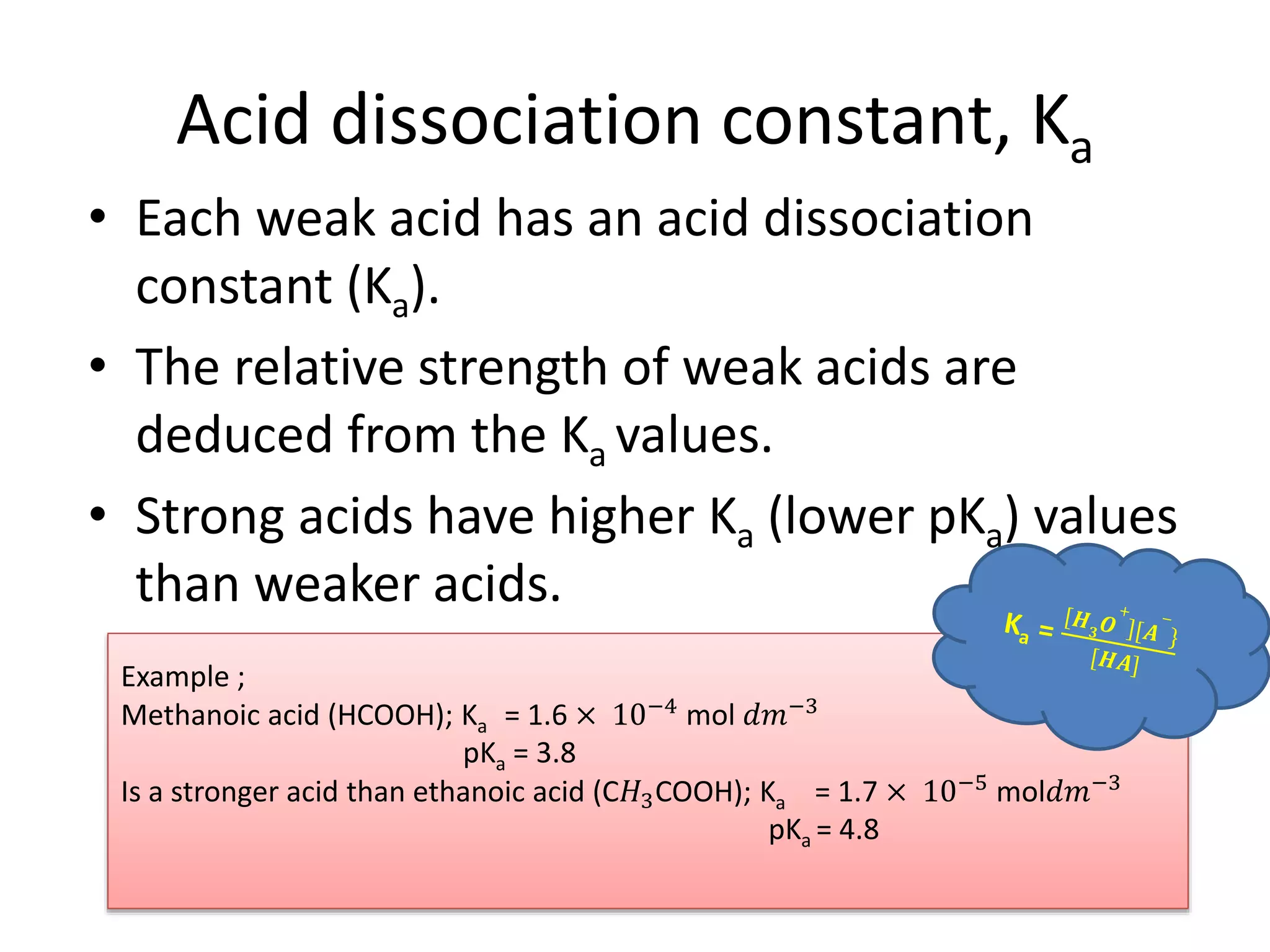
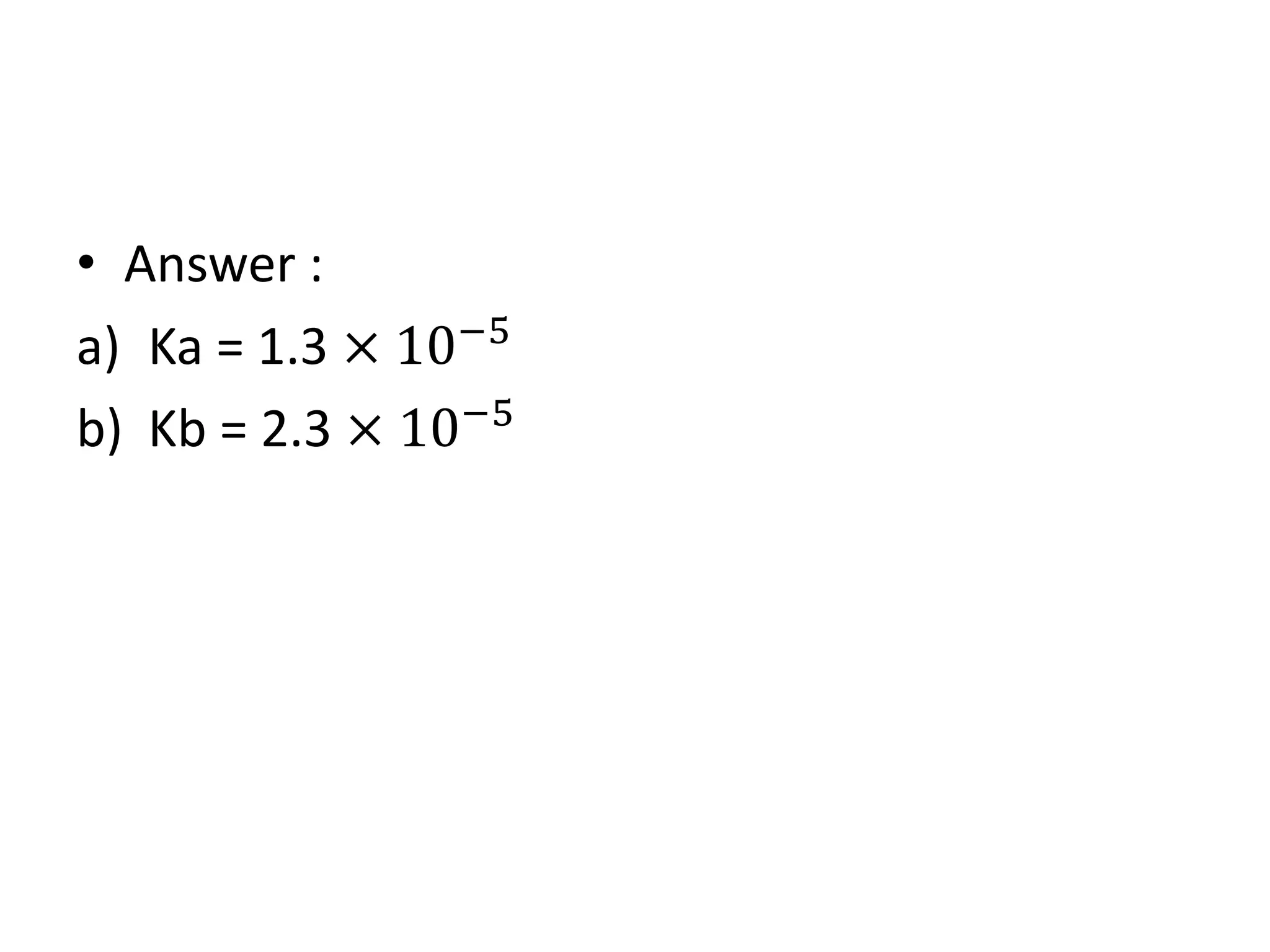The document discusses the concepts of pH, pOH, and the dissociation of acids and bases. It includes calculations for pH and ion concentrations from various strong and weak acids and bases, along with examples and exercises. The text emphasizes the relationship between the concentrations of H3O+ and OH- ions in solutions and the use of equilibrium laws to determine dissociation constants.
