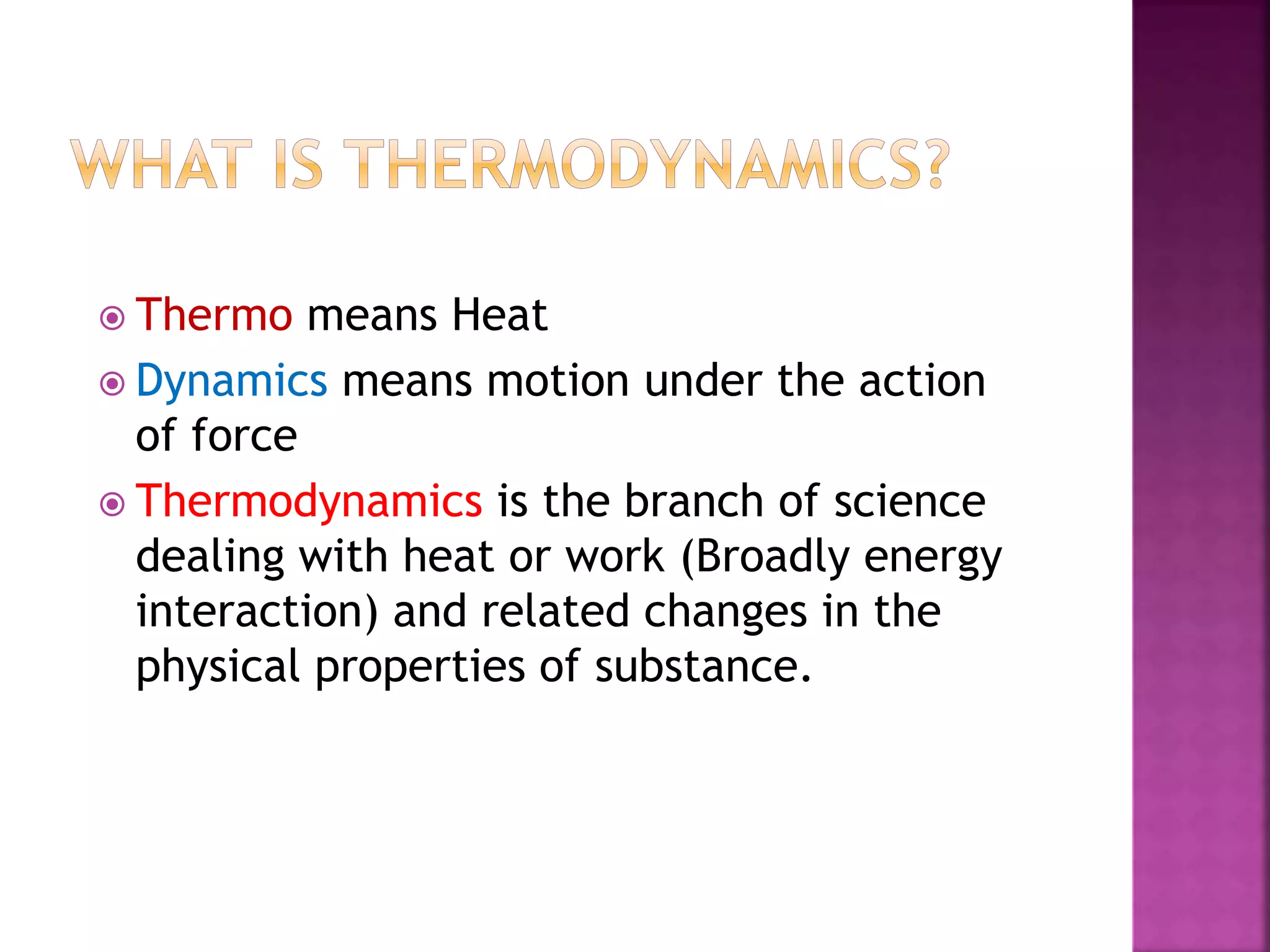
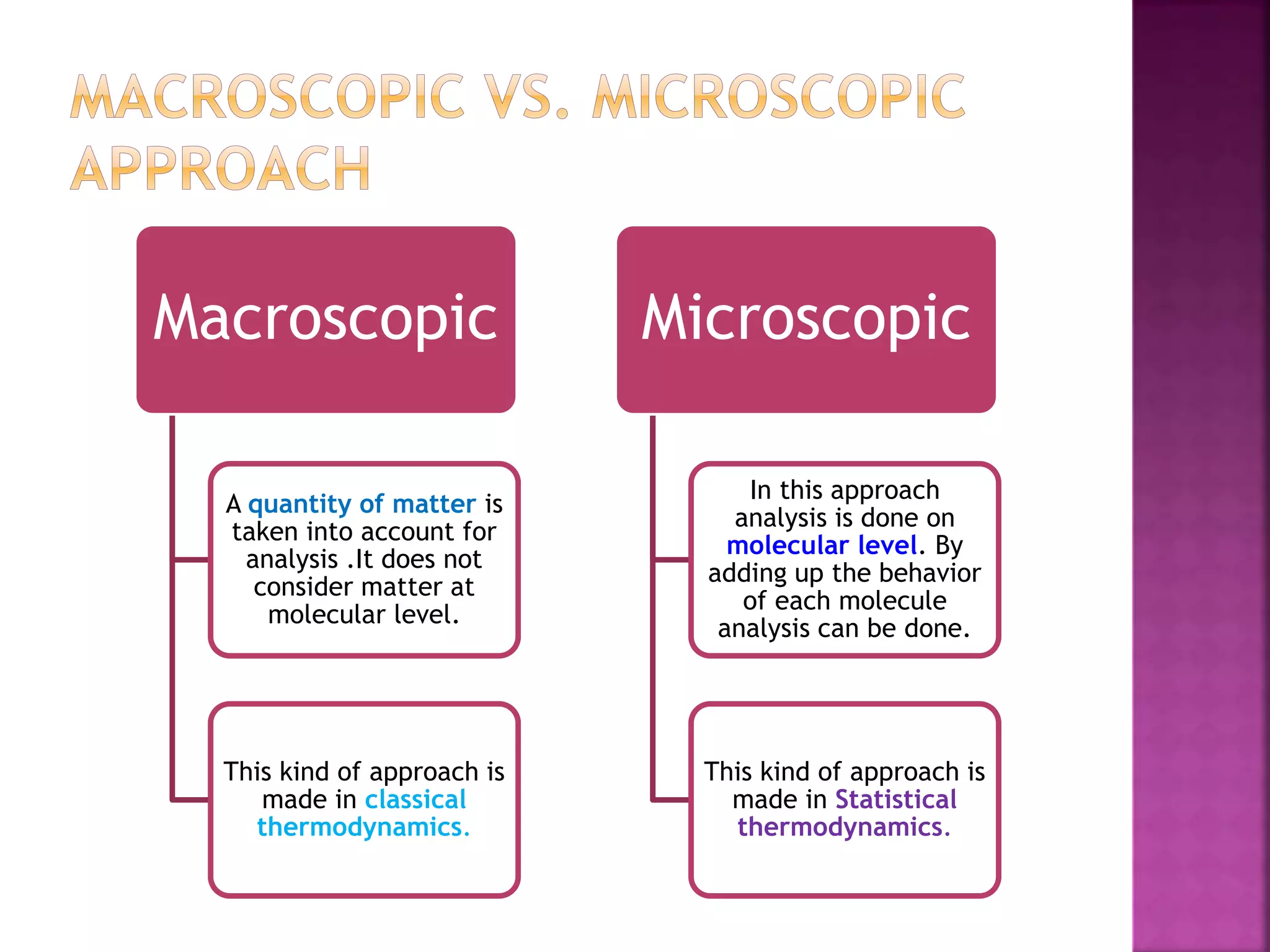
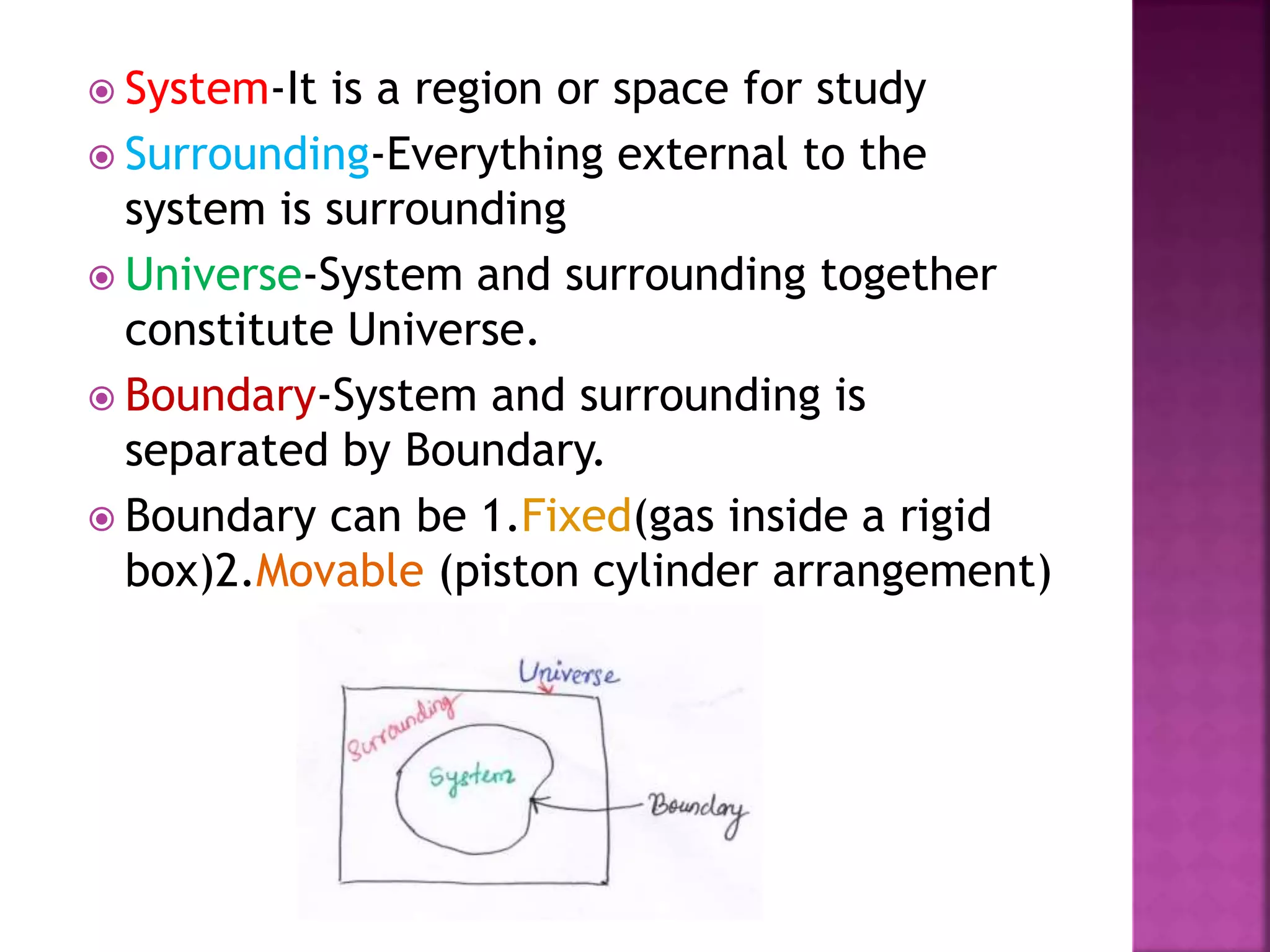
