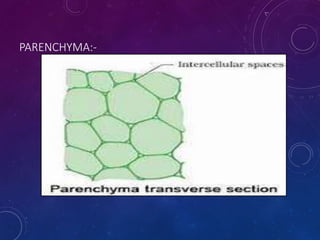
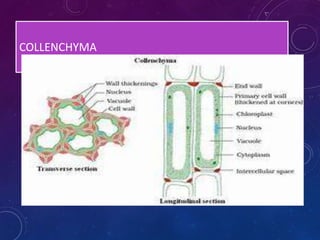
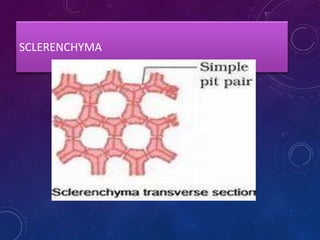
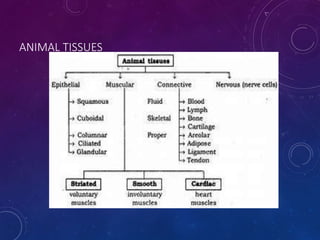
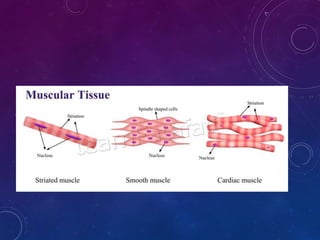
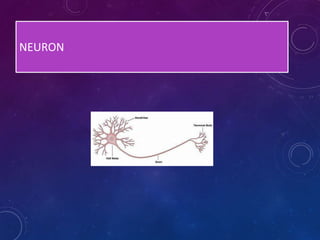
Plant tissues are categorized as meristematic and permanent tissues. Meristematic tissues are growth tissues found in growing regions that continuously divide, while permanent tissues take on specific roles and do not divide further. The main plant tissues include parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, epidermis, cork, xylem and phloem. Animal tissues include four main types - epithelial tissue, muscular tissue, connective tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line organs and cavities. Muscular tissues include striated, smooth and cardiac muscle. Connective tissues connect and support other tissues. Nervous tissues transmit signals in the body.