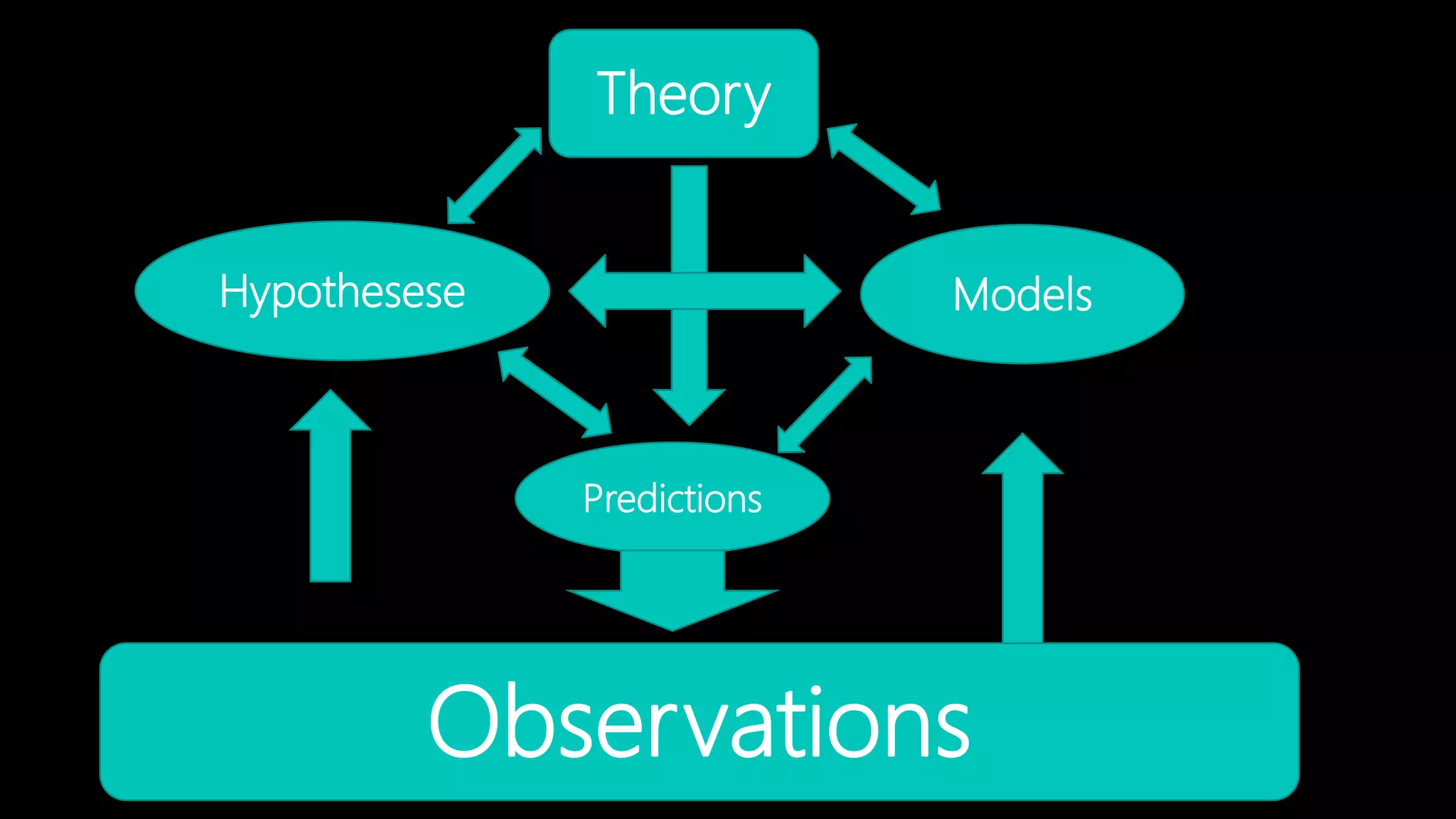
Science is a method of understanding the natural world through making observations and developing testable explanations known as hypotheses. Scientists form hypotheses and models to make predictions that can be observed, and theories are explanations that have been well tested to unify broad observations. The scientific process involves observations, developing hypotheses and models, making predictions, and building theories through testing to best explain natural phenomena.