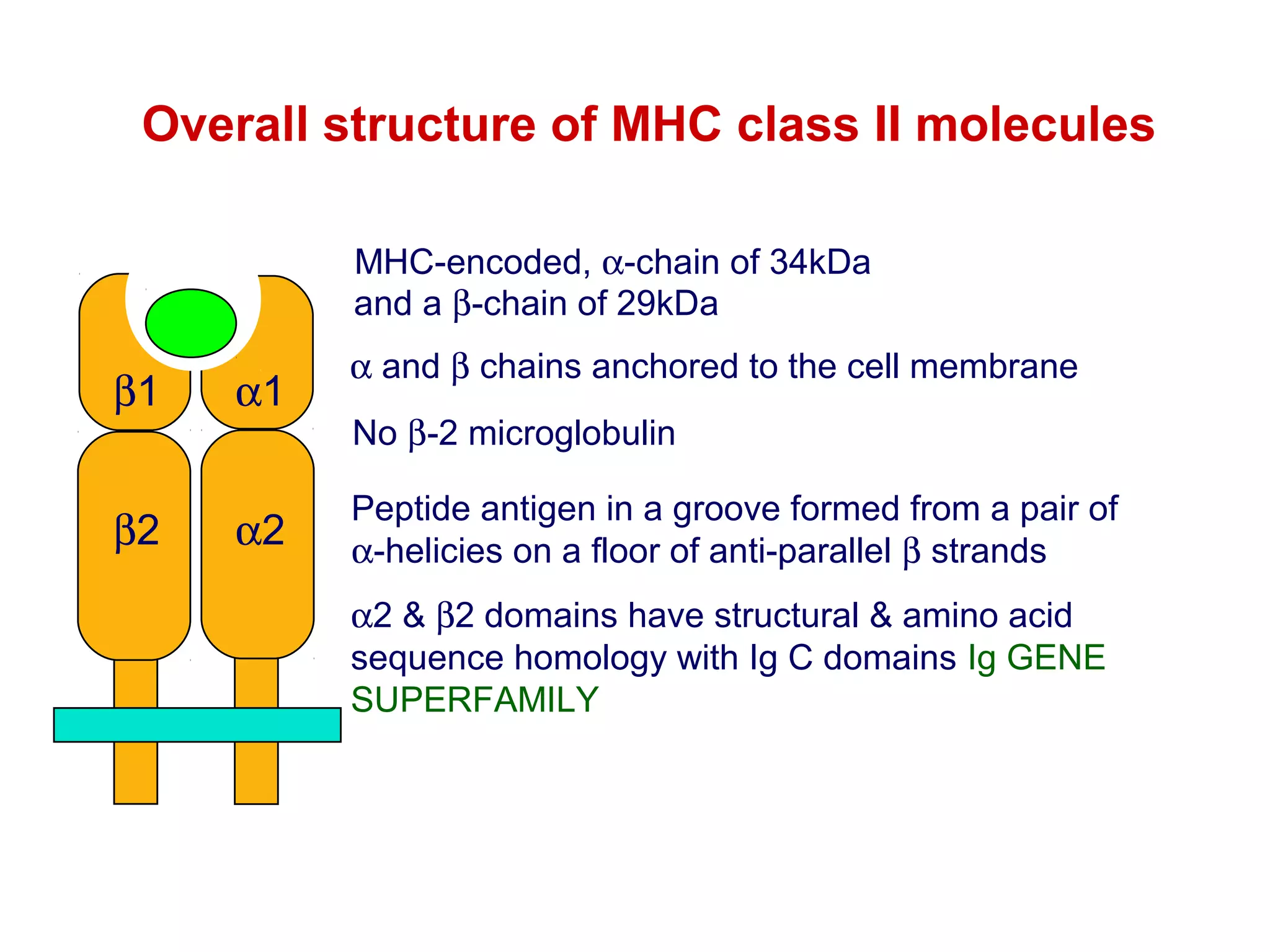
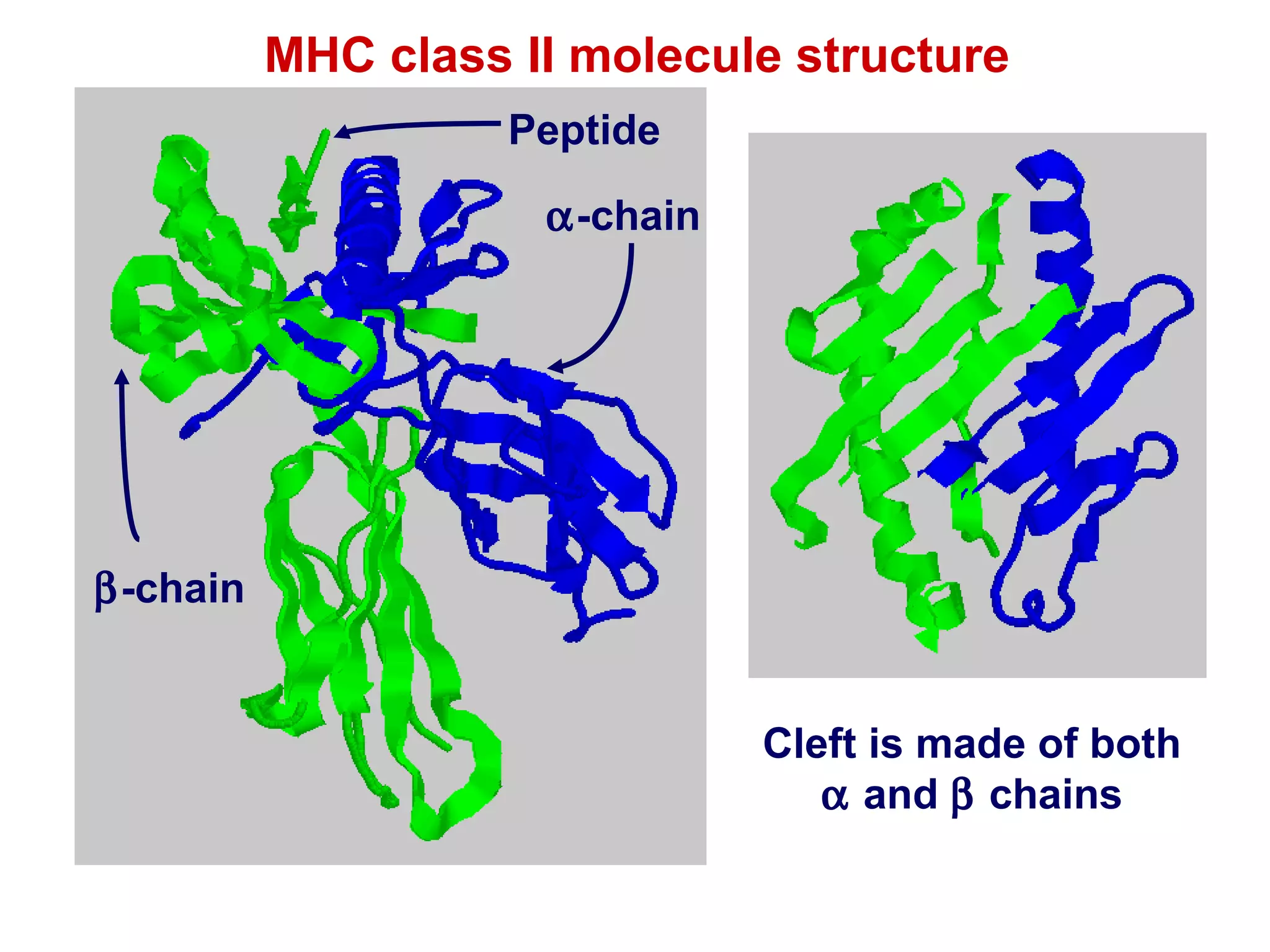
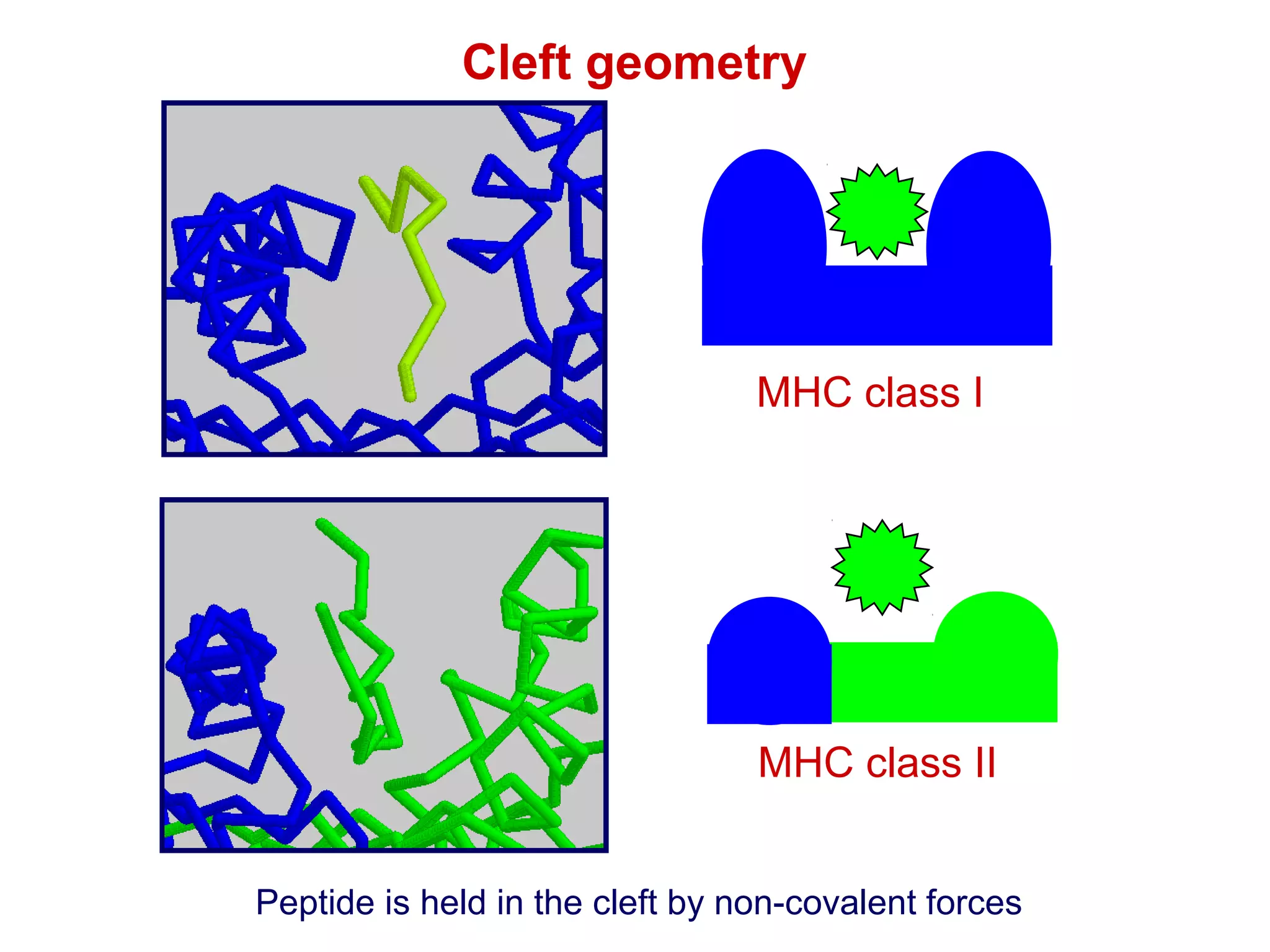
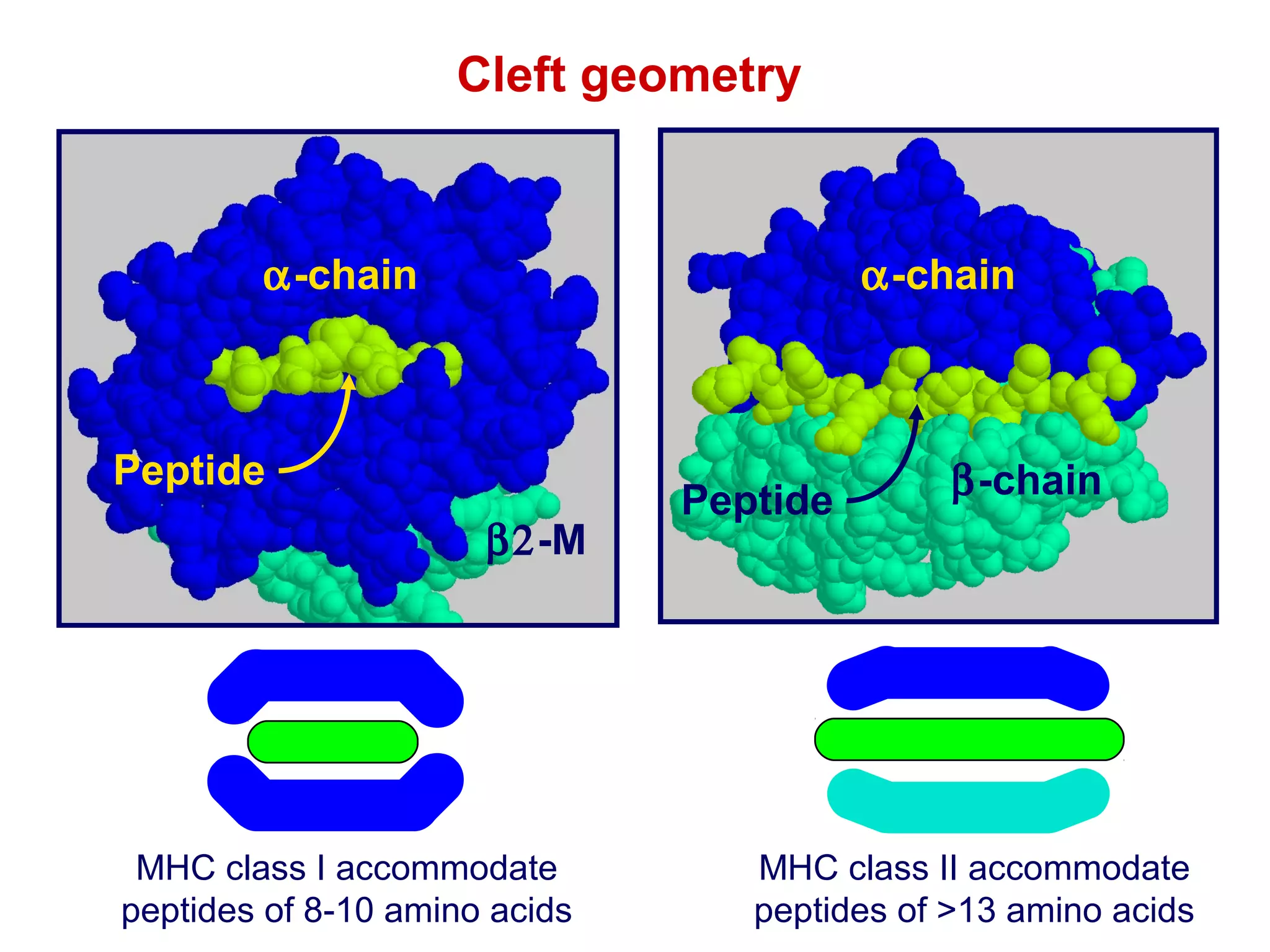
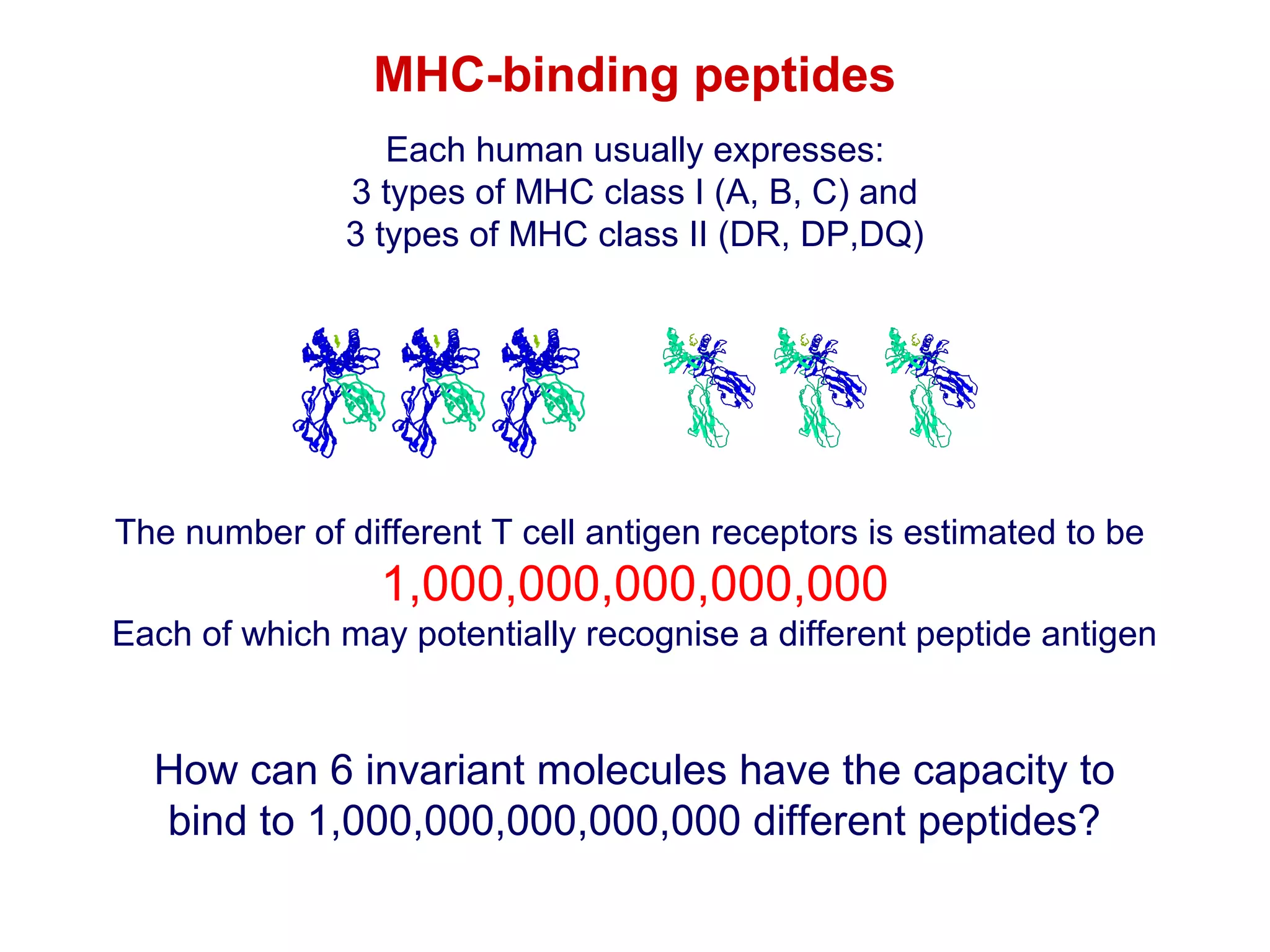
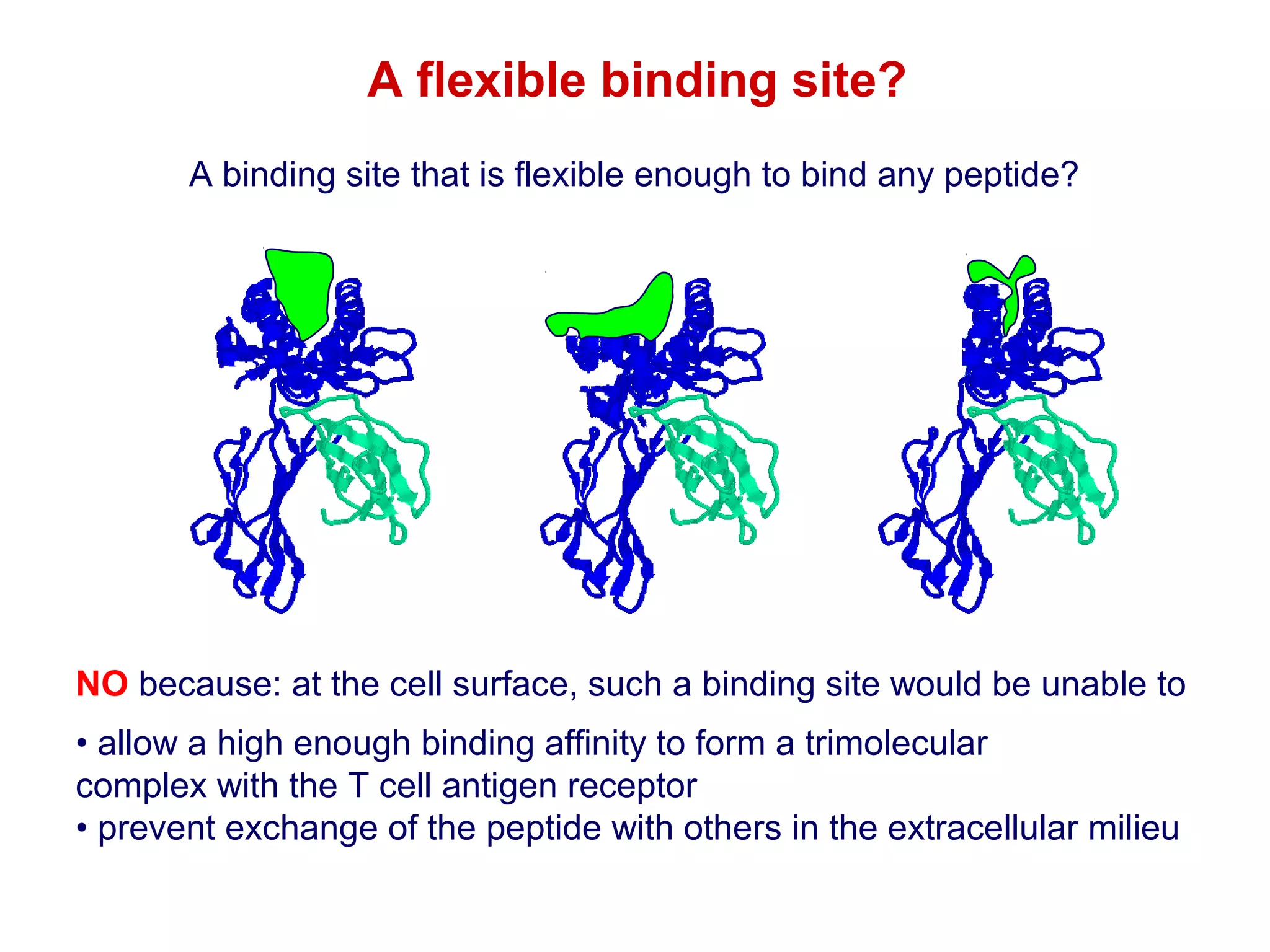
