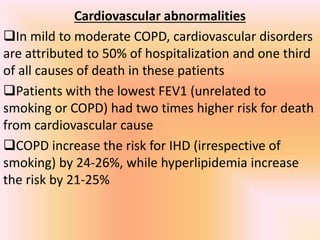
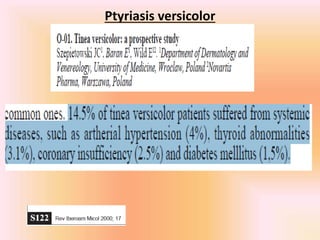
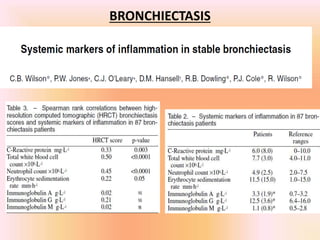
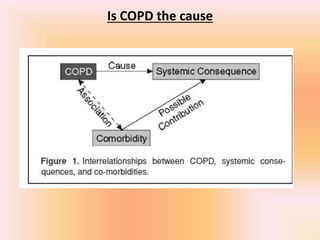
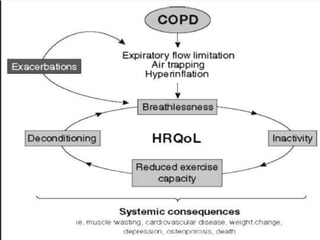
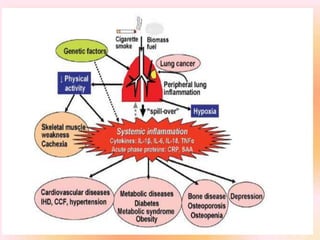
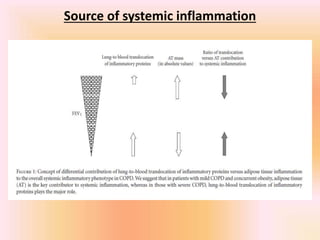
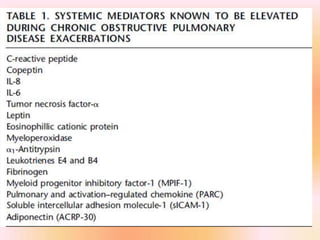
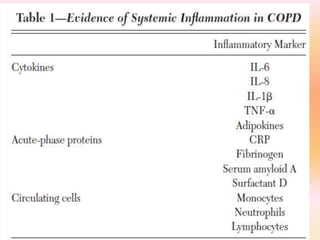
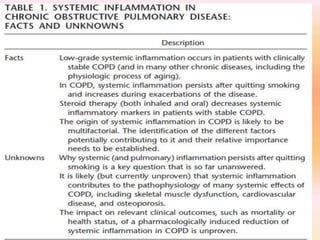
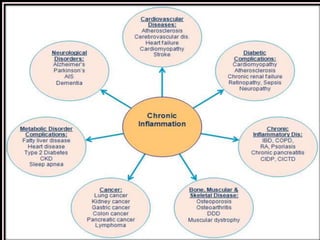
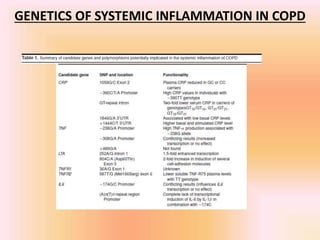
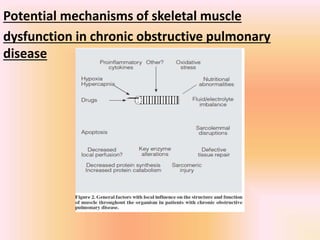
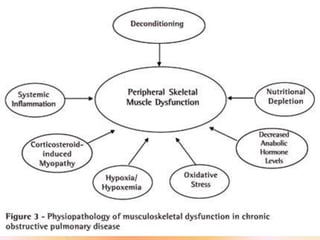
COPD is associated with systemic inflammation that can lead to several extra-pulmonary effects and comorbidities. Low-grade systemic inflammation in COPD patients is characterized by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and acute phase proteins. This systemic inflammation may originate from pulmonary inflammation spilling over into the systemic circulation, or from other sources like smoking, hypoxia, or bacterial products during exacerbations. Systemic inflammation in COPD has been implicated in several systemic effects and comorbidities including weight loss, muscle dysfunction, cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, and depression. Treatments like pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking cessation, and some medications can help reduce systemic inflammation and its associated manifestations in COPD.


























![Obesity paradox
Obesity increase the cardiovascular and all cause
mortality in stage one and two COPD]
Obesity decrease the relative mortality risk in stage
three and four COPD
These findings are also found in malignancies,
chronic heart diseases, renal failure and AIDS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copdsystemicinflammationorsystemicmanifestations-170622235400/85/Copd-systemic-inflammation-or-systemic-manifestations-39-320.jpg)