1. The document discusses different types of tissues in plants and animals. It defines tissue as a group of cells organized to perform a specific function.
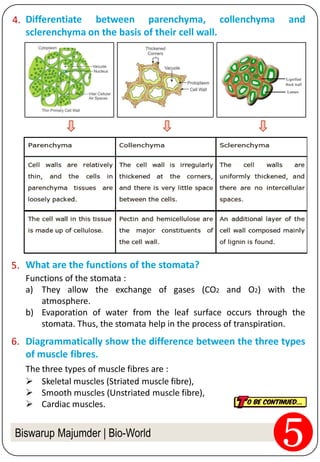
2. Simple tissues include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. Complex tissues include xylem and phloem. Muscular tissue is responsible for movement in the body.
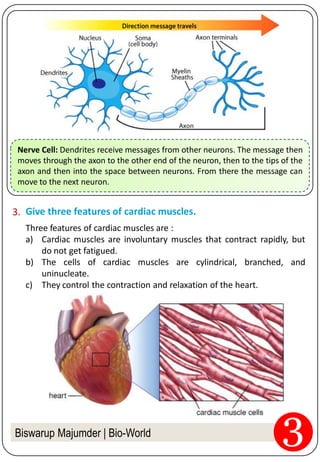
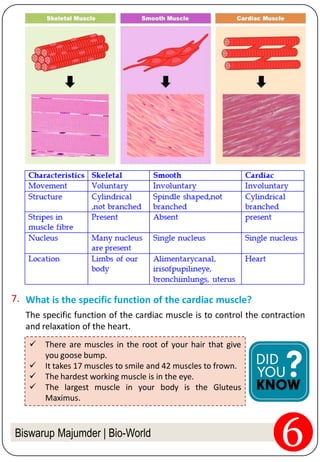
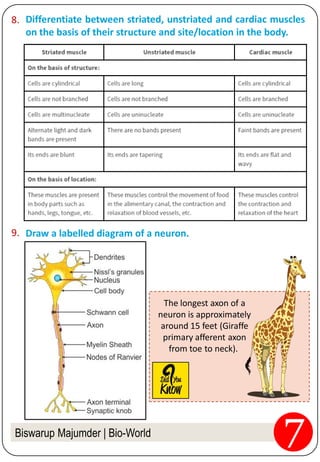
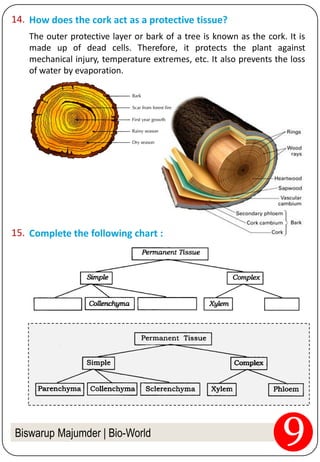
3. The document provides examples of different tissues, their structures, and functions. It discusses tissues in plants like epidermis, cork, and vascular bundles. It also covers the three types of muscle fibers and the role of neurons.