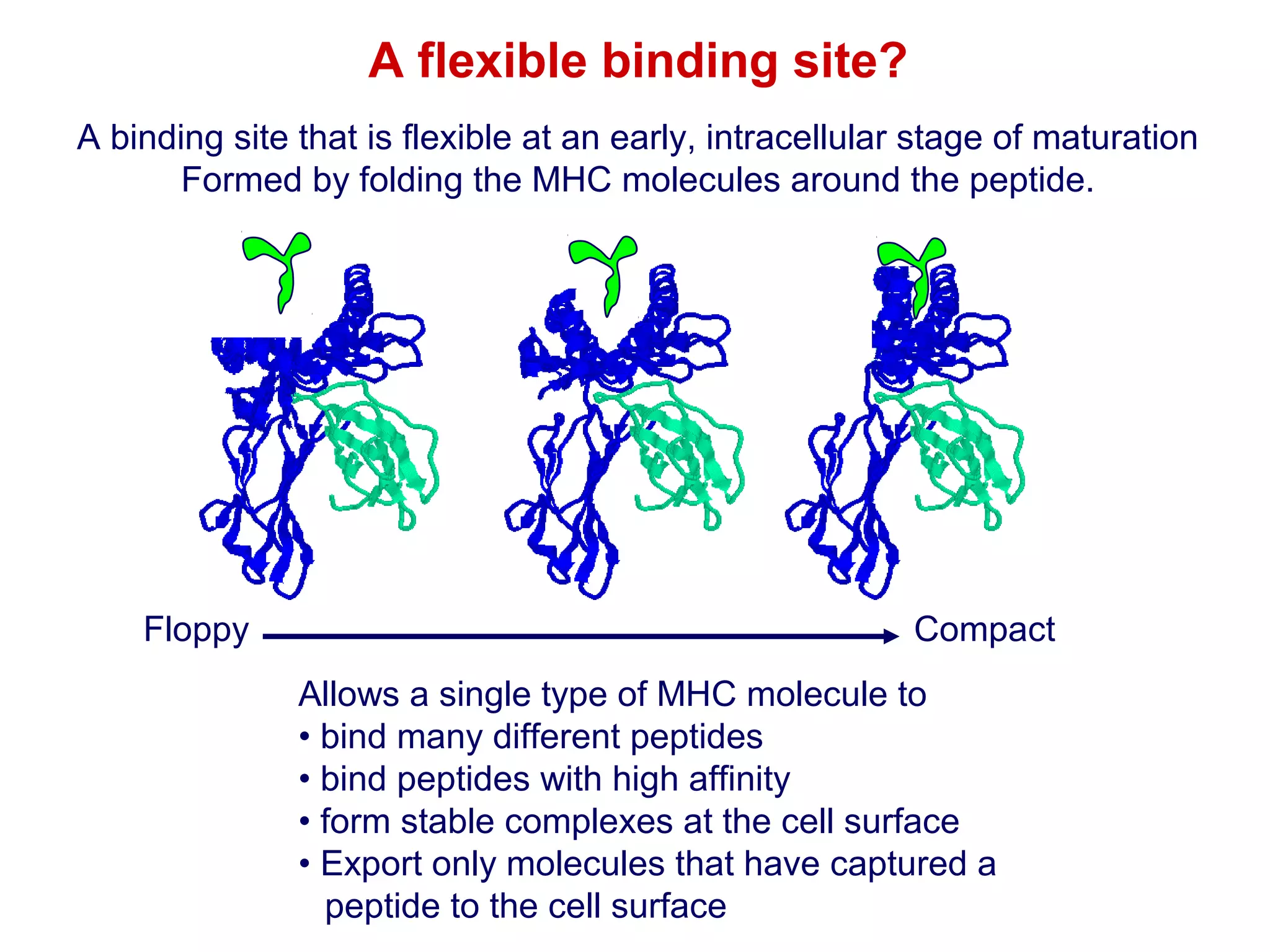
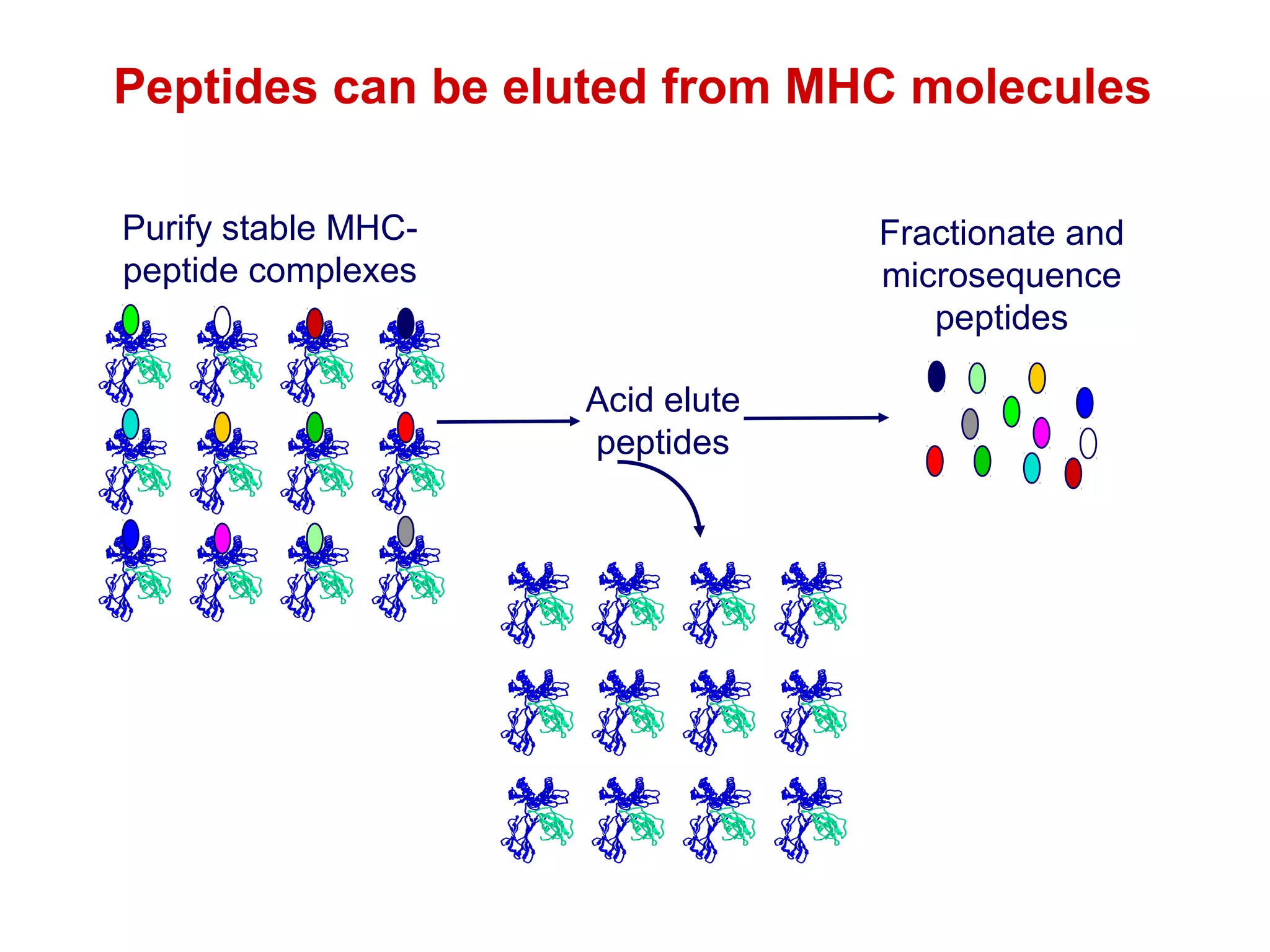
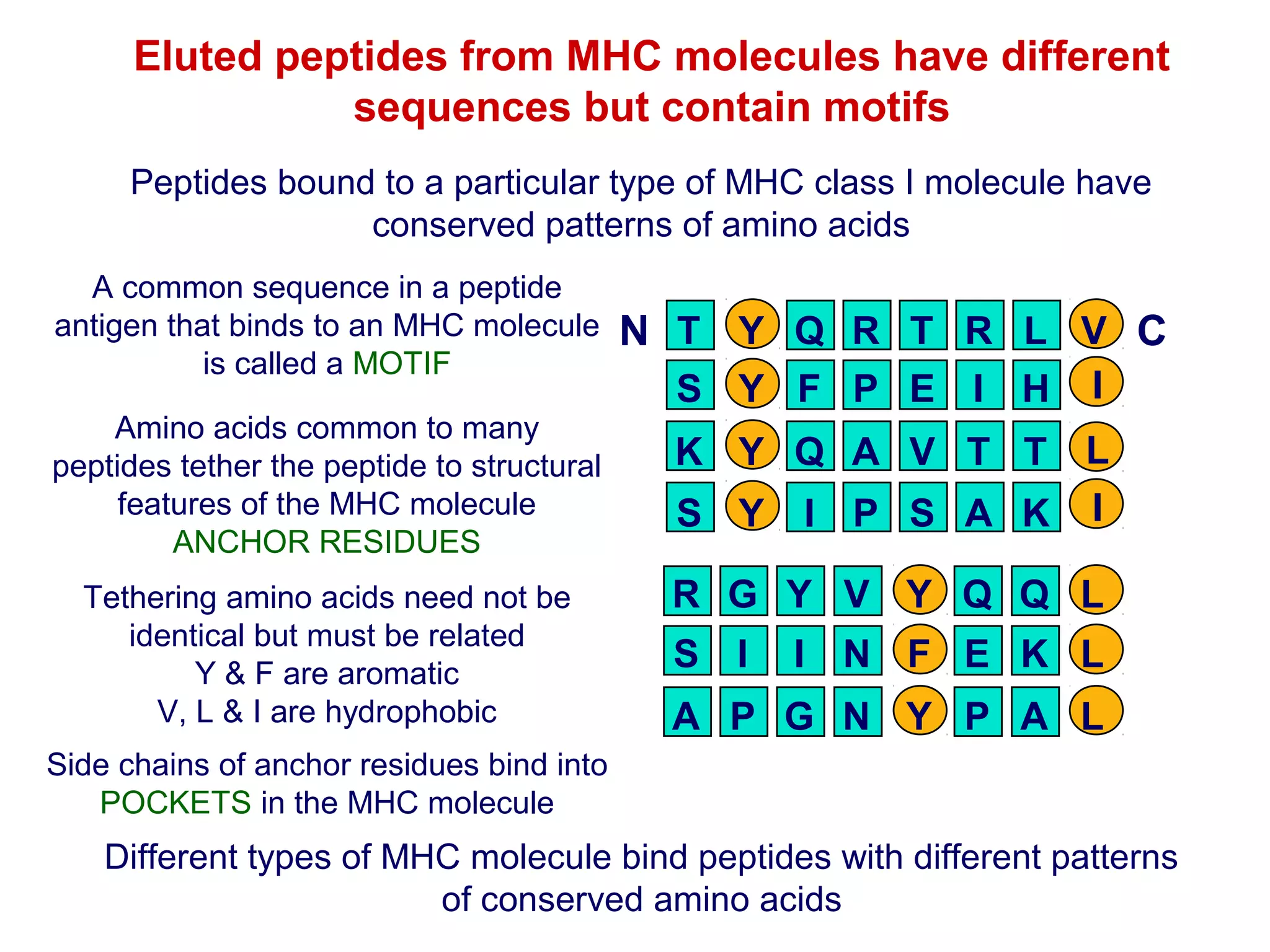
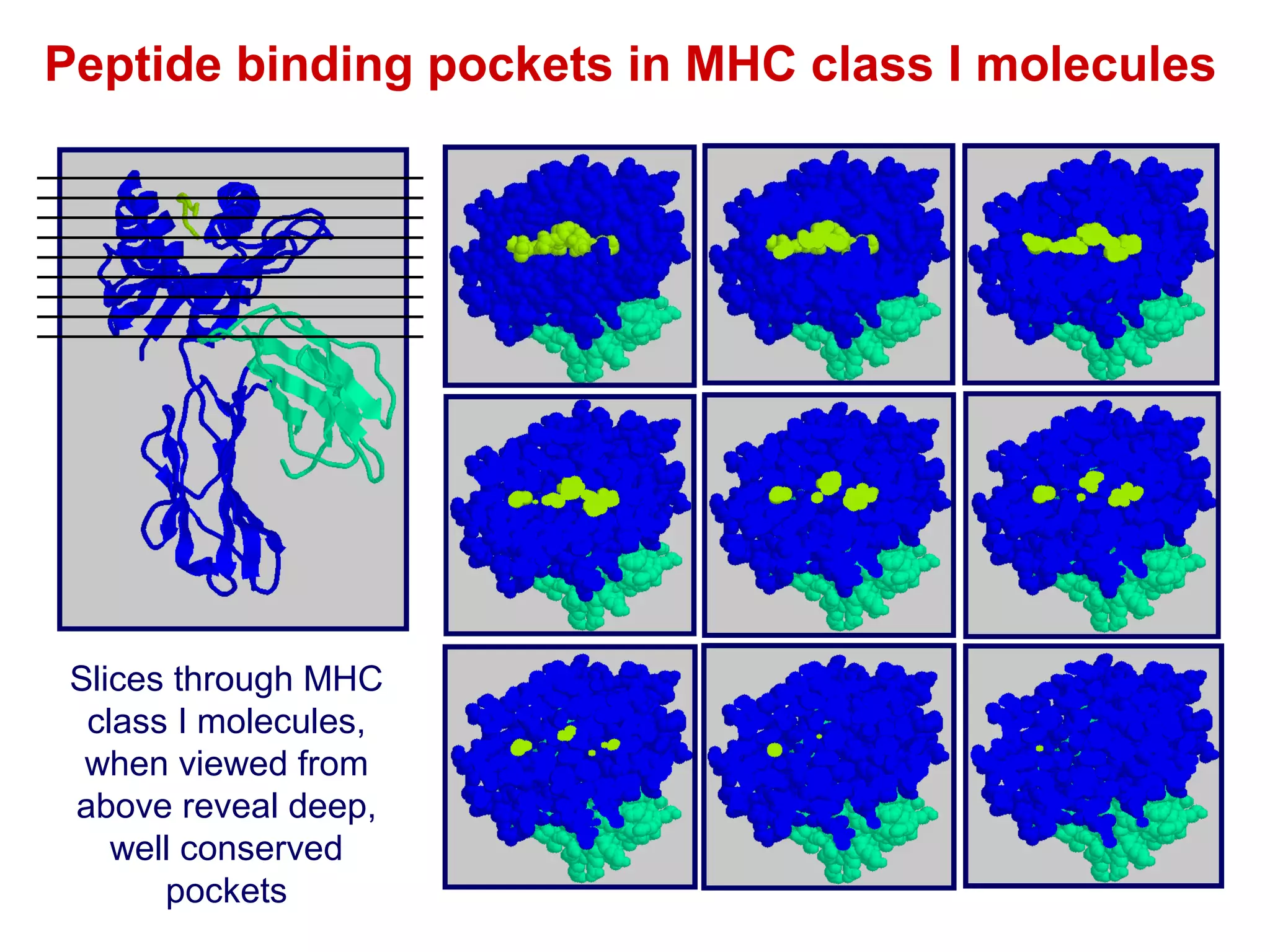
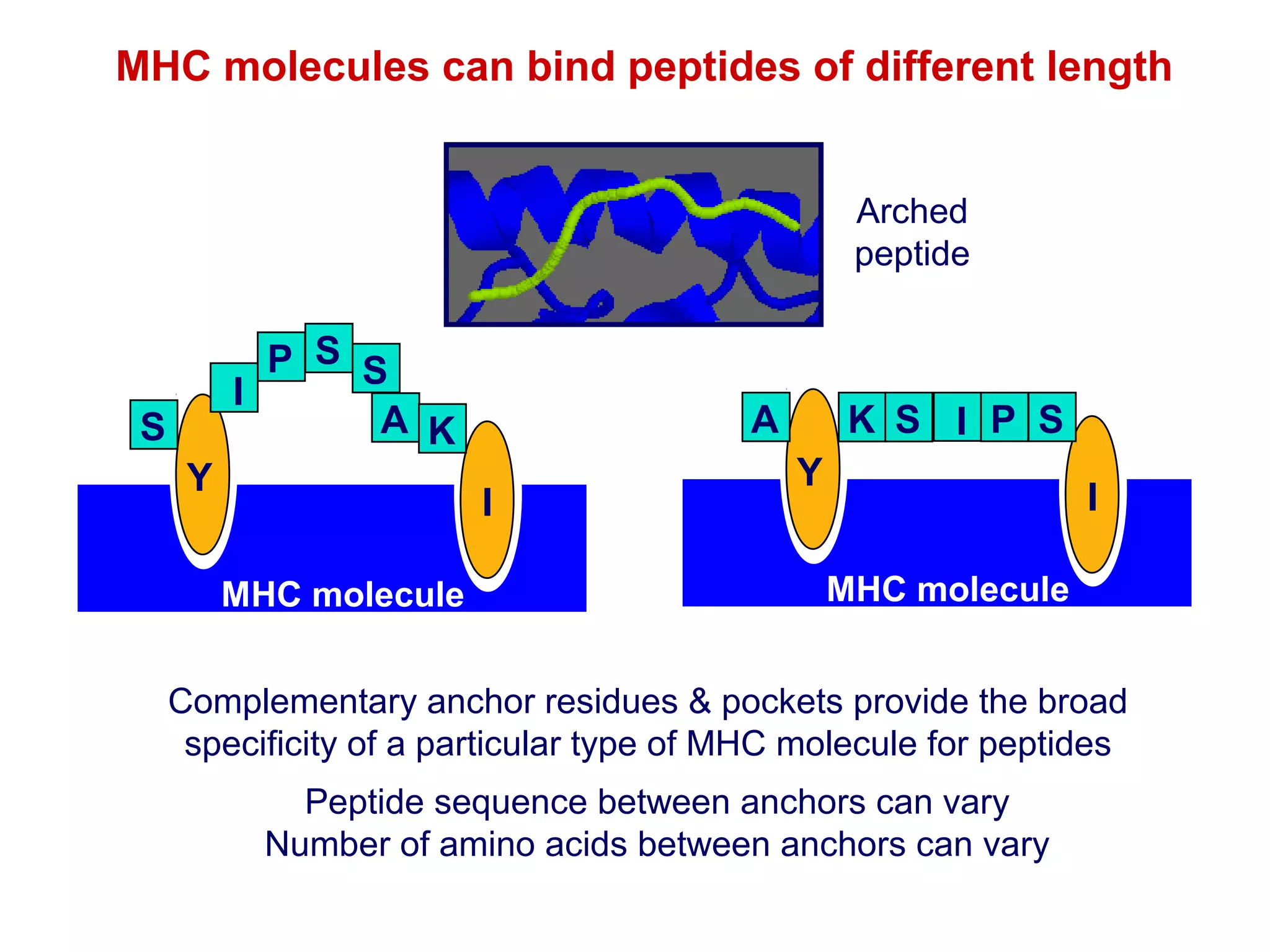
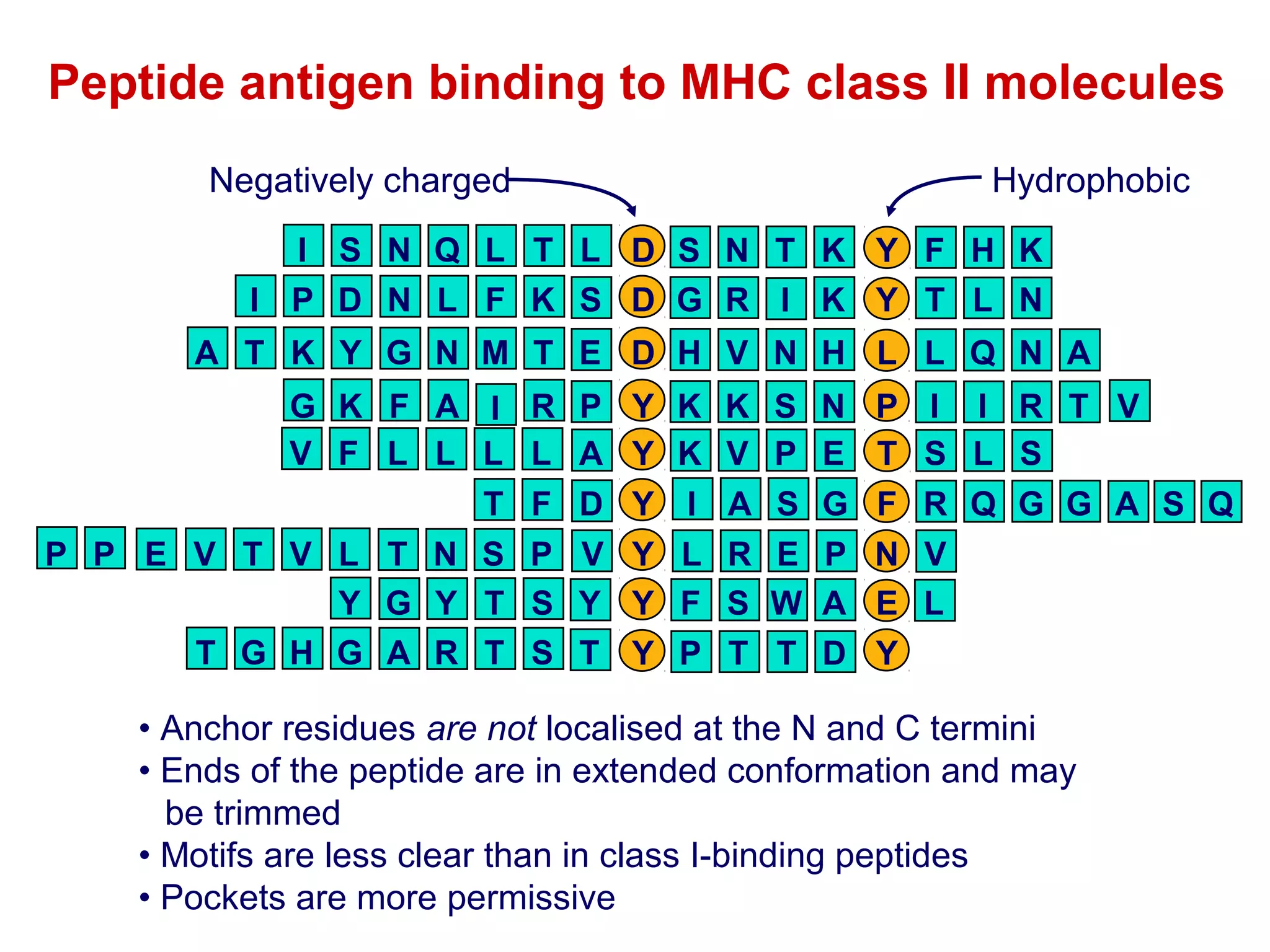
