This document discusses thread properties in Java, including:
1. The Thread class which provides constructors, methods, and fields to work with threads.
2. Common constructors of the Thread class like Thread(), Thread(String name), and Thread(Runnable target).
3. Methods of the Thread class like start(), run(), sleep(), getName(), and setName().
4. Fields of the Thread class like Thread priorities MAX_PRIORITY, NORM_PRIORITY, and MIN_PRIORITY.
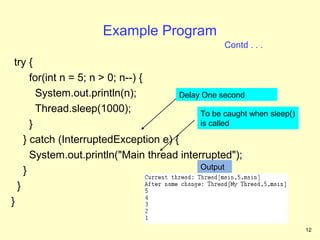
5. Examples of using threads for monitoring resources, listening to events, and long-running operations.
The document provides an overview of the key aspects of working with threads in Java through










![Example Program
// A simple program to demonstrate the currentThread()
method
// It also uses the setName() method Use of currentThread()
class CurrentThreadDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("Current thread: " + t); of setName()
Use
// change the name of the thread
t.setName("My Thread");
System.out.println("After name change: " + t);
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9cm604-40-130222071742-phpapp01/85/ThreadProperties-11-320.jpg)