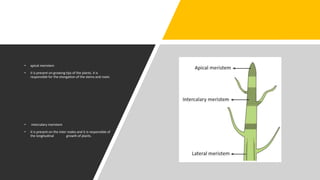
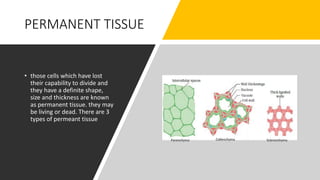
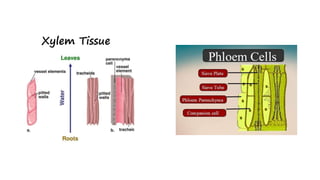
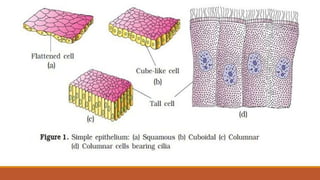
The document outlines the types of plant and animal tissues, highlighting their structures and functions. In plants, there are meristematic and permanent tissues, each with specific roles in growth and support, while animal tissues include epithelial, connective, muscle, and neural tissues, which serve various functions in the body. Key examples include xylem and phloem for plants and different muscle types for animals.