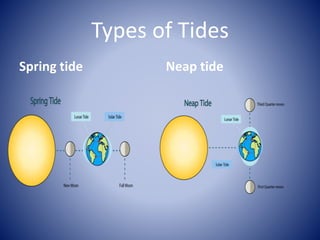
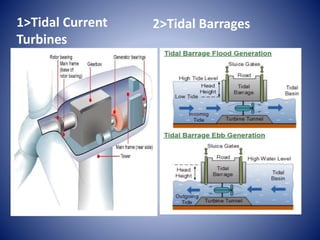
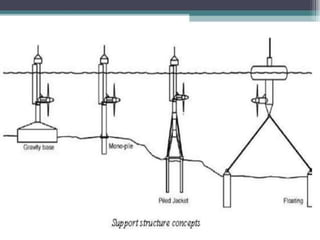
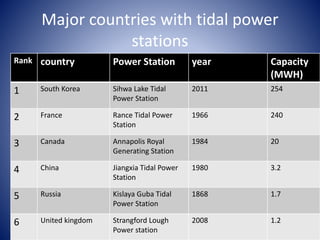
Ocean energy can be harnessed from tidal, wave, and ocean thermal sources. Tidal energy is a form of hydropower that uses the predictable rise and fall of tides, driven by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, to generate electricity. The first tidal mill was established in 619 AD in Northern Ireland, and the first tidal power station was built in 1966 in Brittany, France. Tidal energy is produced via tidal current turbines that operate during flood and ebb tides, or tidal barrages built across estuaries with turbines, sluice gates, and locks. While tidal energy is renewable and predictable, the high costs and limited suitable locations have prevented widespread adoption.