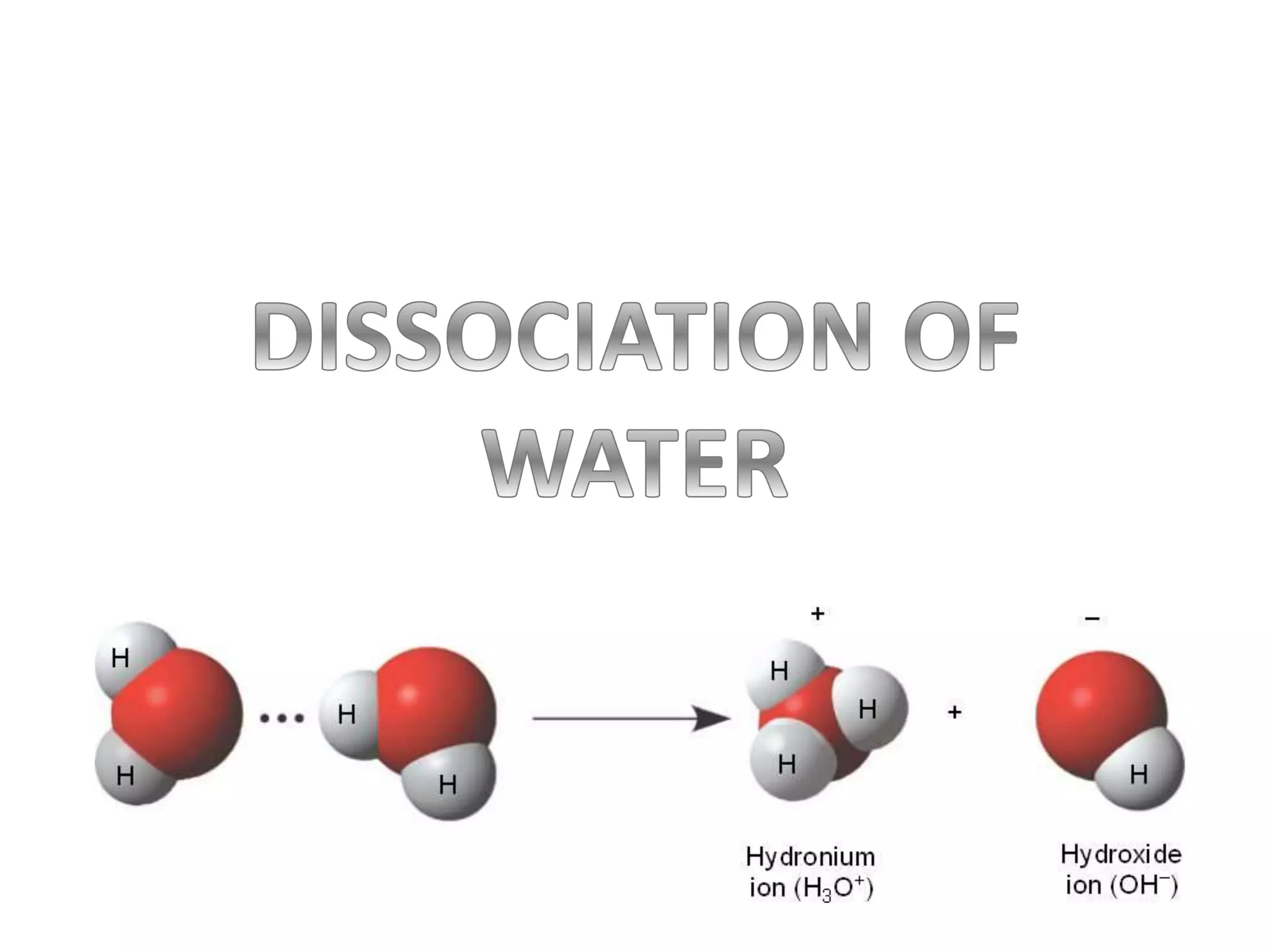
![H2O + H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH-
Acid Base
Kw = [H3O+] [OH-]
Where,
Kw: water dissociation
constant for pure
water at 25 ˚C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-2-2048.jpg)
![• [H3O+] = [OH-] = 1.0 × 10−7
mol dm-3
• Thus,
Kw = [H3O+] [OH-]
= (1.0 × 10−7
) (1.0 × 10−7
) mol2 dm-6
= 1.0 × 10−14
mol2 dm-6
• log [H3O+] + log[OH-] = log (1.0 × 10−14
)
log [H3O+] + log[OH-] = -14.0
-log [H3O+] + log[OH-]= 14.0
