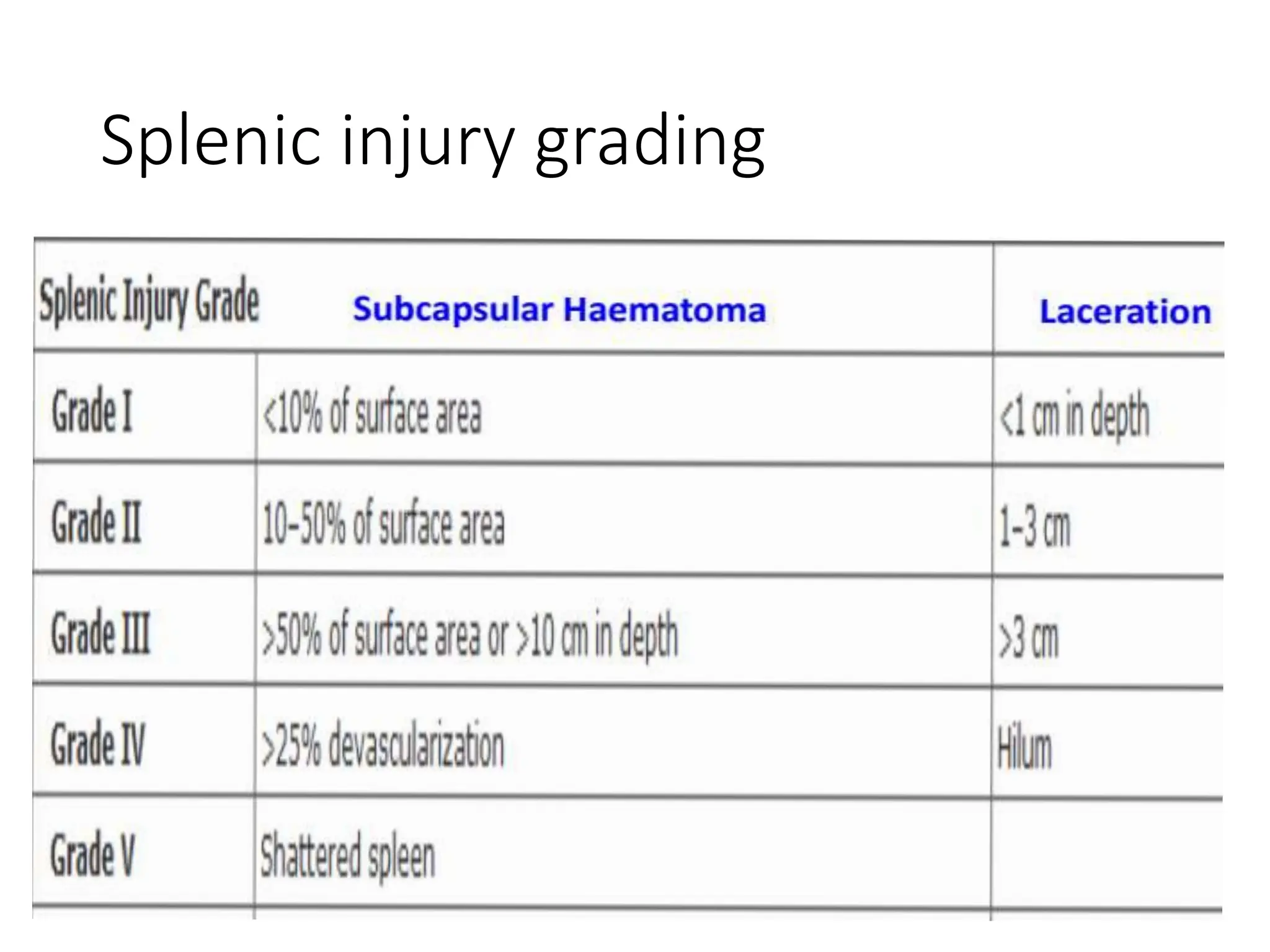
The document discusses trauma to the thorax and abdomen. It begins with an introduction to trauma epidemiology and classifications. It then covers early management principles including the primary and secondary surveys. Specific thoracic injuries discussed include pneumothorax, hemothorax, flail chest, and cardiac tamponade. Abdominal injuries addressed include injuries to solid organs like the spleen and liver as well as hollow organ injuries. Diagnostic tools and management strategies are provided for each type of injury.