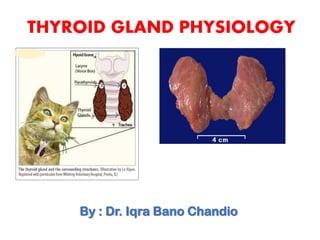
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones including thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin, which regulate metabolic rate and calcium levels. Its structure consists of spherical follicles composed of follicle cells that synthesize thyroglobulin and parafollicular cells that produce calcitonin. Thyroid disorders include hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, with goiter signifying an enlarged thyroid.