• Thus, pH + pOH = 14.0
or pH + pOH = pKw (-log = p)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-3-2048.jpg)

![• Ba(OH)2 (aq) Ba2+
(aq) + 2OH-
(aq)
• pOH = -log [OH-]
= -log (0.50)
= 0.3
Initial
molarity (mol
dm-3)
0.25 0 0
Final molarity
(mol dm-3)
0 0.25 0.50
pH = 14.0 – 0.3
= 13.7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-5-2048.jpg)
![What is the molarity of OH- in an aqueous
solution of NaOH if its pH is 13.5?
• pOH = 14.0 – pH
= 14.0 – 13.5
= 0.5
• pOH = -log [OH-]
0.5 = -log [OH-]
log [OH-] = -0.5
[OH-] = 0.3 mol dm-3
SOLUTION :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-6-2048.jpg)

![• HNO3 H+ + NO2
-
1.0 × 10−8
1.0 × 10−8
1.0 × 10−8
• pH = -log [H+]
= -log (1.0 × 10−8
)
= 8
• For acid, pH <7, [H3O+]> 1.0 × 10−7
consider
[H3O+] from dissociation of water.
• ∴ [H3O+] = [H3O+]w + [H3O+]acid = 1.0 × 10−7
+
1.0 × 10−8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-8-2048.jpg)

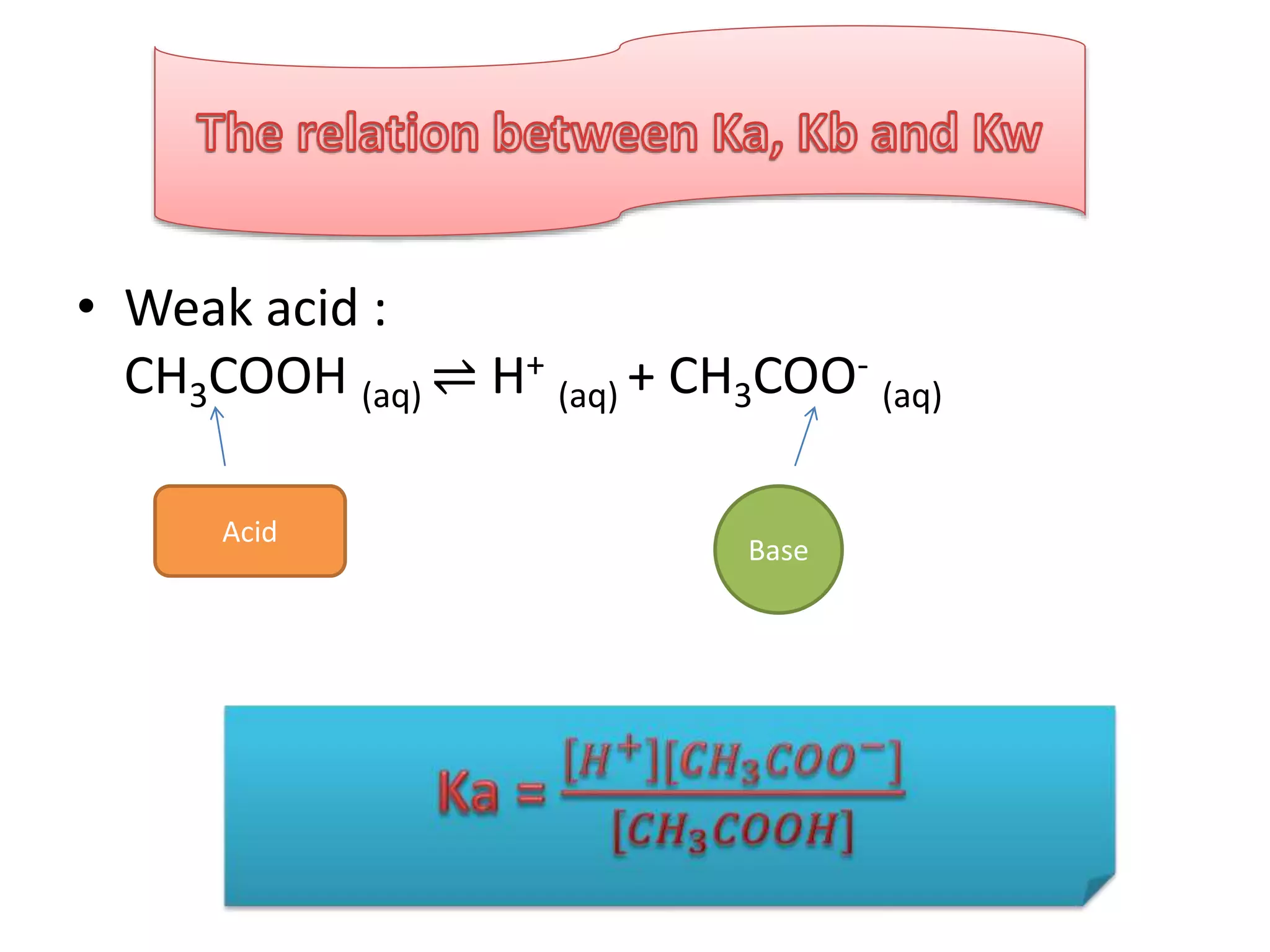

![• Ka . Kb =
𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻 [𝑂𝐻−]
[𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝑂𝑂−]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-12-2048.jpg)



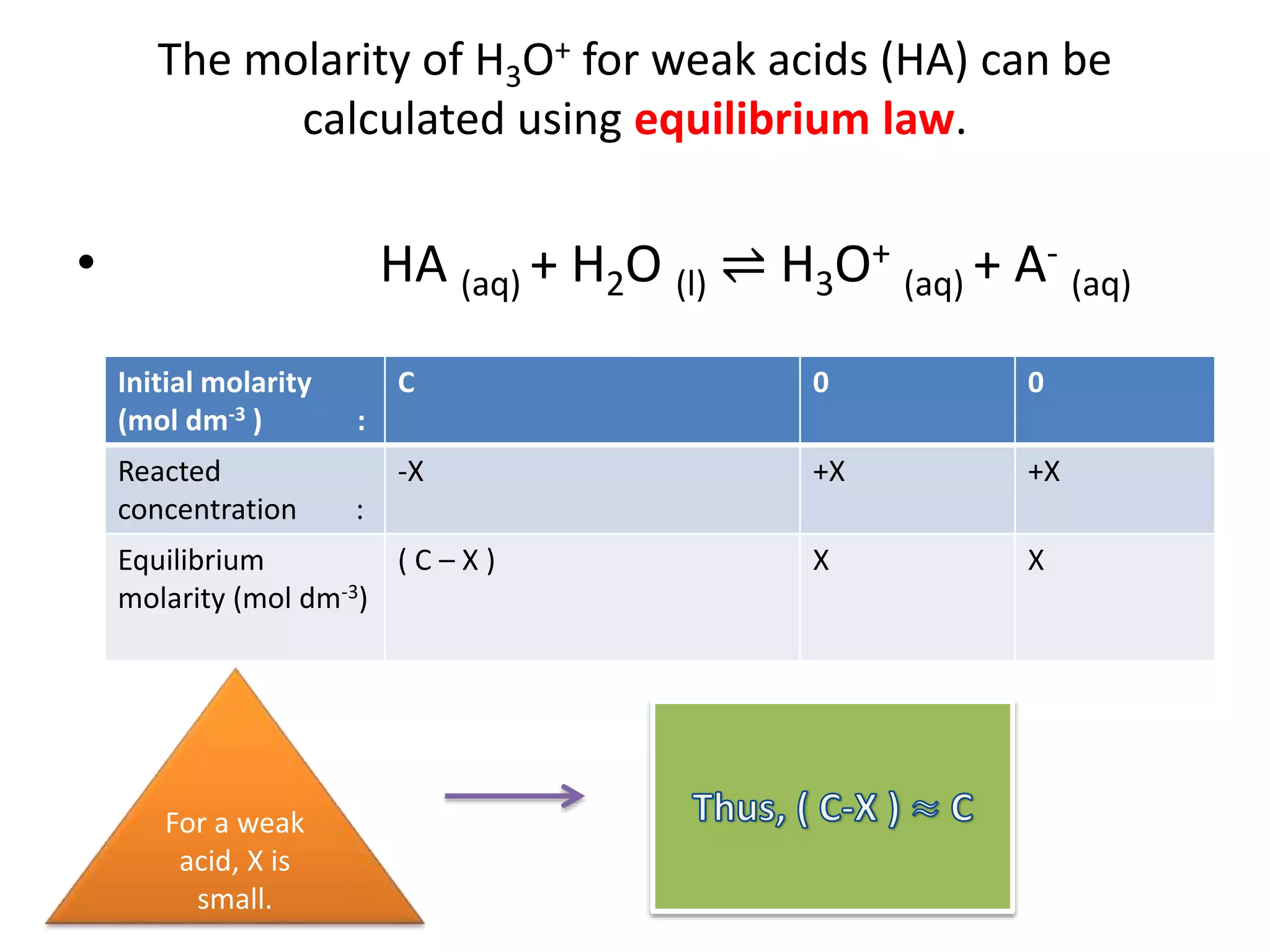
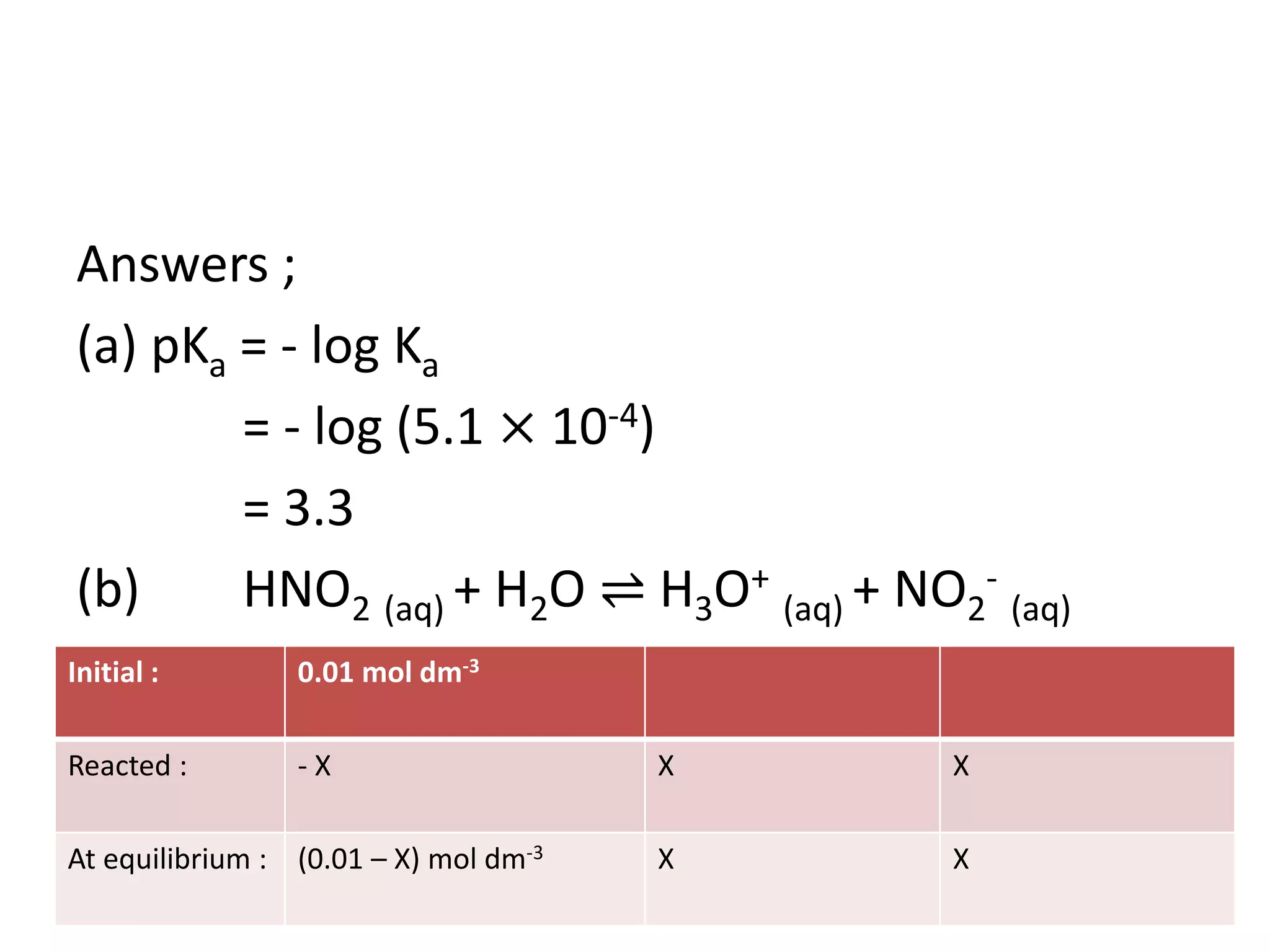
![Example;
Calculate (a) pKa, (b) pH, and (c) degree of
dissociation , of 0.01 mol dm-3 nitrous acid,
HNO2 [Ka = 5.1 × 10-4 mol dm-3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-18-2048.jpg)
![Ka =
𝐻3
𝑂
+
[𝑁𝑂2
−
]
[𝐻𝑁𝑂2
]
5.1 × 10-4 M =
𝑋2
0.01 −𝑋 𝑀
, X is small
∴ (0.01 – X) ≈ 0.01
=
𝑋2
0.01 𝑀
X2 = 5.1 × 10−6
M2
X = 2.26 × 10−3
M
∴ [H3O+] = 2.26 × 10−3
M
pH = -log [H+]
= -log (2.26 × 10−3
)
= 2.6
X = 𝑲𝒂 . 𝑪
= 𝟓. 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟒(𝟎. 𝟎𝟏)
= 𝟓. 𝟏 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟔
= 2.26 × 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 M
Or :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-20-2048.jpg)





![Example ;
Calculate (a) pKb, (b) pH and (c) degree of
dissociation of 0.1 moldm-3 NH2OH.
