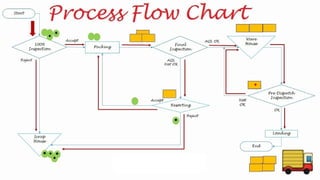
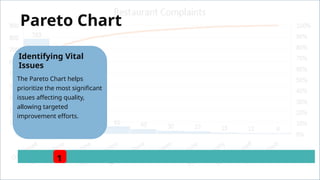
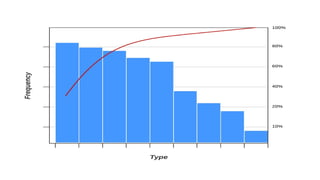
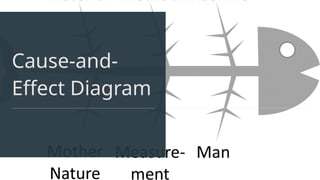
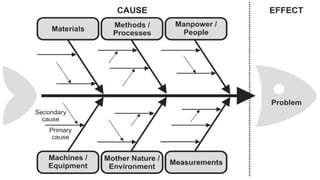
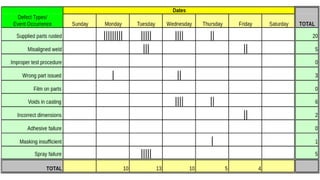
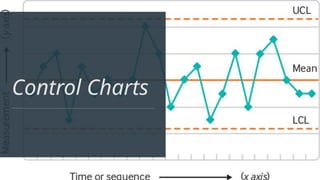
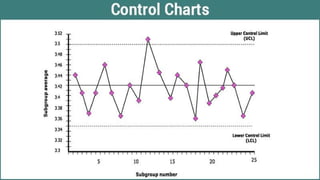
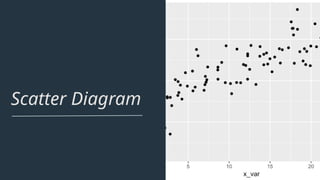
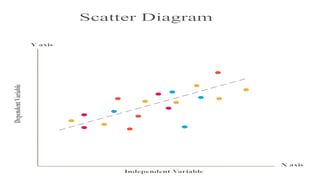
The document discusses various quality control (QC) tools essential for maintaining product quality and operational efficiency, including flowcharts, Pareto charts, cause-and-effect diagrams, check sheets, control charts, histograms, and scatter diagrams. These tools facilitate data collection, analysis, and identification of issues, ultimately supporting continuous improvement and standardized processes within organizations. By leveraging these QC tools, businesses can make informed decisions that promote sustainable growth and quality excellence.