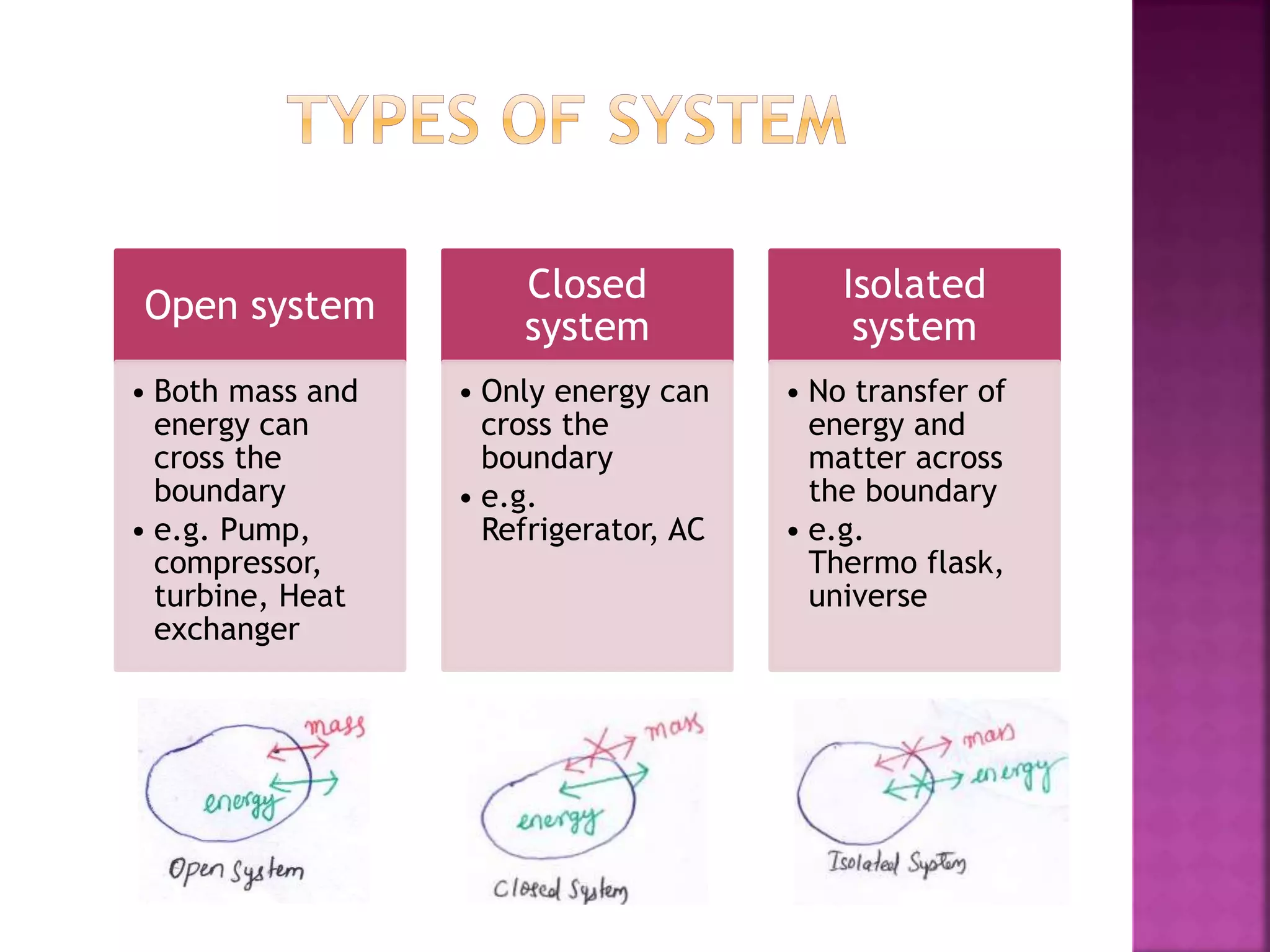
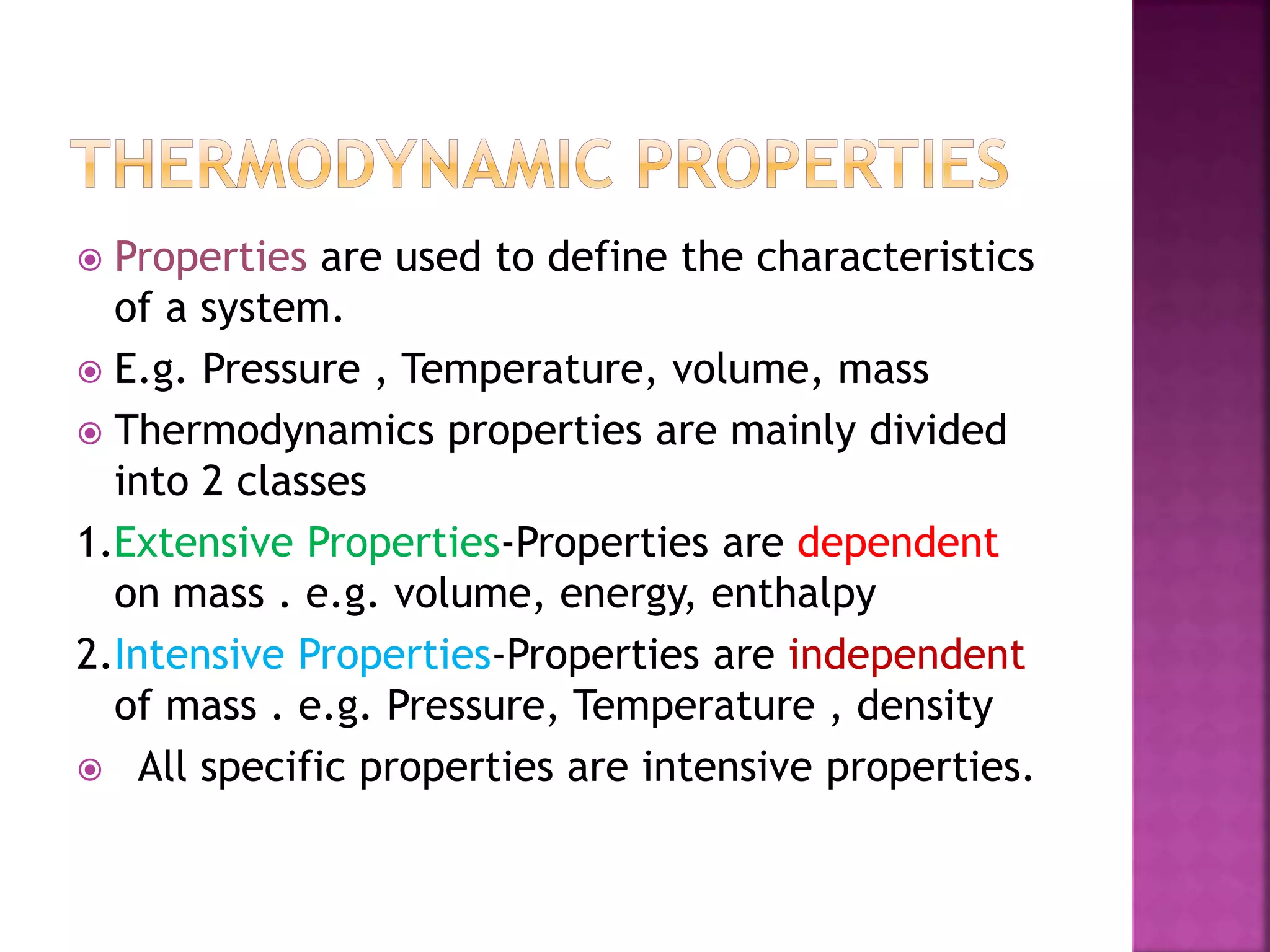
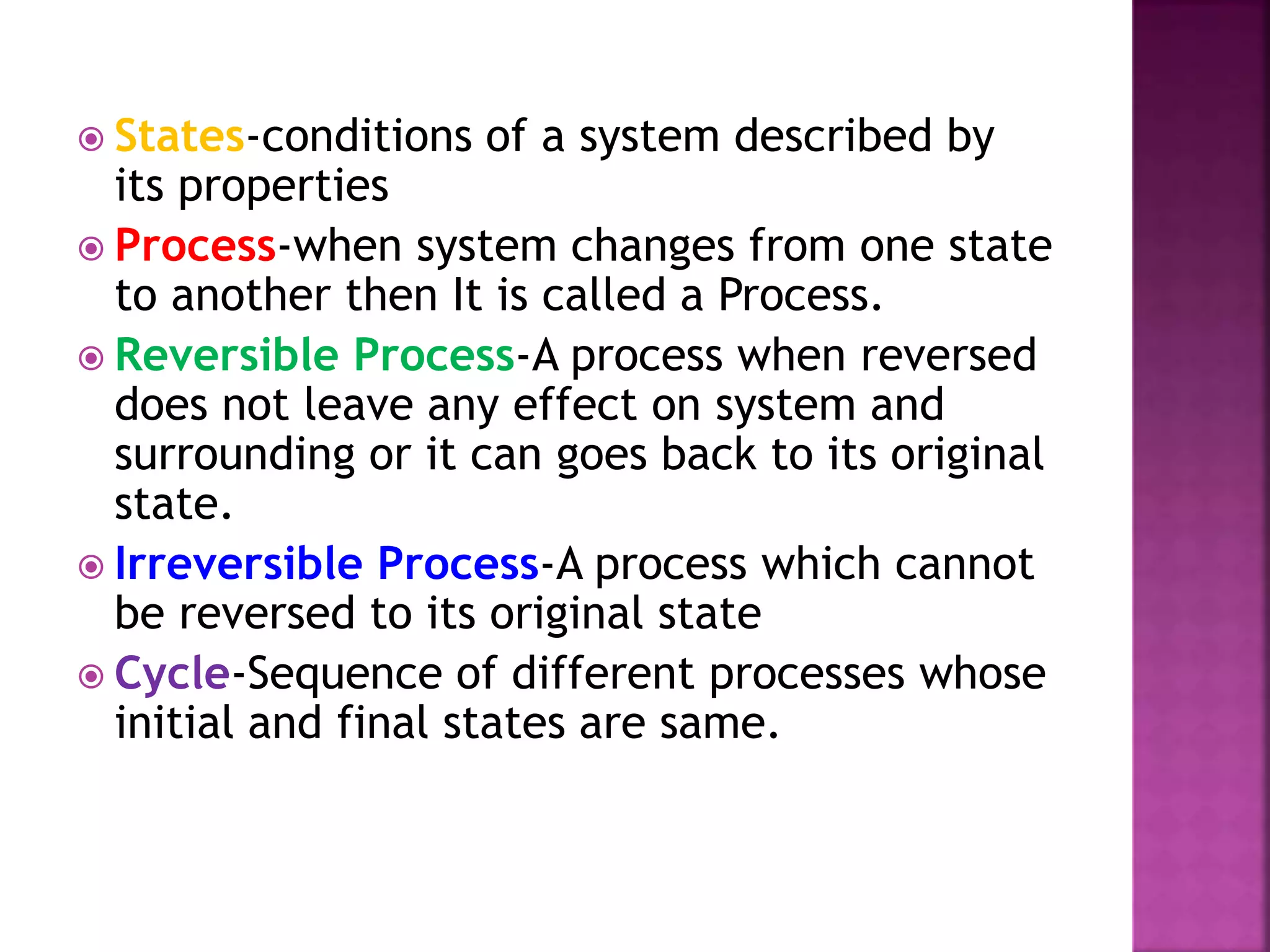