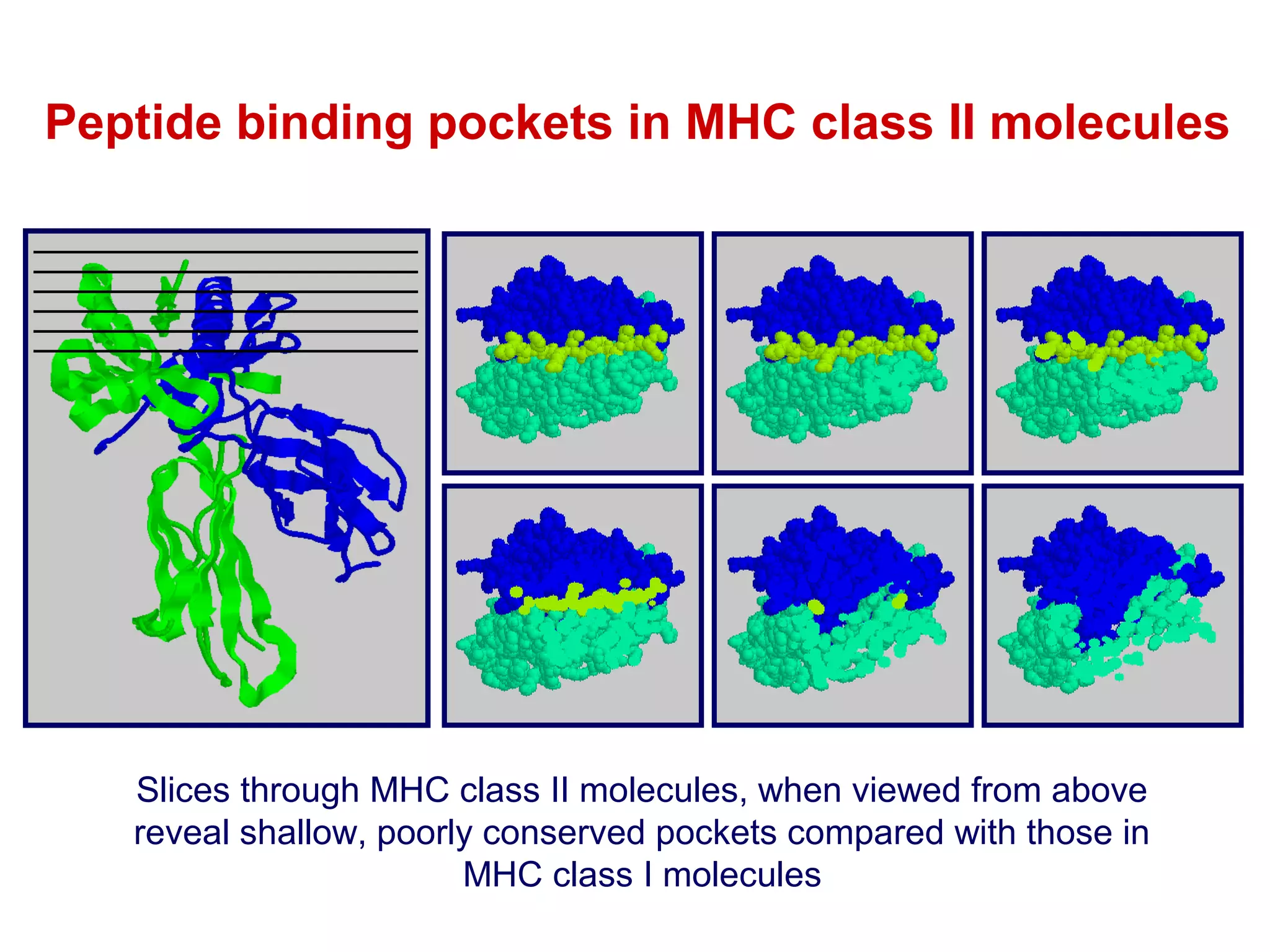
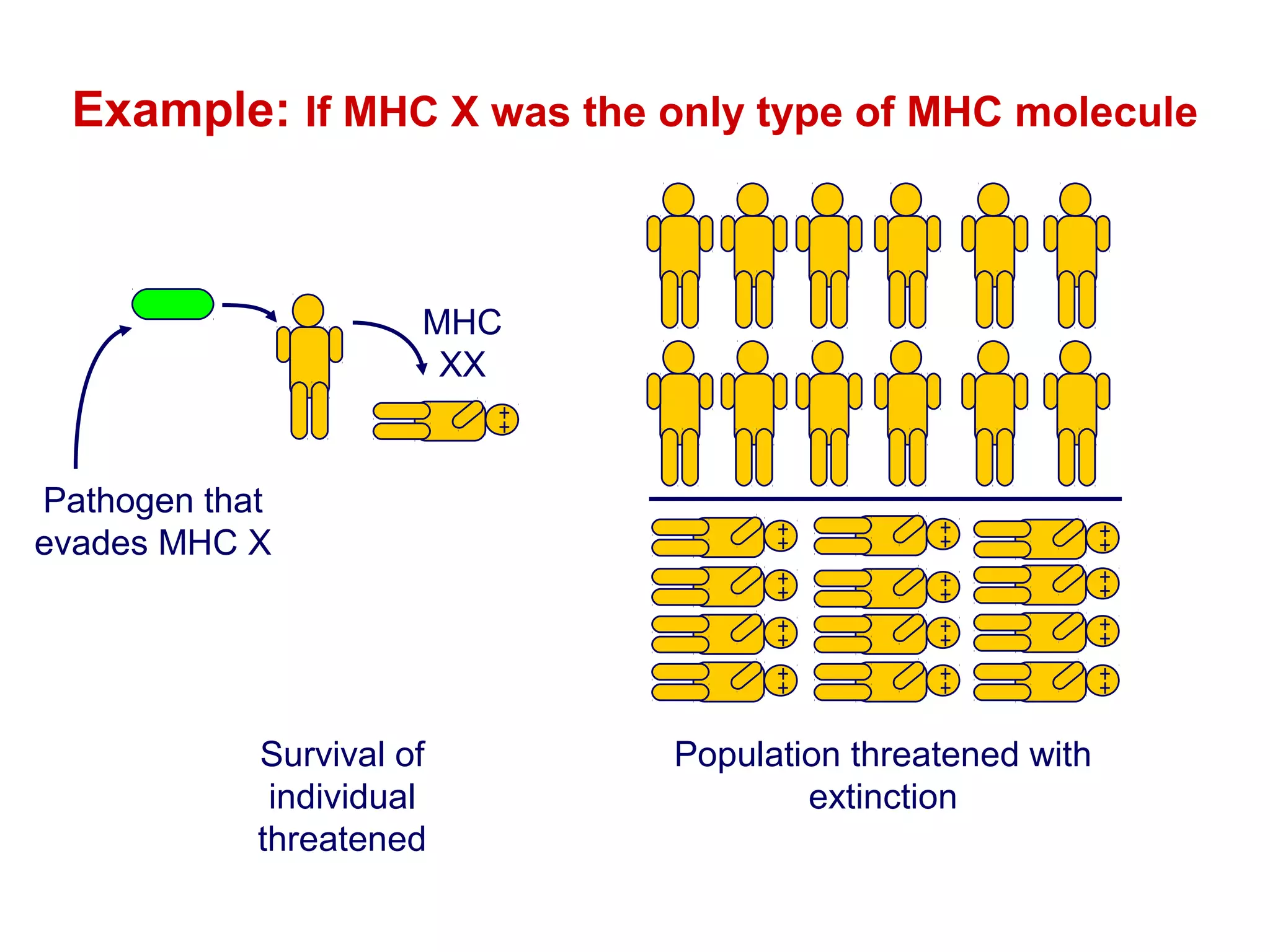
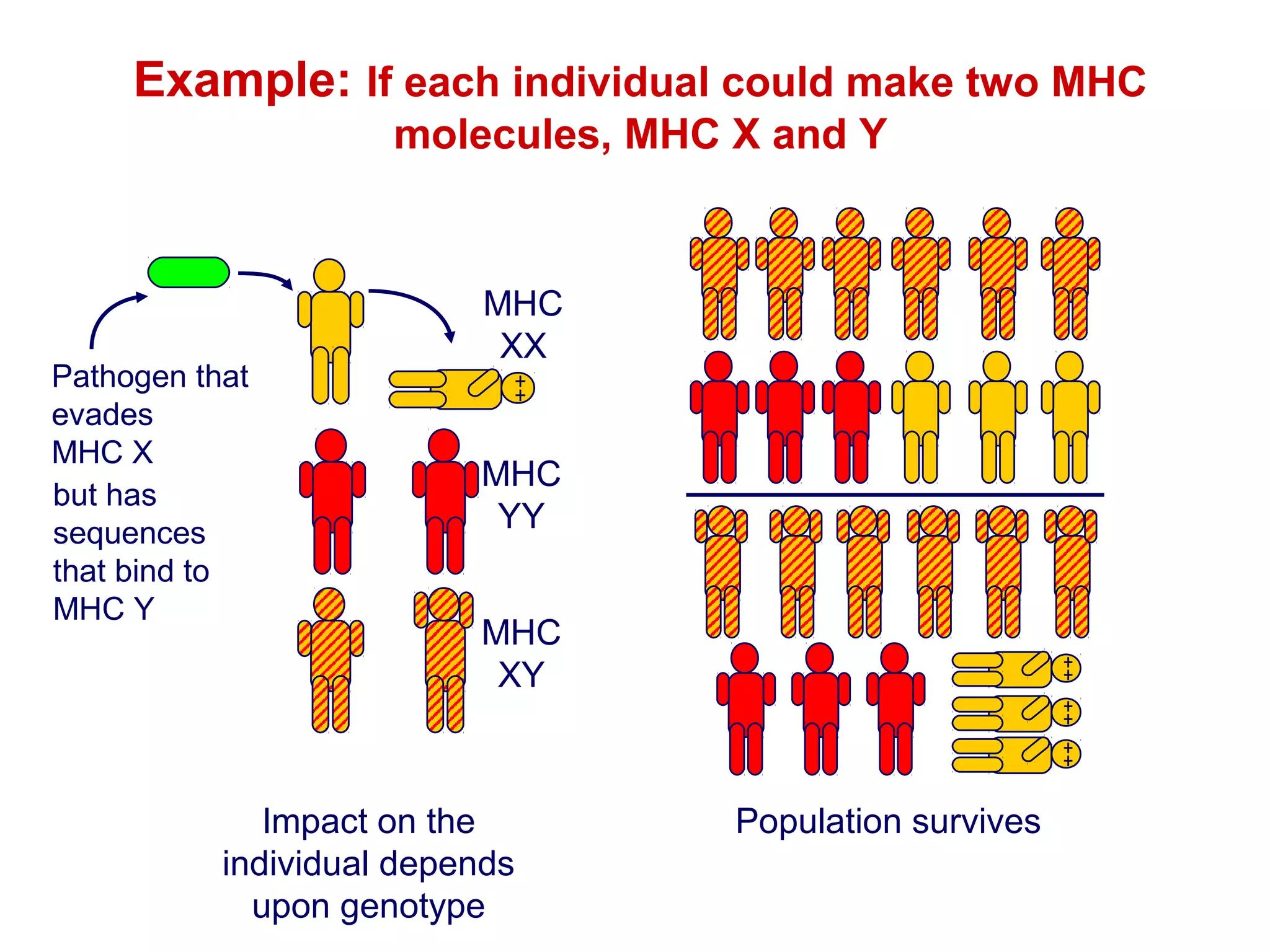
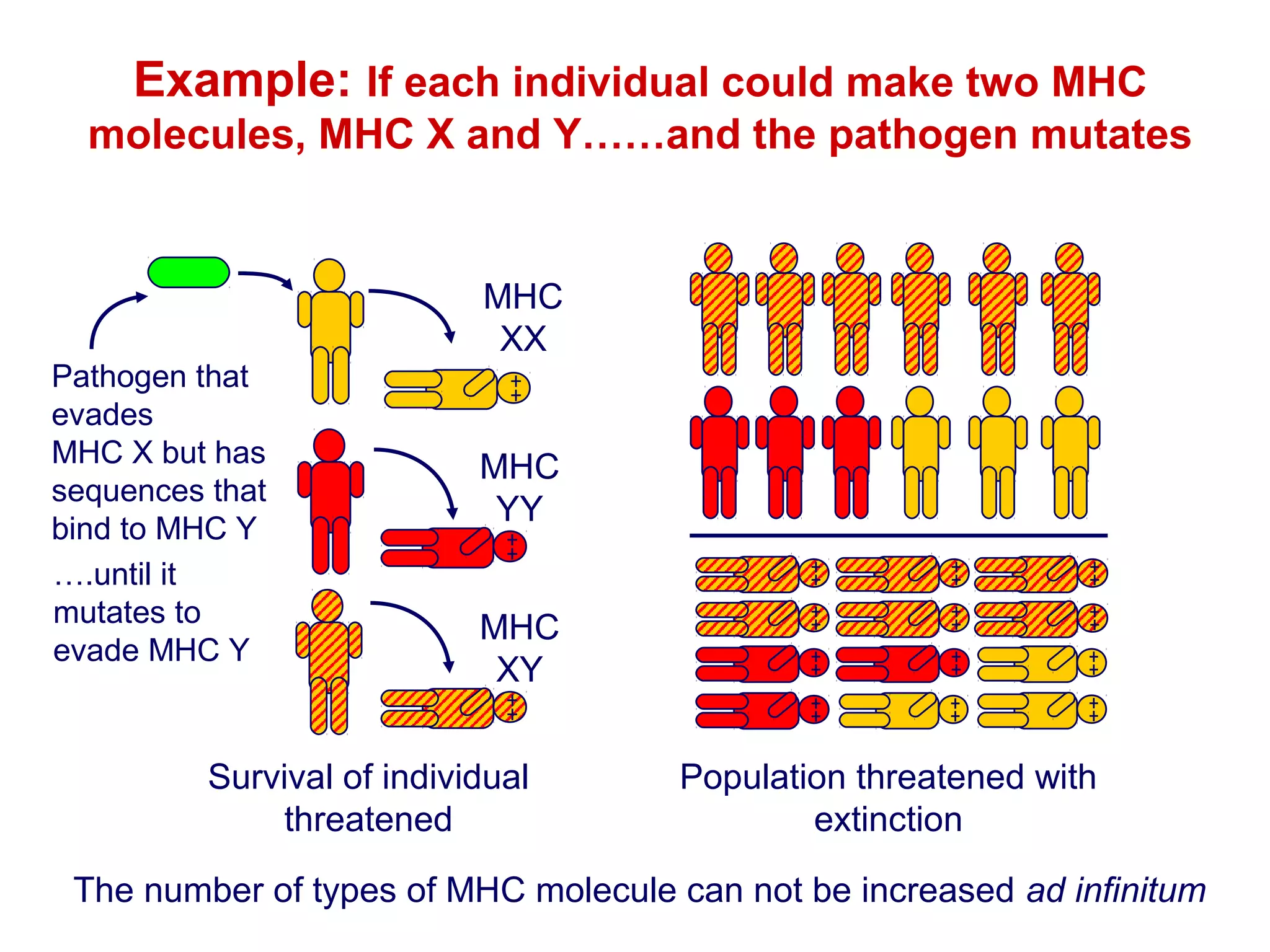
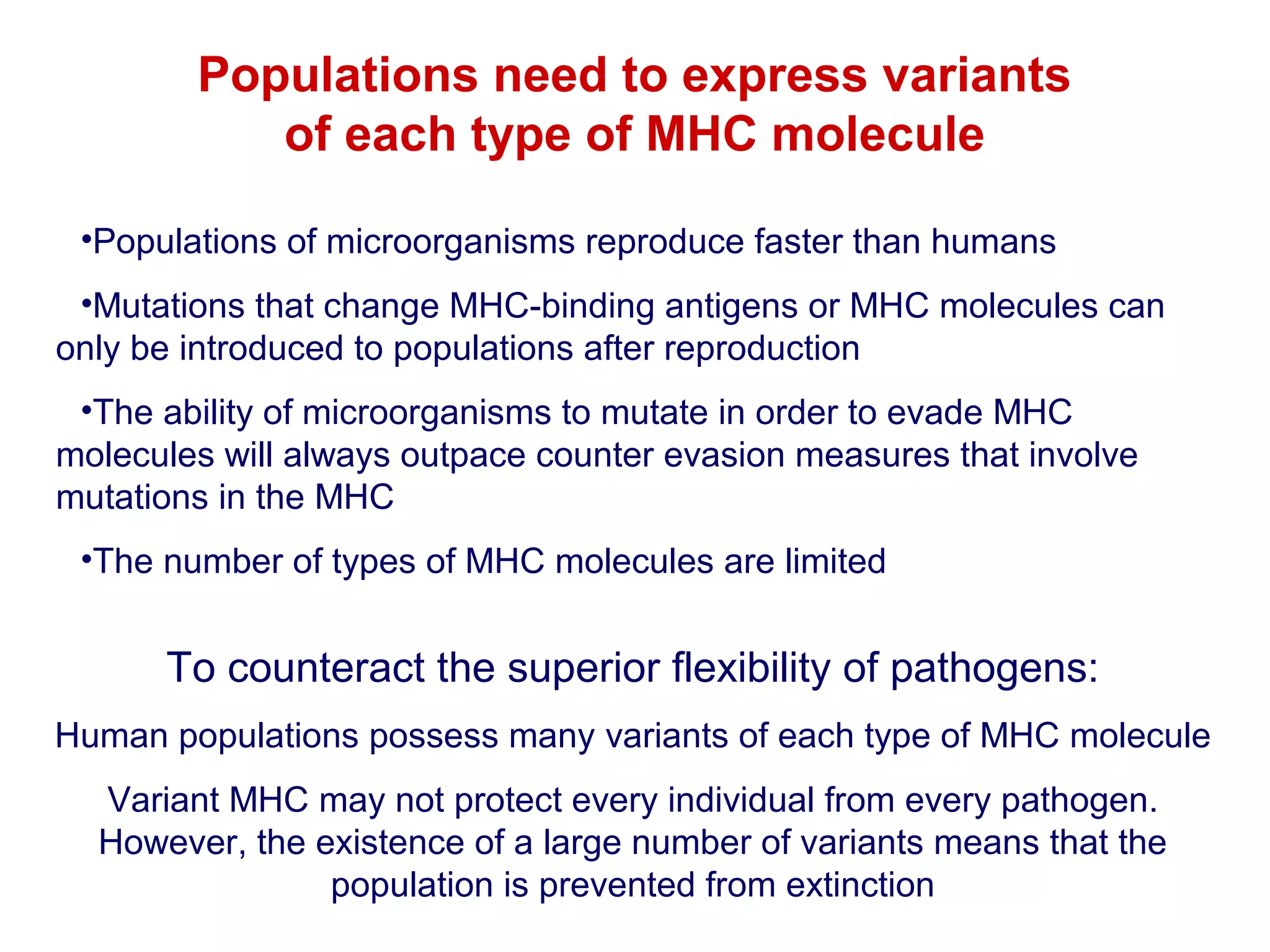
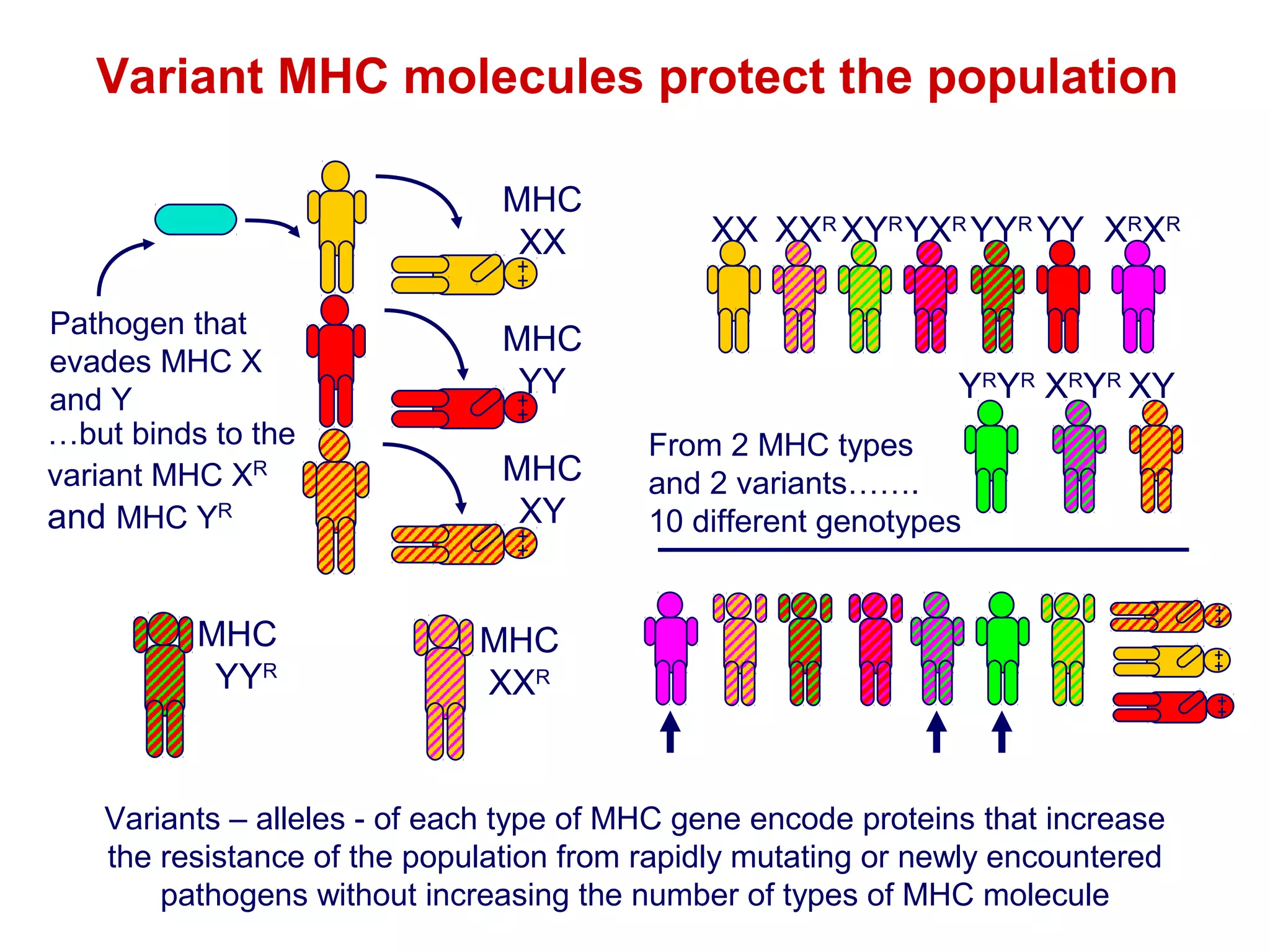
