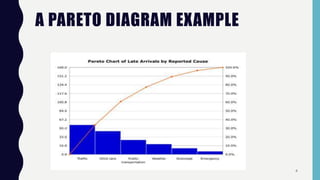
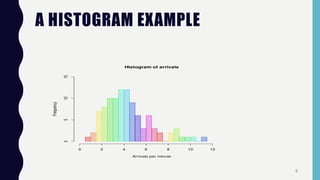
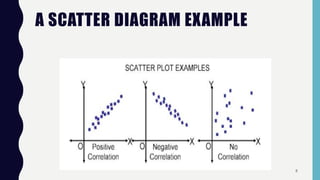
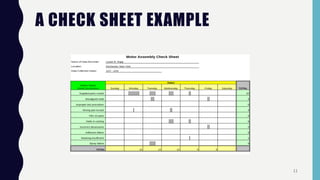
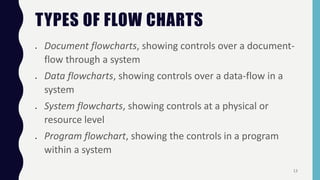
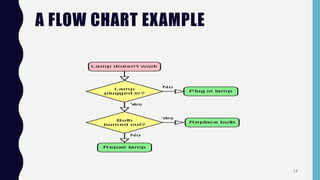
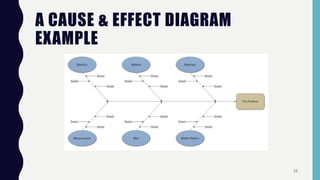
Quality control tools are used to collect and analyze data to identify root causes and measure quality improvements. The main tools discussed are Pareto charts, histograms, scatter diagrams, check sheets, flow charts, cause and effect diagrams, and control charts. Pareto charts arrange defects by category to identify the most common issues. Histograms depict the distribution of a variable through frequency bars. Scatter diagrams show the relationship between two variables with data points on an x-y graph. Check sheets systematically collect specified data. Flow charts document processes through a series of boxes and arrows. Cause and effect diagrams break down potential root causes in successive layers of detail. Control charts determine if a process should be examined by distinguishing between random and assignable variation. Examples