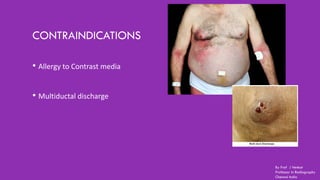
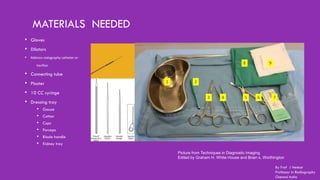
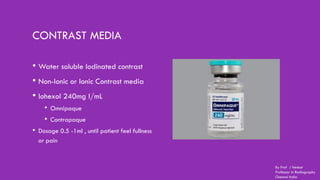
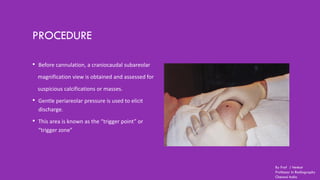
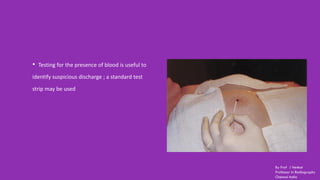
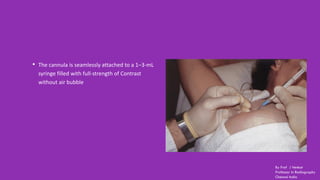
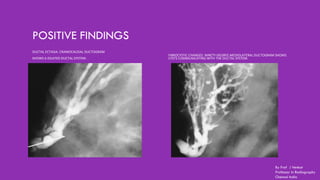
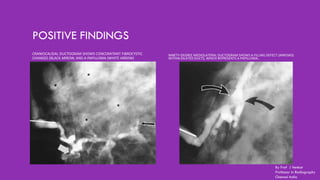
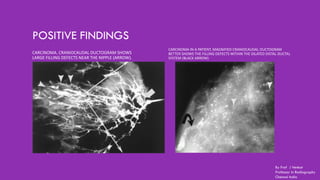
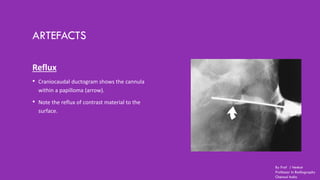
Ductography is a specialized imaging technique for evaluating breast ducts, often used to diagnose conditions like intraductal papillomas and abnormal nipple discharge. The document details the anatomy of the breast, indications, contraindications, required equipment and materials, and the procedural steps involved in ductography. Additionally, it discusses potential findings, complications, and post-procedural care.