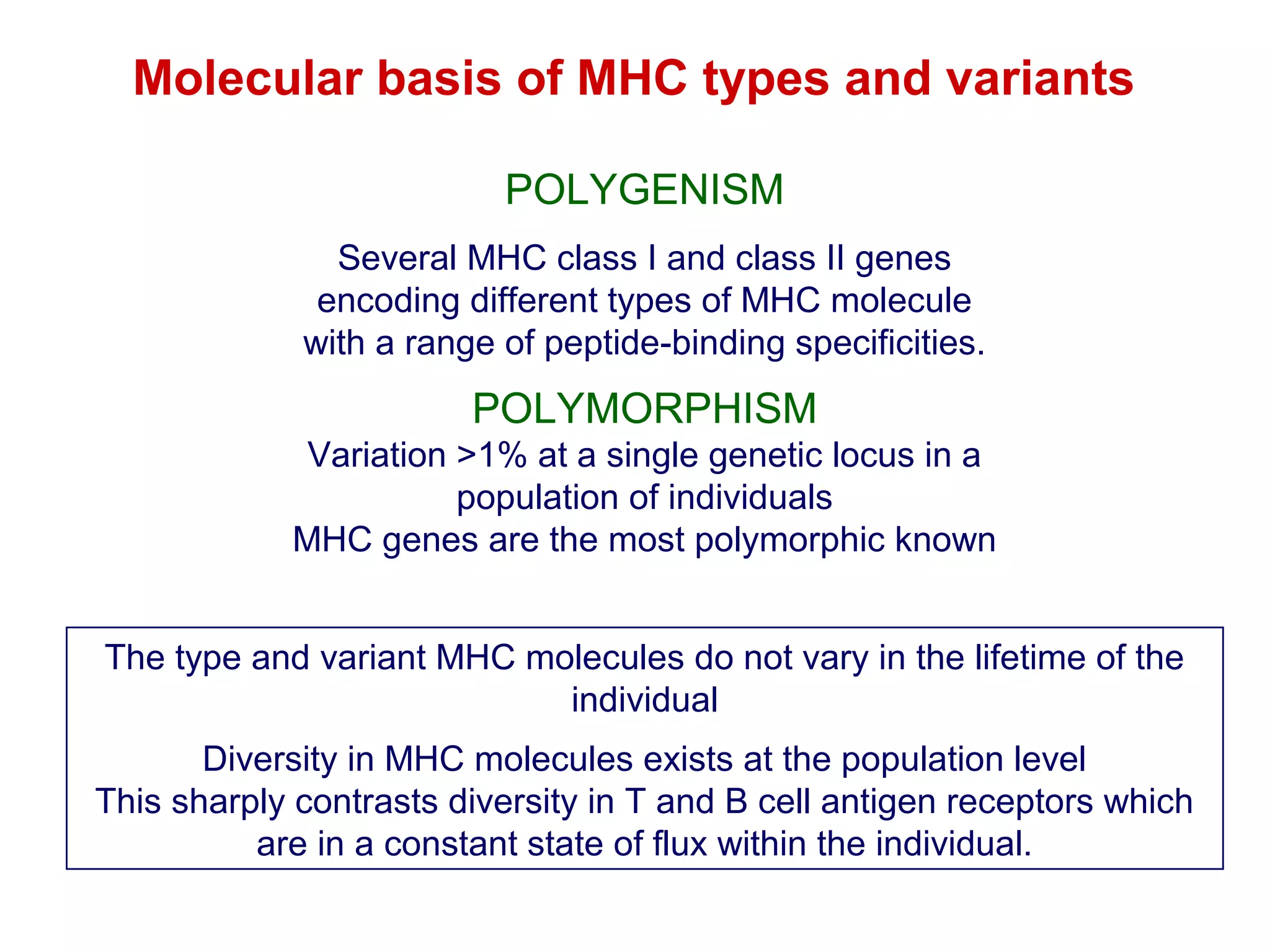
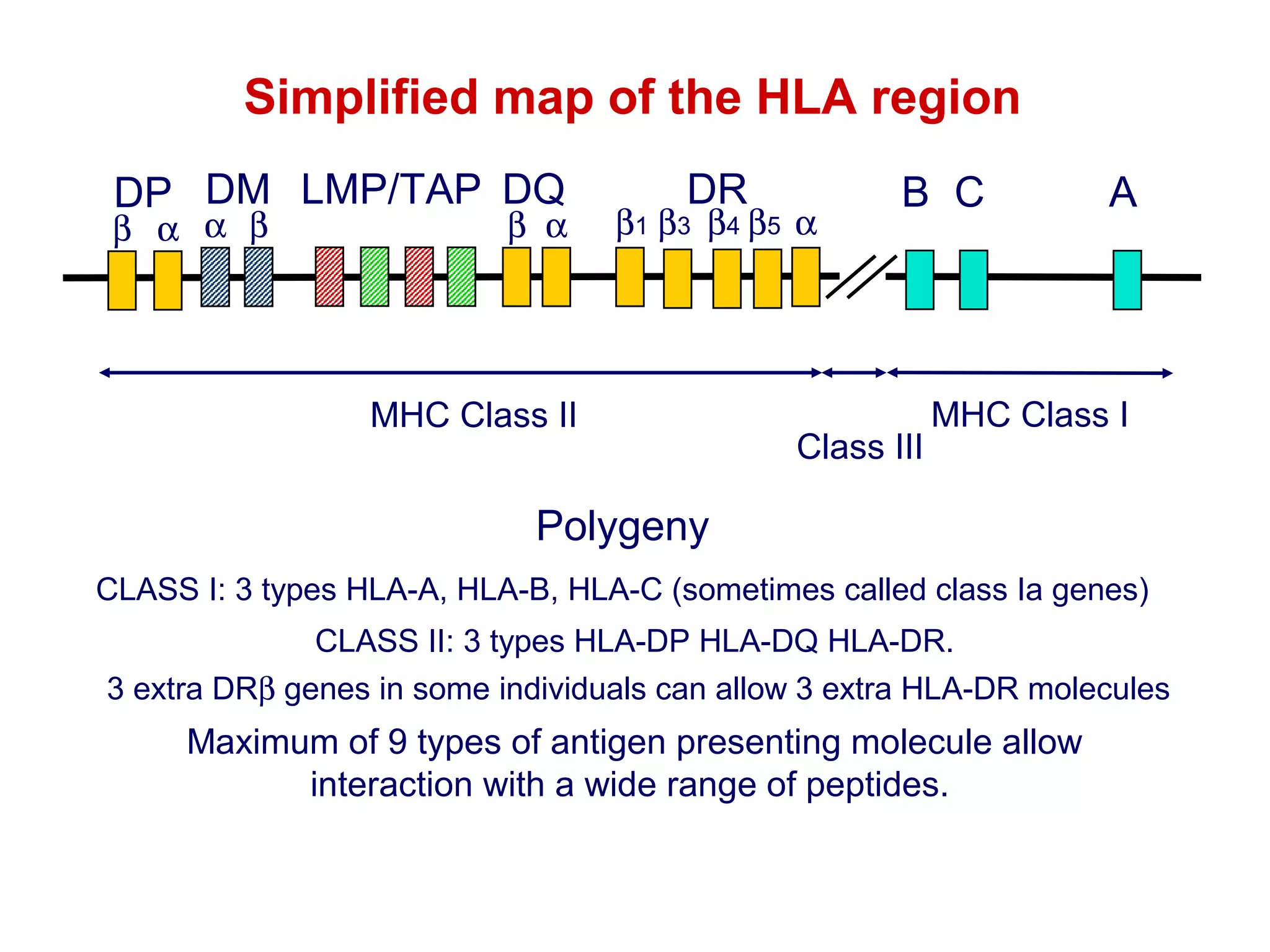
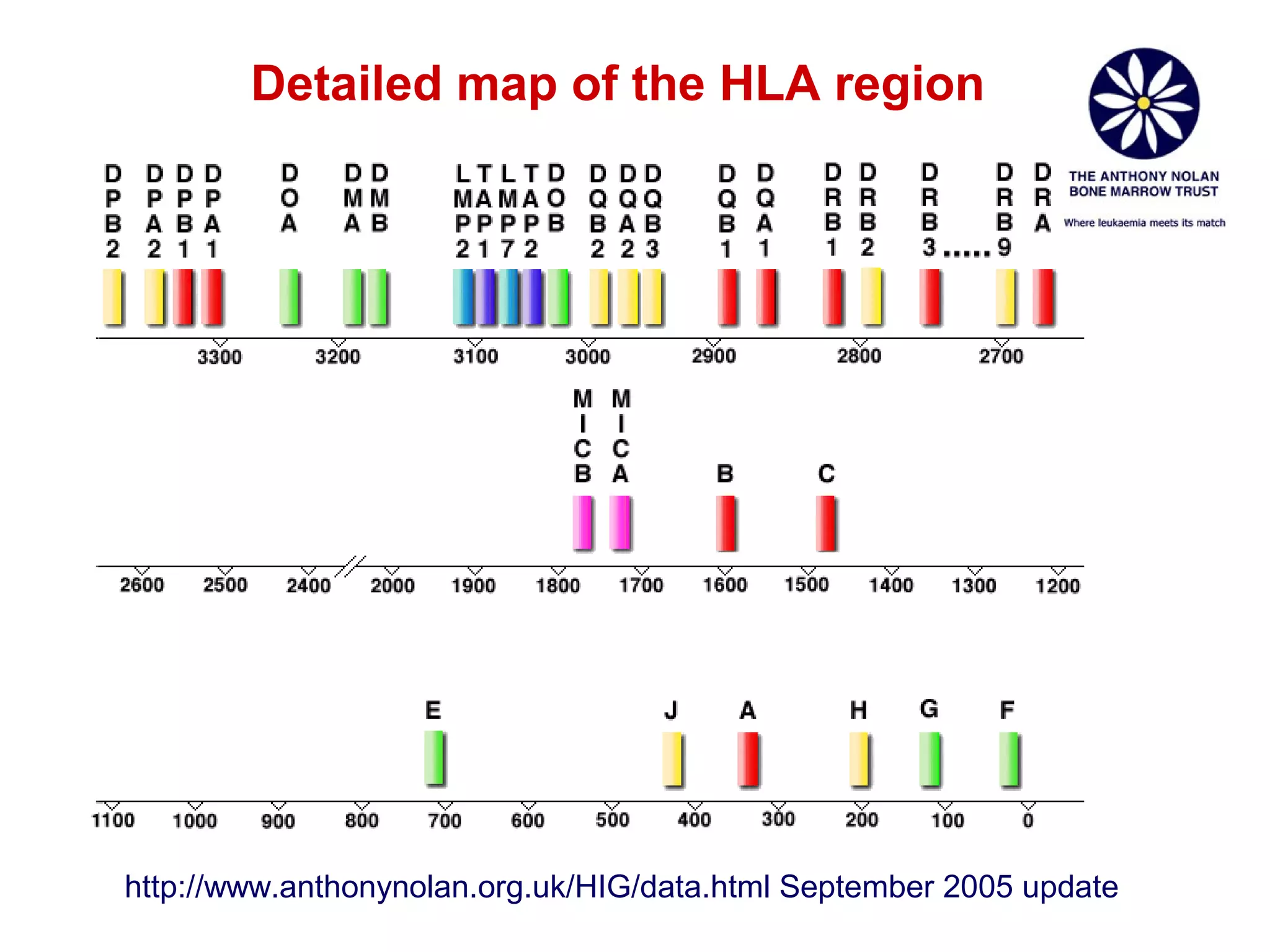
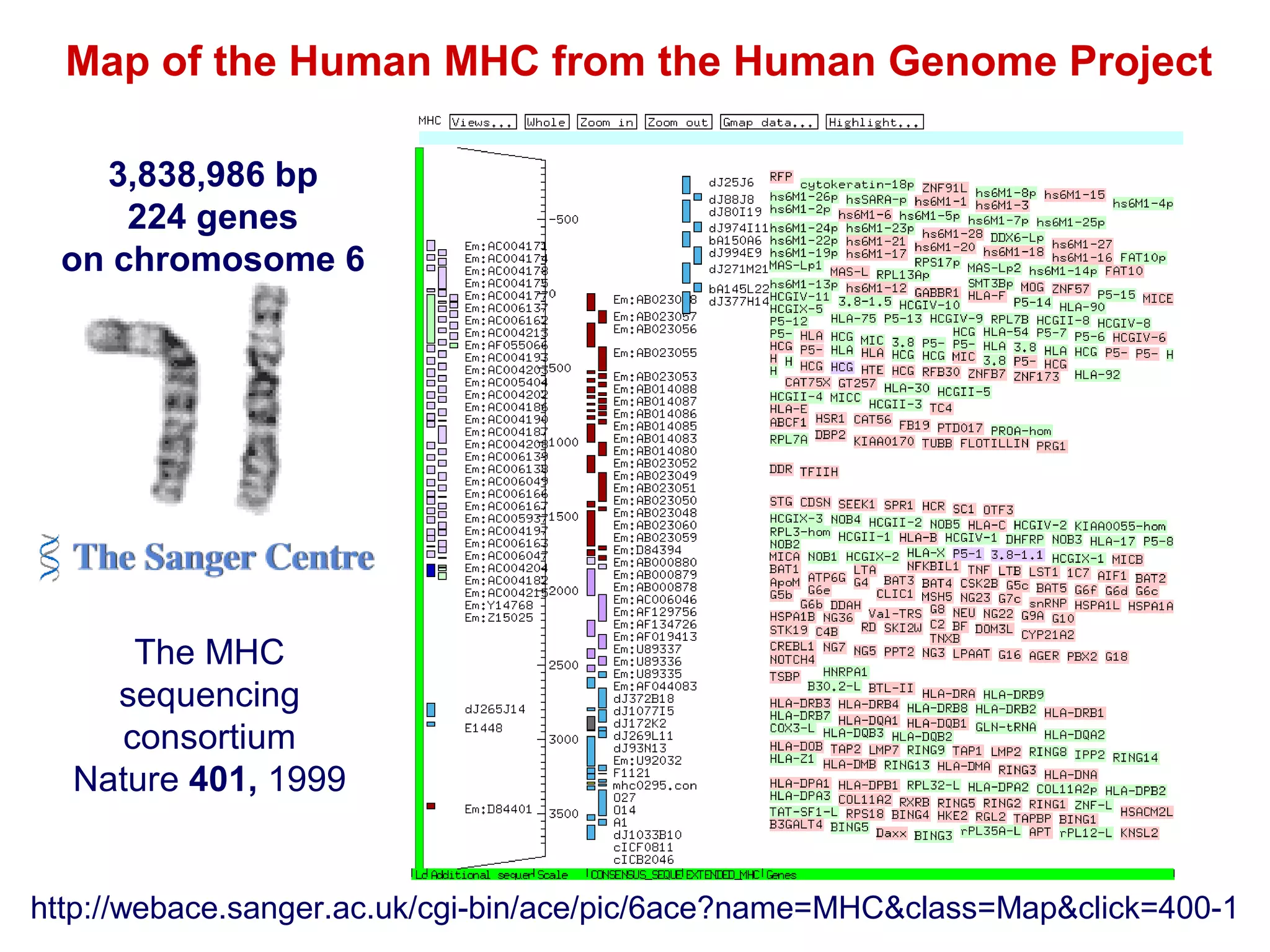
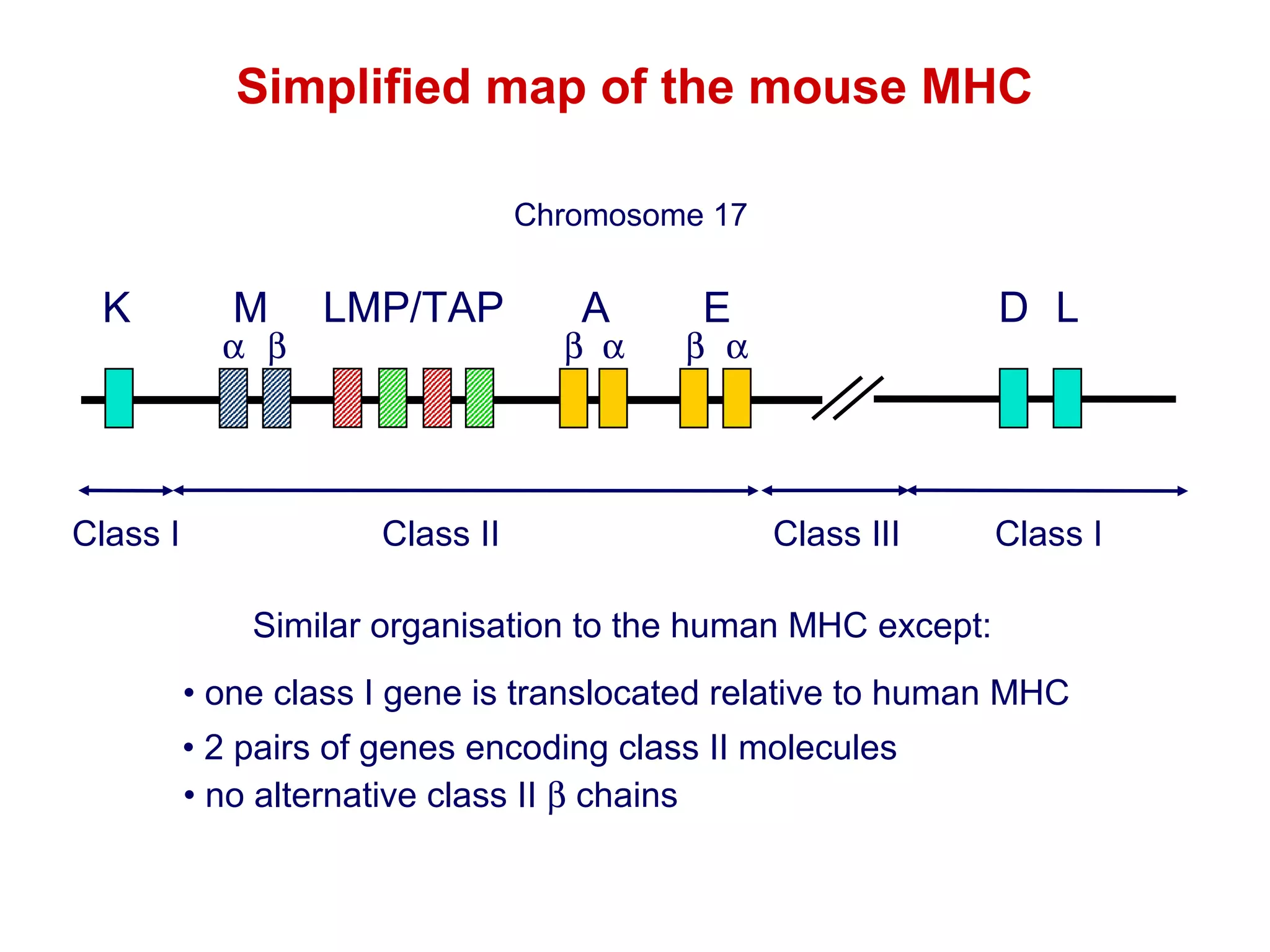
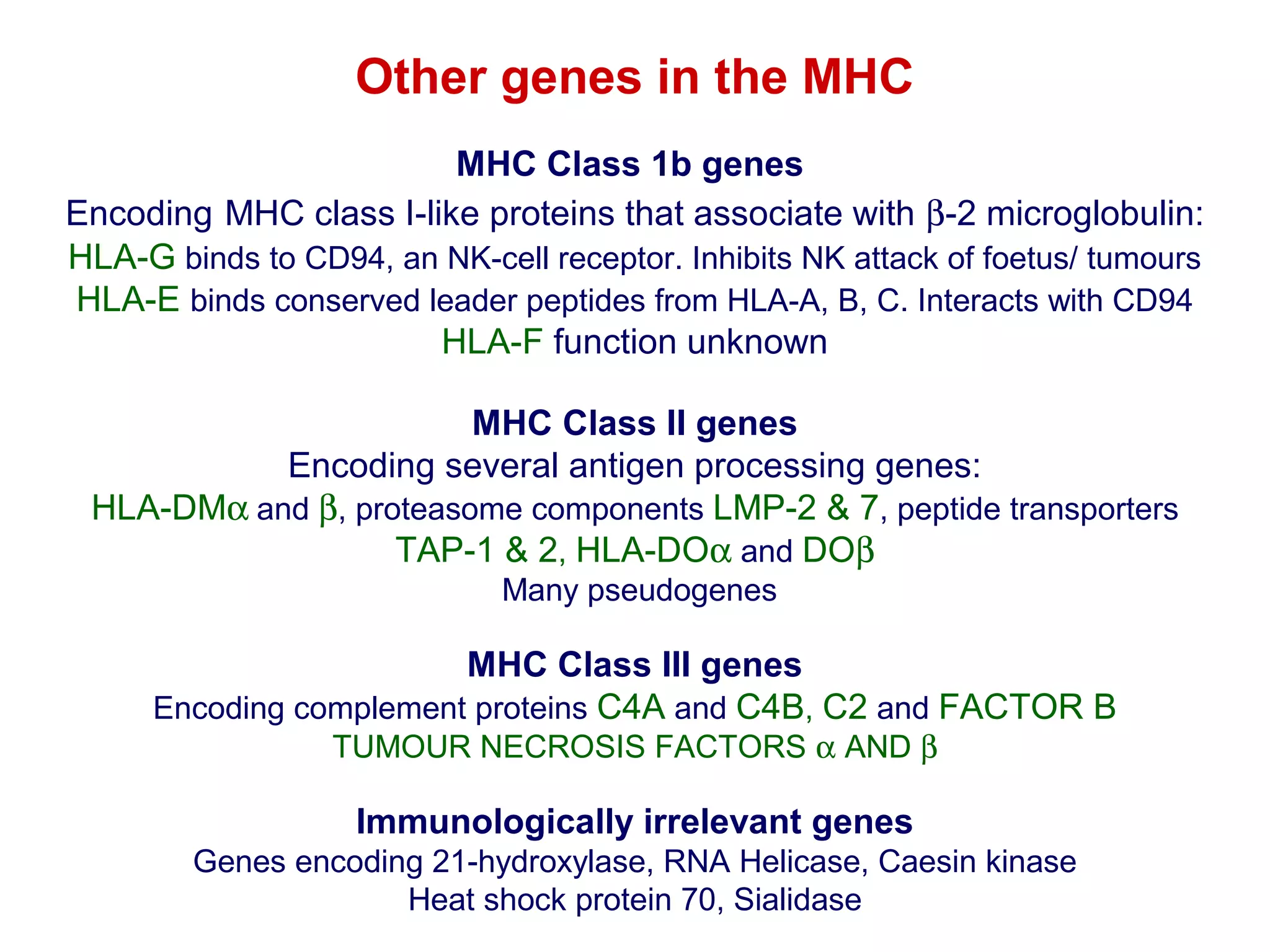
