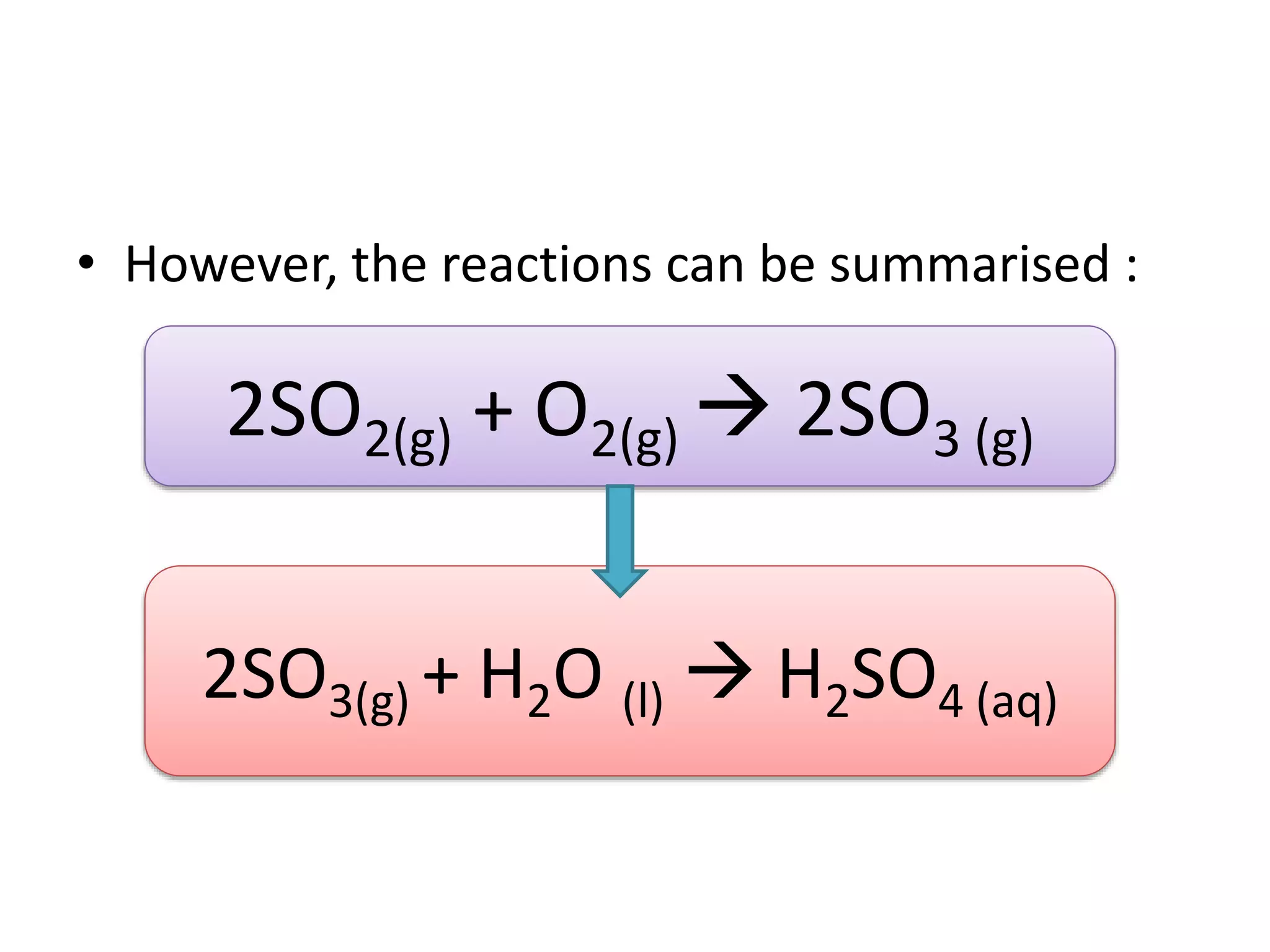
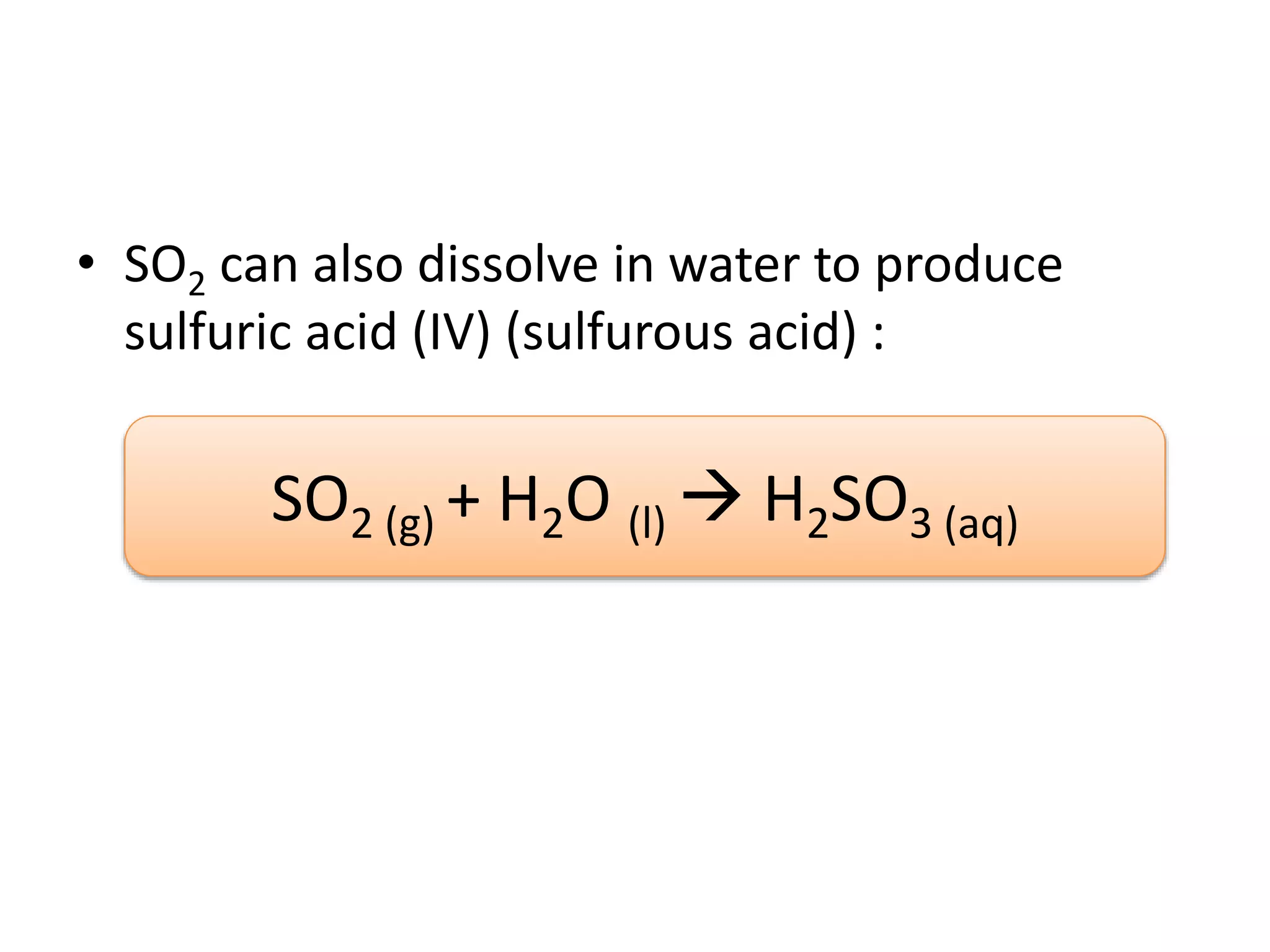
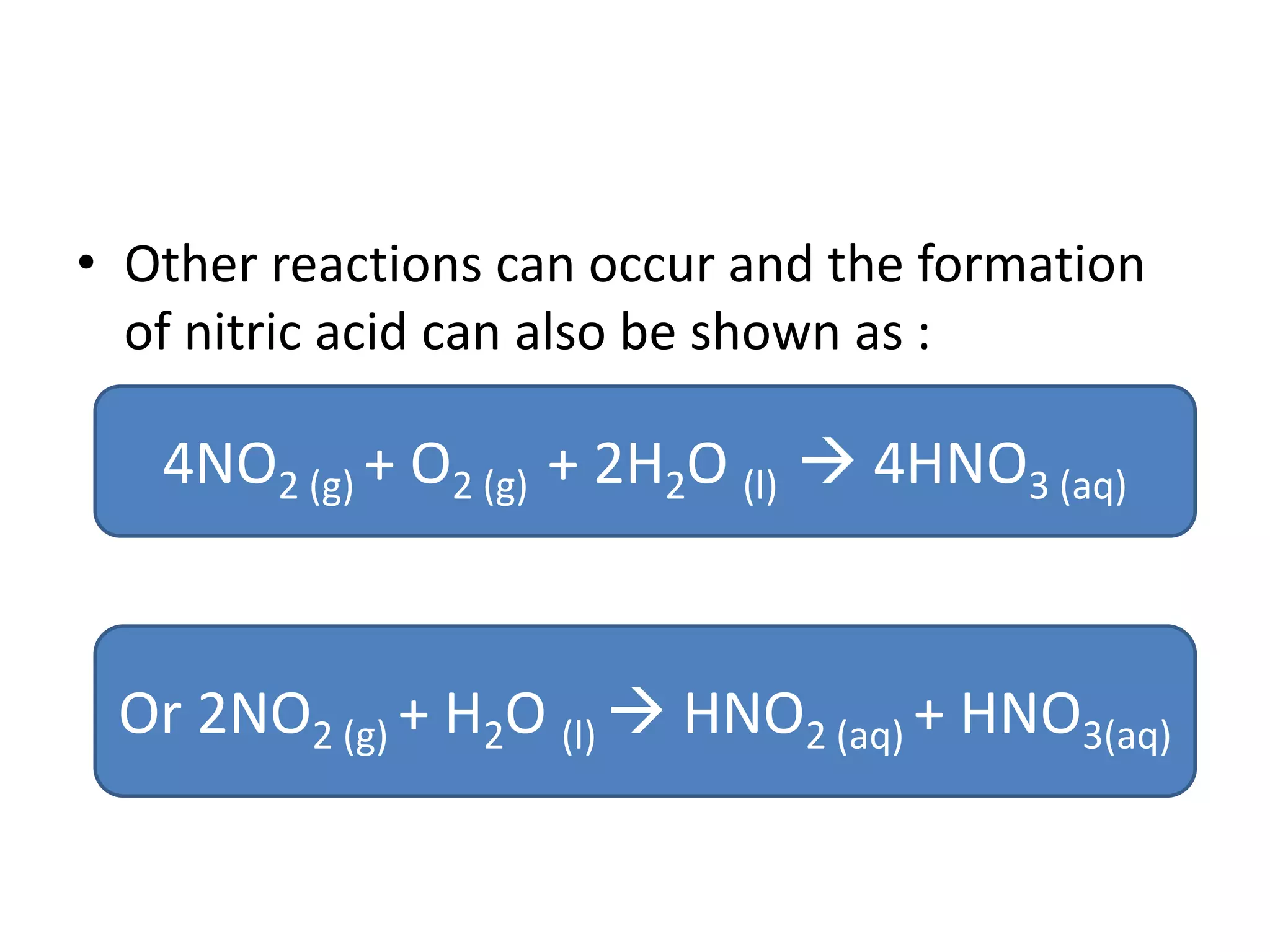
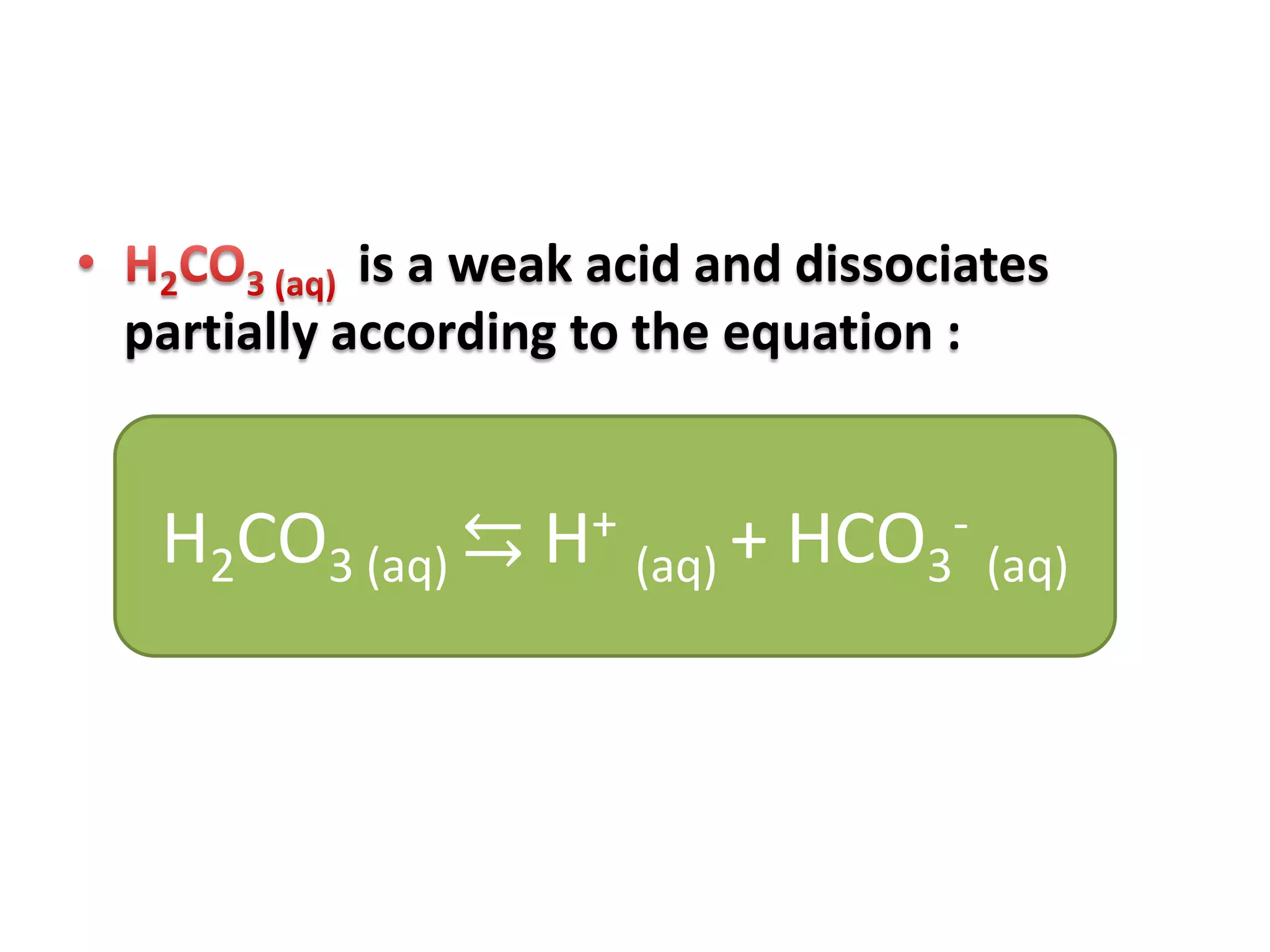Acid deposition occurs when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides emitted from the burning of fossil fuels react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals in the atmosphere to form acids. These acids can fall to Earth as rain, snow, fog or dry particles. Natural processes also produce acid deposition, but human activities such as burning coal and oil have increased acid deposition levels. Acid rain has a pH lower than 5.6 and can damage sensitive forests and lakes. The main pollutants that cause acid rain are sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.