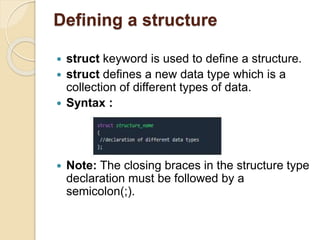
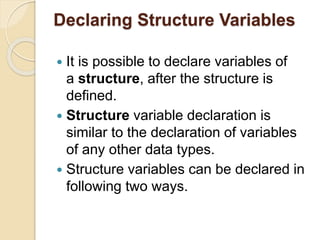
Structures in C allow the user to define a custom data type that combines different data types to represent a record. A structure is similar to an array but can contain heterogeneous data types, while an array only holds the same type. Structures are defined using the struct keyword followed by structure tags and member lists. Structure variables are declared like other variables and members can be accessed using the dot operator. Arrays of structures and nested structures are also supported.









![Array of Structure
We can also declare an array of structure.
Each element of the array represents a
structure variable.
Example : struct employee emp[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresv122102017-1-180831193305/85/Structures-in-c-language-12-320.jpg)


