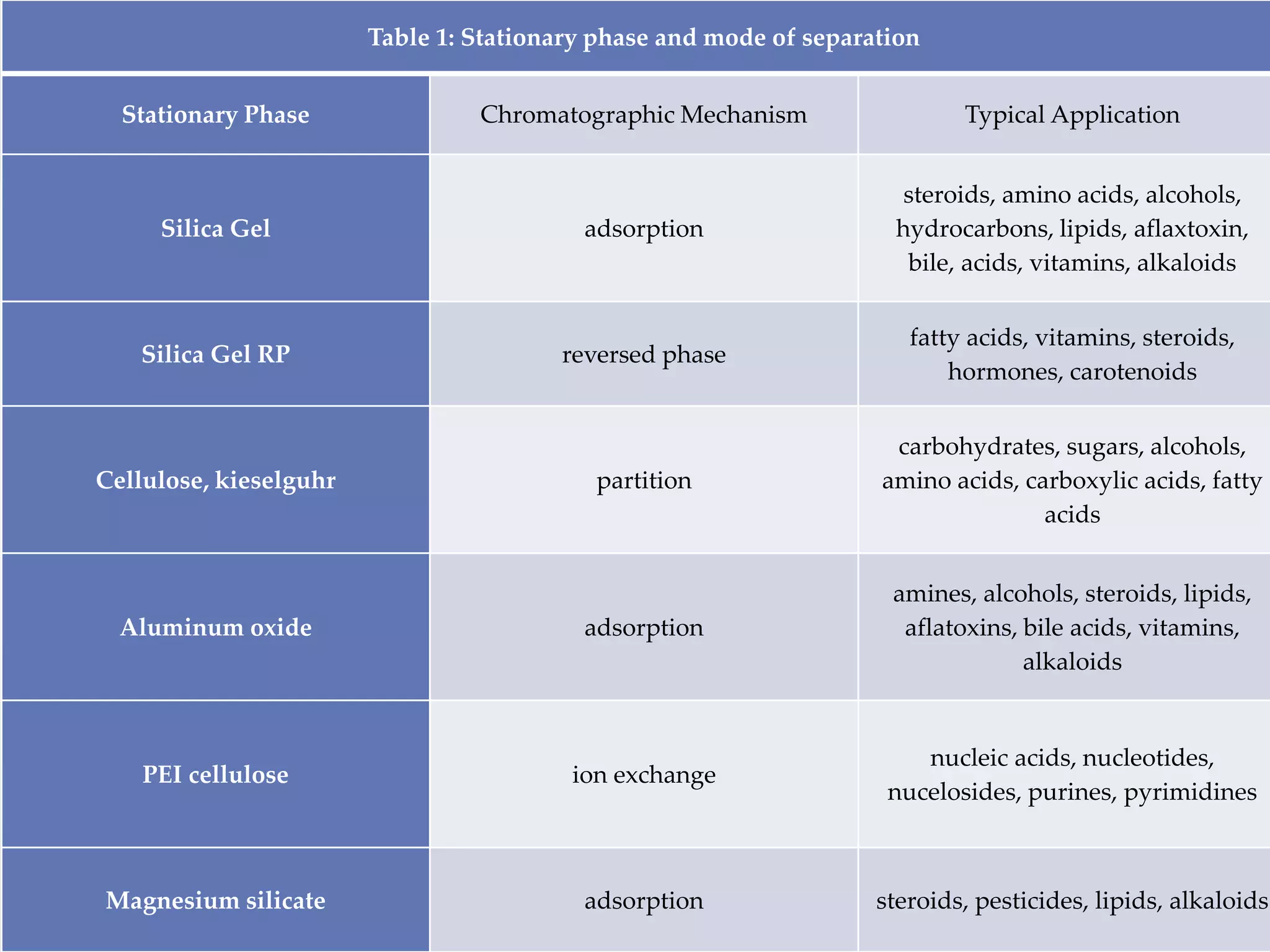
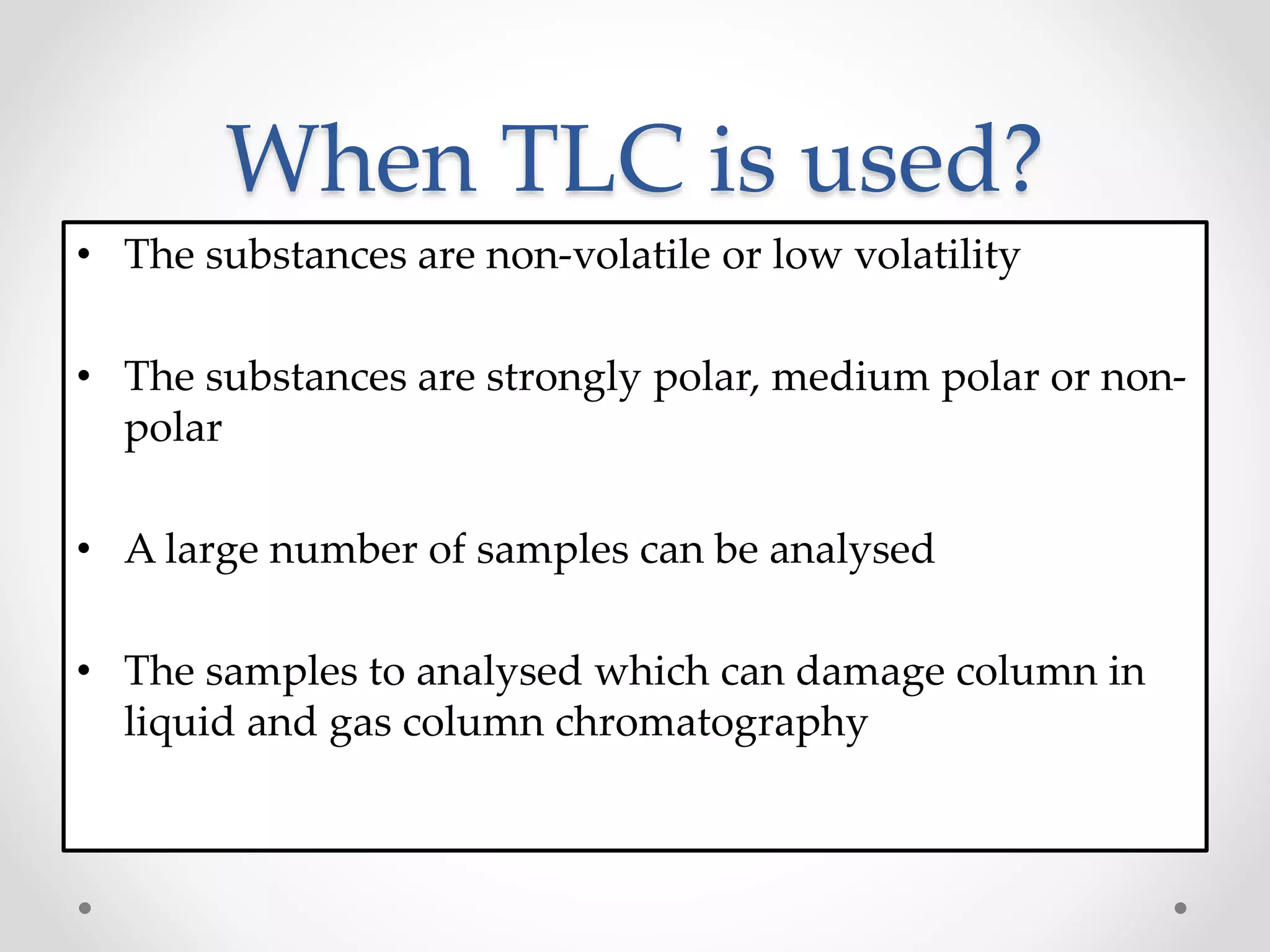
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a technique used to separate mixtures by distributing the components between a stationary phase, such as silica gel coated onto a plate, and a mobile phase, such as a solvent that moves across the plate. TLC involves spotting a sample onto the plate, developing it by allowing the mobile phase to travel up the plate, and visualizing the separated components, which travel at different rates depending on how they partition between the phases. TLC is a simple, fast, and inexpensive method used to analyze organic compounds and test purity across various fields like pharmaceuticals, clinical chemistry, and food analysis.