[Kb = 9.1 × 10−9
mold𝑚−3
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-26-2048.jpg)

![Kb =
𝑁𝐻3 𝑂𝐻+ 𝑂𝐻−
𝐵
9.1 × 10−9
M =
𝑋 2
0.1 −𝑋 𝑀
, X is small, (0.1 – X) ≈ 0.1
=
𝑋2
0.1 𝑀
𝑋2
= 9.1 × 10−10
M2
X = 9.1 × 10−10 M2
X = 3.02 × 10−5
M
∴ [OH-] = 3.02 × 10−5
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-28-2048.jpg)
![POH = -log [OH-]
= -log (3.02 × 10−5
)
= 4.5
pH = 14.0 – 4.5
= 9.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-29-2048.jpg)
![(c) degree of dissociation, ∝
∝ =
𝑋
𝐶
× 100%
=
[𝑂𝐻
−
]
[𝑁𝐻2
𝑂𝐻]
× 100%
=
3.02 ×10−5 𝑀
0.1 𝑀
× 100%
= 0.03 %
NH2OH is a very
weak base.
!
NOTE :
Both in (a) and (b)-
neglected the
contribution of the
autoionization of
water to [H+]and[OH-]
because 1.0 × 10−7M is
so small compared with
1.0 × 10−3
M and
0.040M.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-30-2048.jpg)


![Answer
a) Ba(OH)2 is a strong base. It ionise completely to
form 1.8 x 10-2 moldm-3 OH-
(aq).
pOH = -log[OH-]
= -log(1.8x10-2)
= 1.74
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 – pOH
= 14 – 1.74
= 12.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-33-2048.jpg)
![(b)
HNO3 is a strong acid.
It ionise completely to form 0.001 moldm-3 H+
(aq).
pH = -log[H+]
= -log(0.001)
= 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-34-2048.jpg)

![Answer
pH = 4.82
pH = -log[H+]
log[H+] = -pH
log10[H+] = -pH
[H+] = 10-pH
[H+] = 10-4.82
= 0.000015
= 1.5 x 10-5 mol dm-3
logab = c
b= ac](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-36-2048.jpg)

![Answer
pH = 3.33
[H+] = ?
pH = -log[H+]
3.33 = -log[H+]
log[H+] = -3.33
log10[H+] = -3.33
[H+] = 10-3.33
= 0.000468
= 4.7 x 10-4 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-38-2048.jpg)
![Question 4
In a NaOH solution, [OH-] is 2.9× 10−4
M.
calculate the pH of the solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-39-2048.jpg)
![Answer
pOH = -log[OH-]
= -log(2.9 x 10-4)
= 3.5
pOH + pH = 14
pH = 14 – pOH
= 14 – 3.5
= 10.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-40-2048.jpg)

![Answer
pOH = -log [OH-]
= -log(0.88)
= 0.055517
= 0.06
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 – pOH
= 14 – 0.06
= 13.94](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-42-2048.jpg)



![∴ [ H+] = 1.0 × 10−3
M
pH = -log (1.0 × 10−3
)
= 3.00](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-46-2048.jpg)
![(b) Ba(OH)2 is a strong base. Each Ba(OH)2 unit
produces two OH- ions:
Ba(OH)2 (aq) Ba2+
(aq) + 2OH-
(aq)
∴ [OH-] = 0.040 M
pOH = -log (0.040)
= 1.40
pH = 14.00 – 1.40
= 12.60
Initial (M) : 0.020 0.00 0.00
Change (M) : - 0.020 + 0.020 + 2(0.020)
Final (M) : 0.00 0.020 0.040](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-47-2048.jpg)




![4.
a) What are [H+] and [OH-] in a 0.020 M solution
of HCl.
b) What are [H+] and [OH-] in a 0.0500 M
solution of NaOH.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-52-2048.jpg)
![5.
a) What is the pH of a solution that is 0.050 M
in H+?
b) What is the pH of a solution for which [OH-] =
0.030 M ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-53-2048.jpg)
![6. What is [H+] of a solution with a pH of 10.60 ?
7. The pH of a 0.10 M solution of a weak acid HX
is 3.30. what is the ionization constant of HX?
(Ka = 2.5 × 10−6
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissociationofwater-161004061845/75/TOPIC-18-ACIDS-AND-BASES-54-2048.jpg)