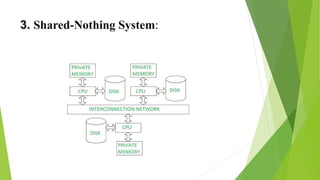
The document describes three main architectures for parallel databases: shared memory, shared disk, and shared nothing. Each architecture has its own advantages and disadvantages regarding data access, scalability, communication, and fault tolerance. The shared memory system is limited by the number of CPUs, the shared disk system allows for independent CPU access to disks but has scalability issues, and the shared nothing system offers better scalability at the cost of higher communication expenses.