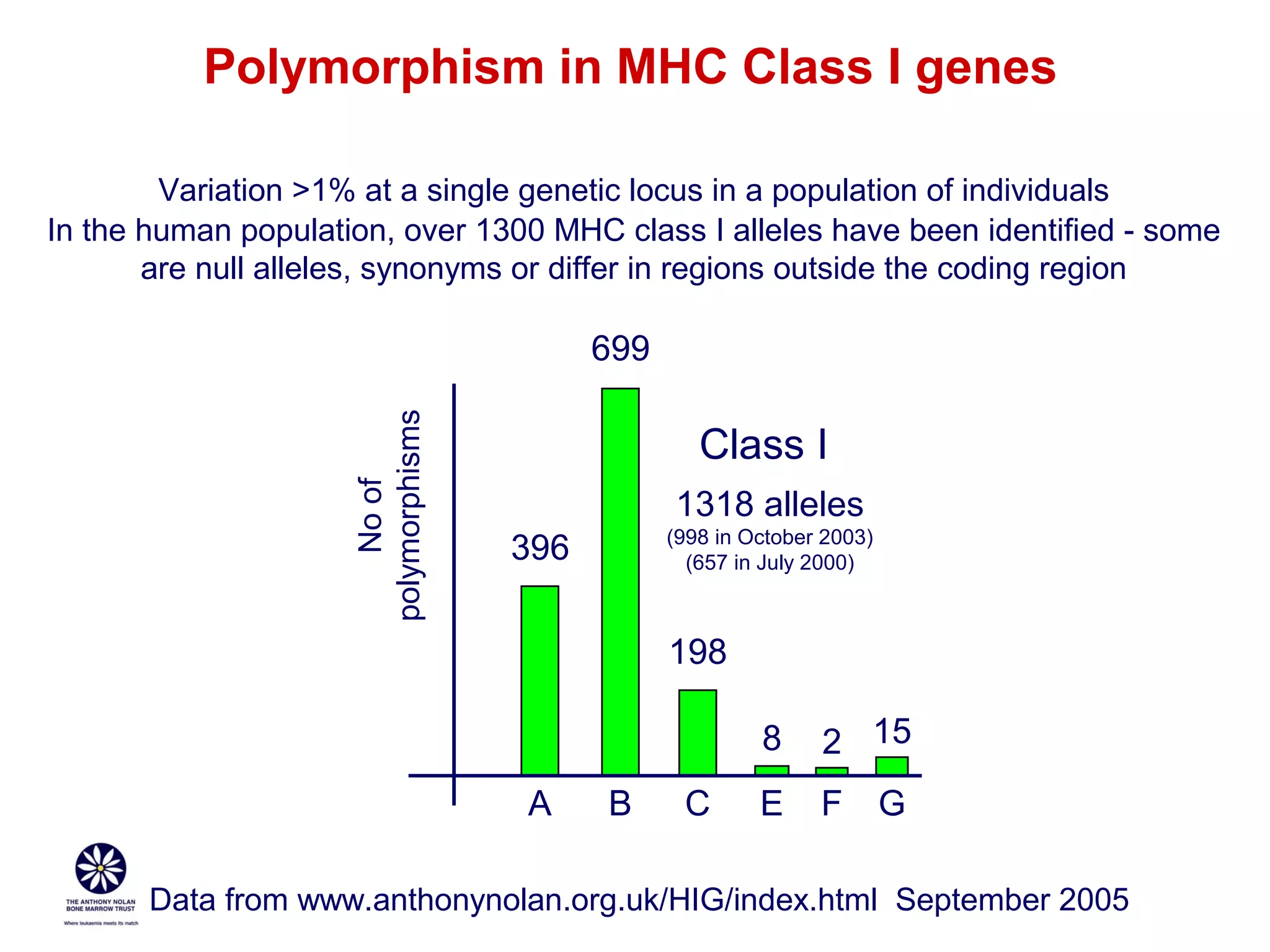
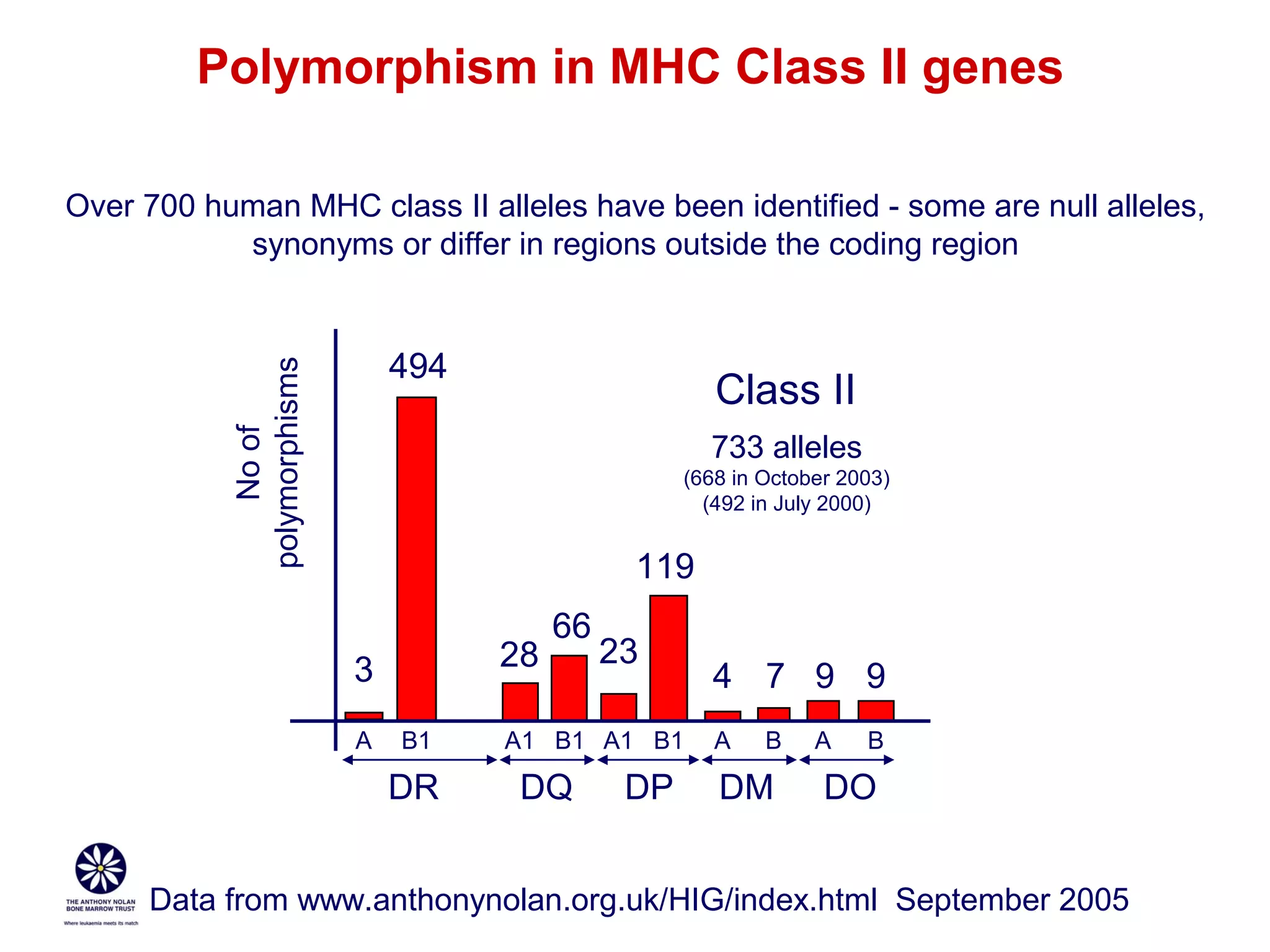
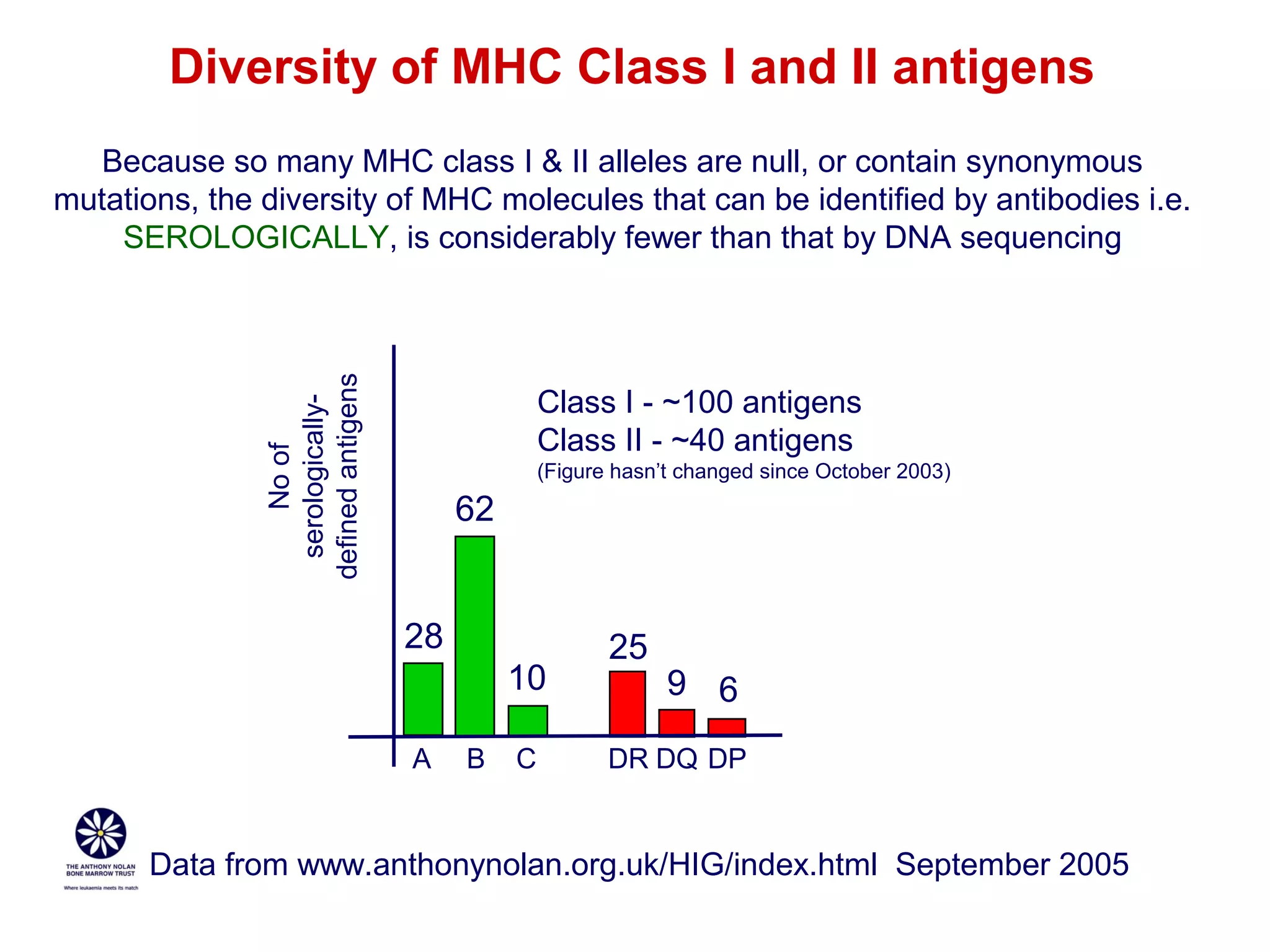
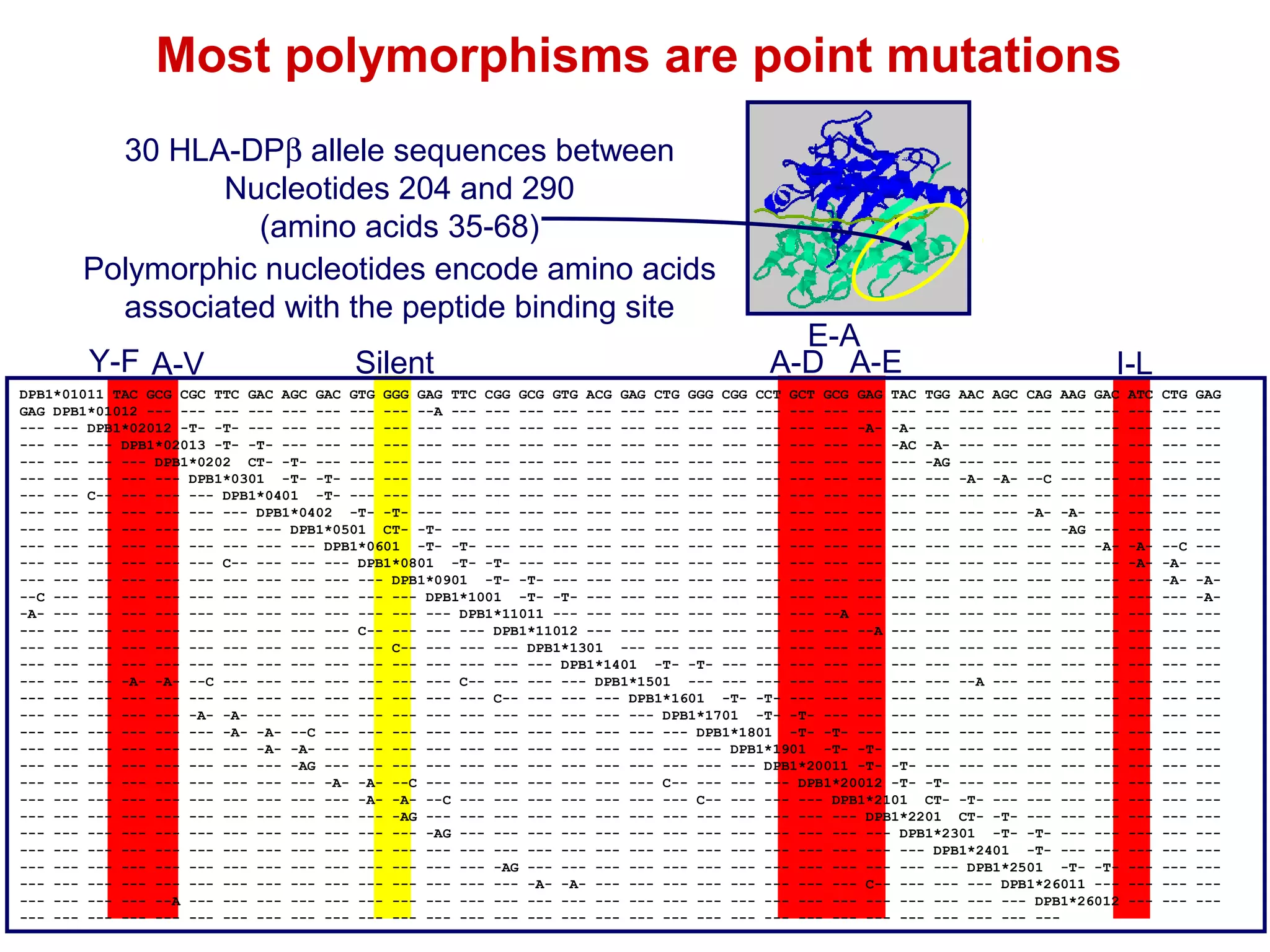
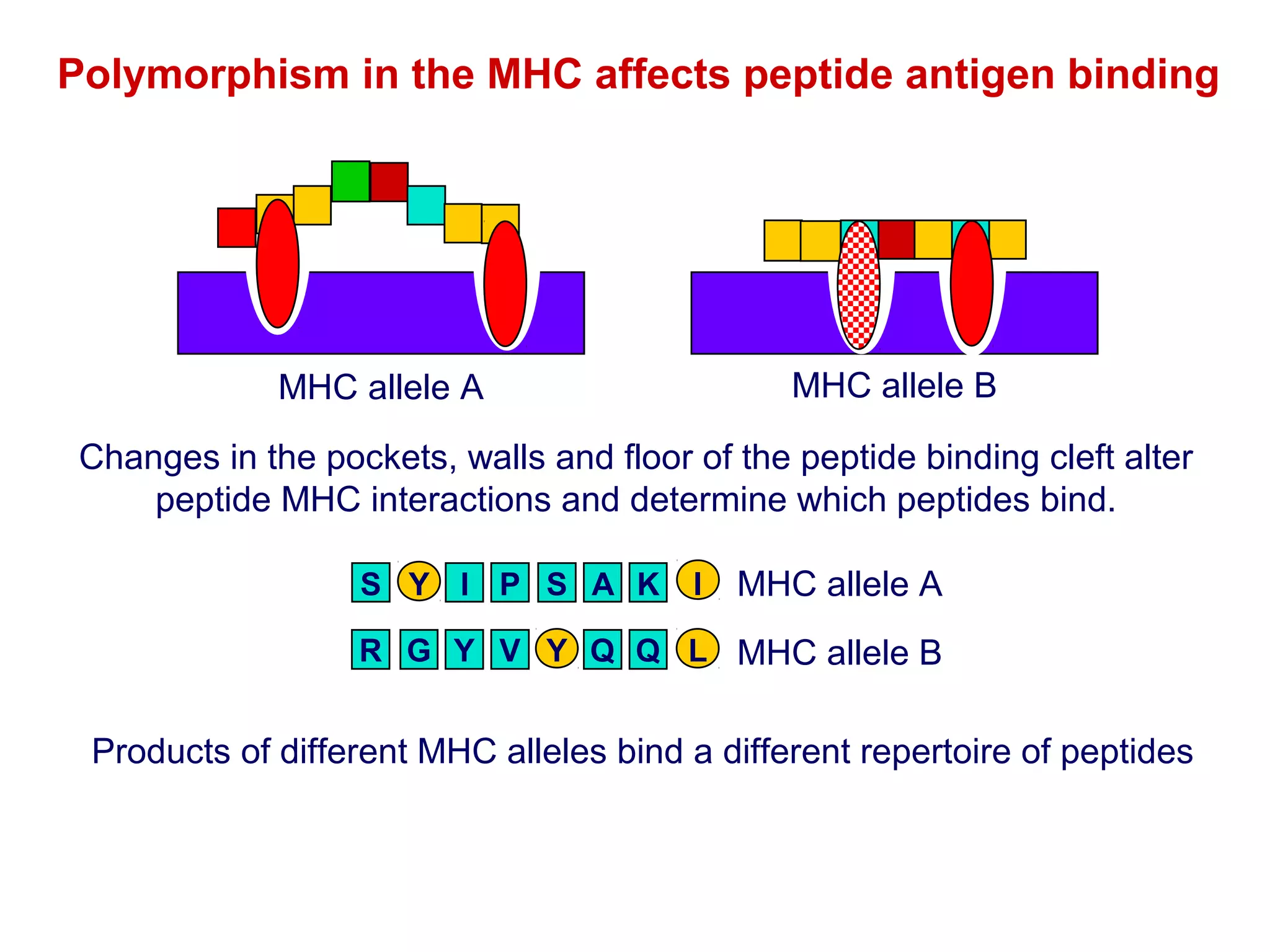
