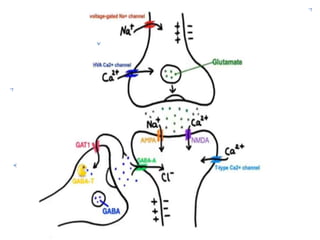
Sodium valproate is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug effective for various seizure types and is also used as a mood stabilizer. The drug has multiple mechanisms of action, is well-absorbed orally, and is contraindicated in certain conditions like pregnancy and liver disorders. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal issues, sedation, and potential for severe liver problems, necessitating careful monitoring and patient education.