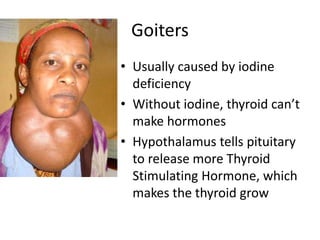
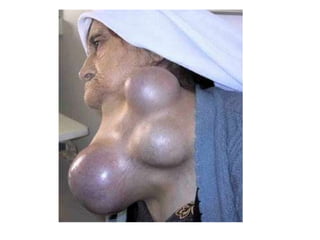
The thyroid gland is located at the base of the throat and produces two hormones: thyroid hormone and calcitonin. Thyroid hormone regulates the rate at which cells convert glucose to energy, while calcitonin decreases blood calcium levels by depositing calcium in bones. The parathyroid glands are four small masses located on the back of the thyroid that produce parathyroid hormone to raise blood calcium levels by stimulating bone cells to release calcium. Disorders of the thyroid can include goiters caused by iodine deficiency, cretinism in newborns from low thyroid hormones, and hyperthyroidism where too much hormone is produced.