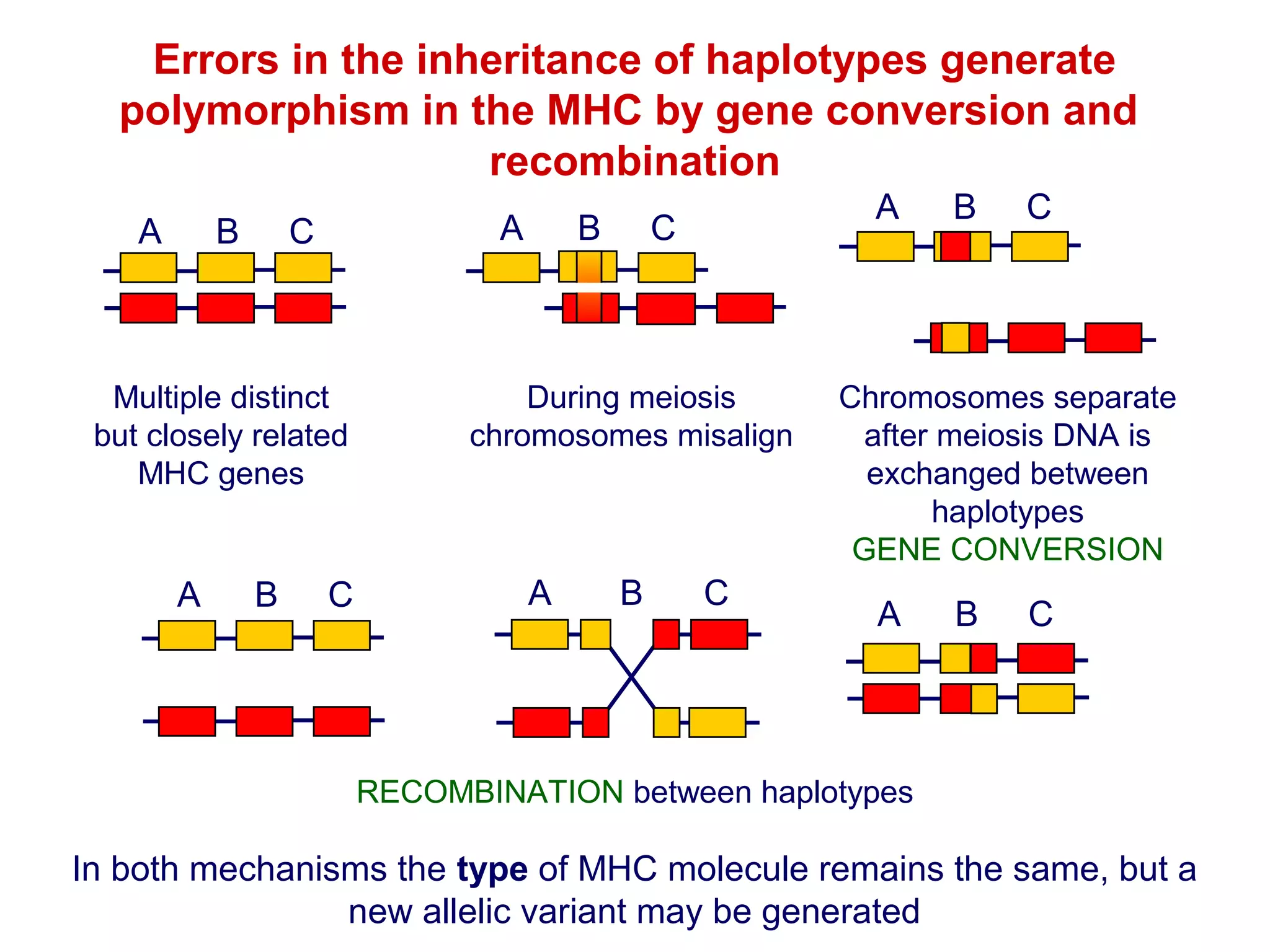
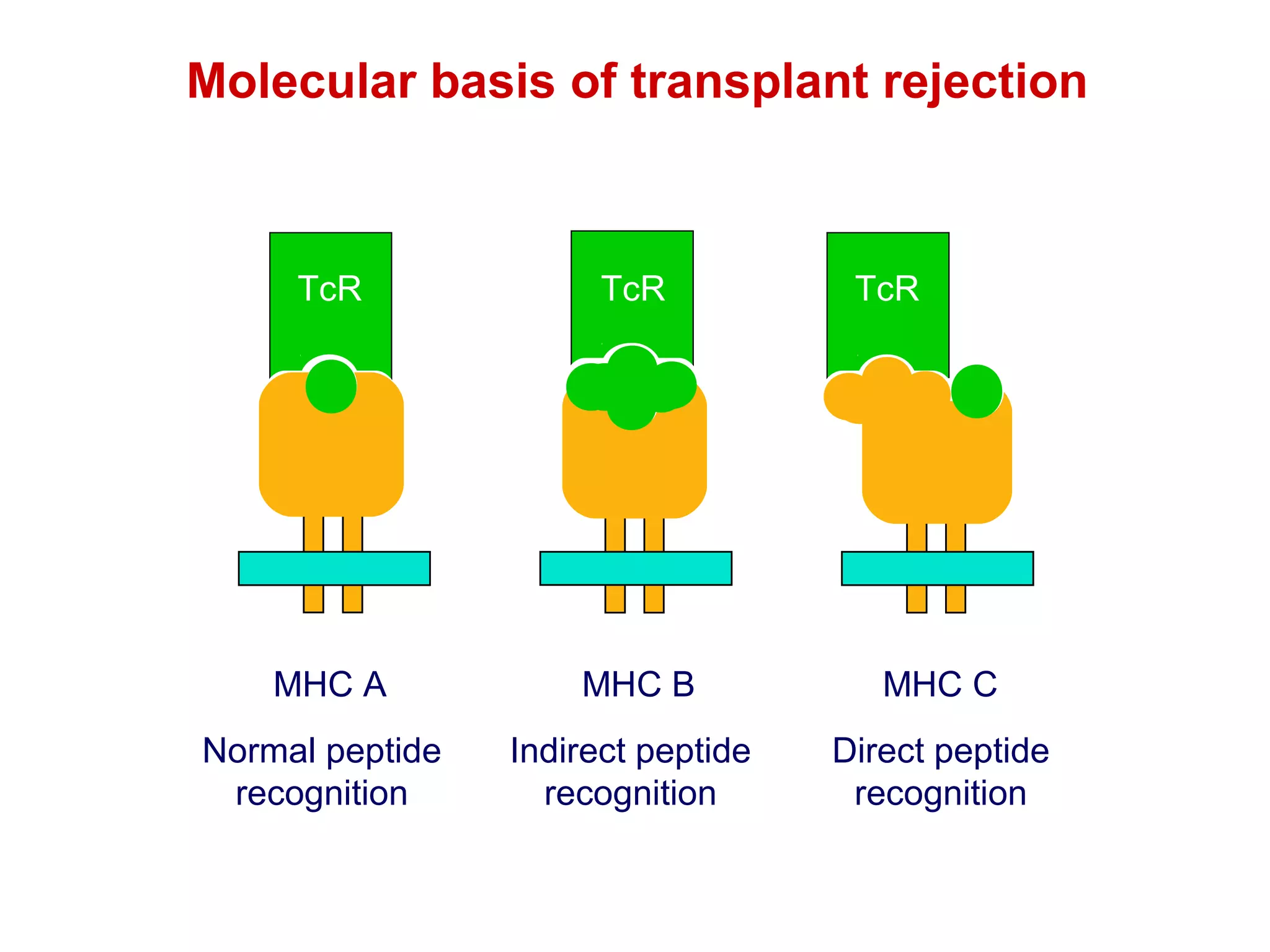
The document provides information about the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), a set of genes that encodes antigen-presenting molecules that play a key role in the immune system's response to foreign substances. It discusses how MHC genes were discovered through studies of transplant rejection between inbred mouse strains, and how MHC molecules present peptide antigens to T cells, triggering an immune response. The document also summarizes the structure and function of MHC class I and class II molecules, how they bind peptides, and their extensive polymorphism in human populations, which helps protect against rapidly mutating pathogens.