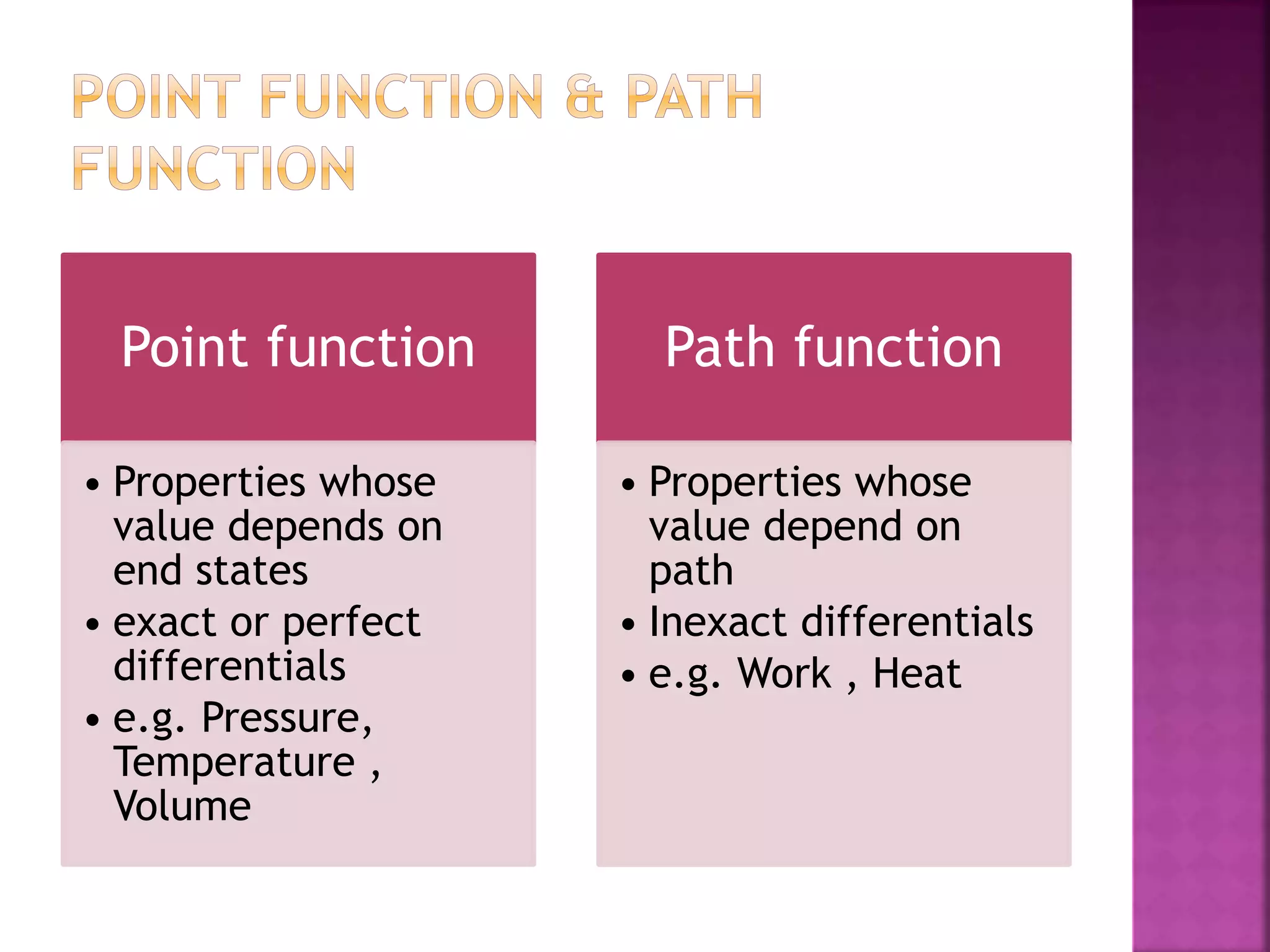
Thermodynamics is the branch of science dealing with heat, work, temperature, and energy. It can be studied from both a macroscopic and microscopic perspective. A system is defined along with its surroundings and boundary. Systems can be open, closed, or isolated depending on what crosses the boundary. Thermodynamic properties are either extensive or intensive, and describe the state of a system. A process is a change in a system's state, and can be reversible or irreversible. Thermodynamic equilibrium requires thermal, mechanical, and chemical equilibrium.