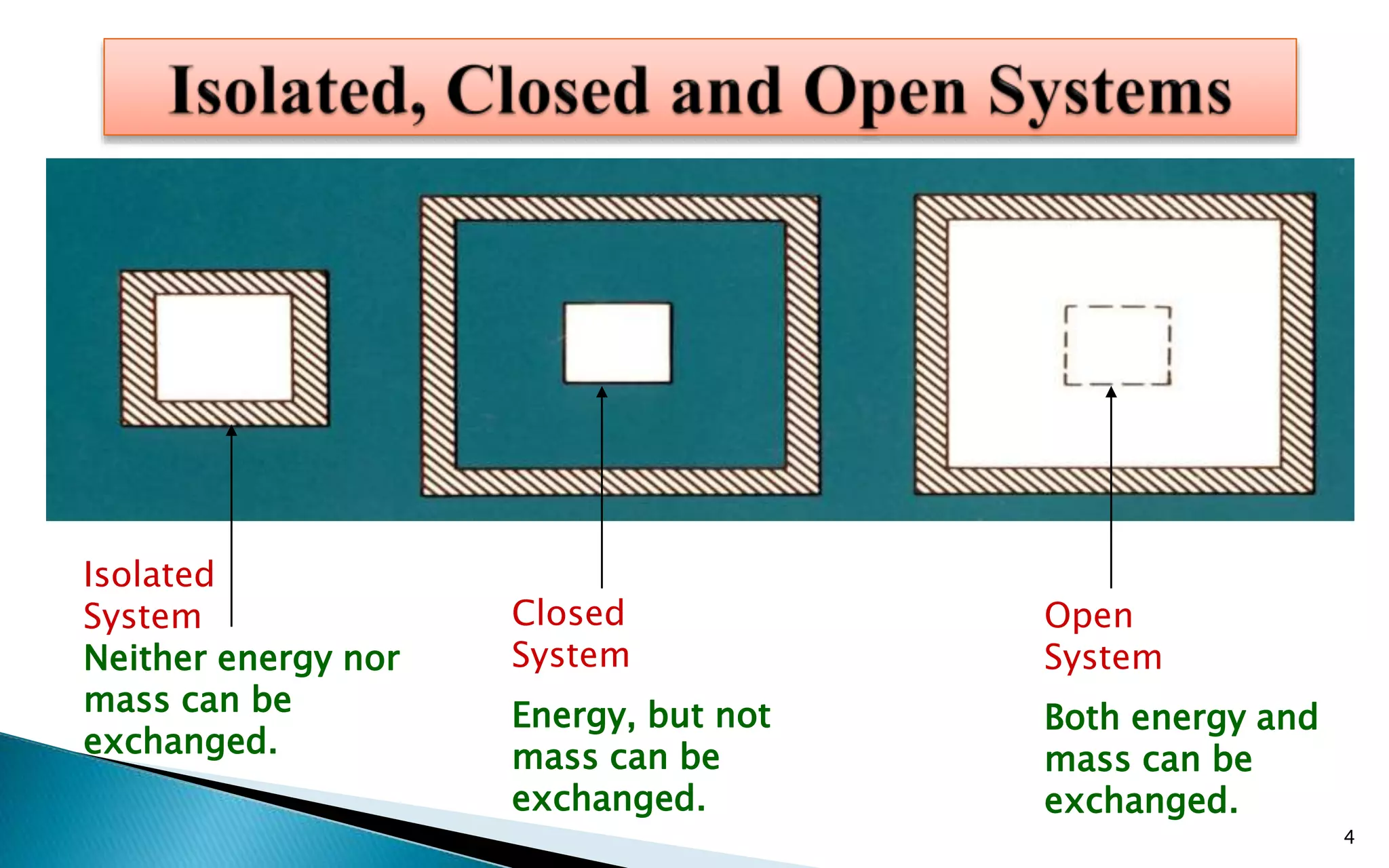
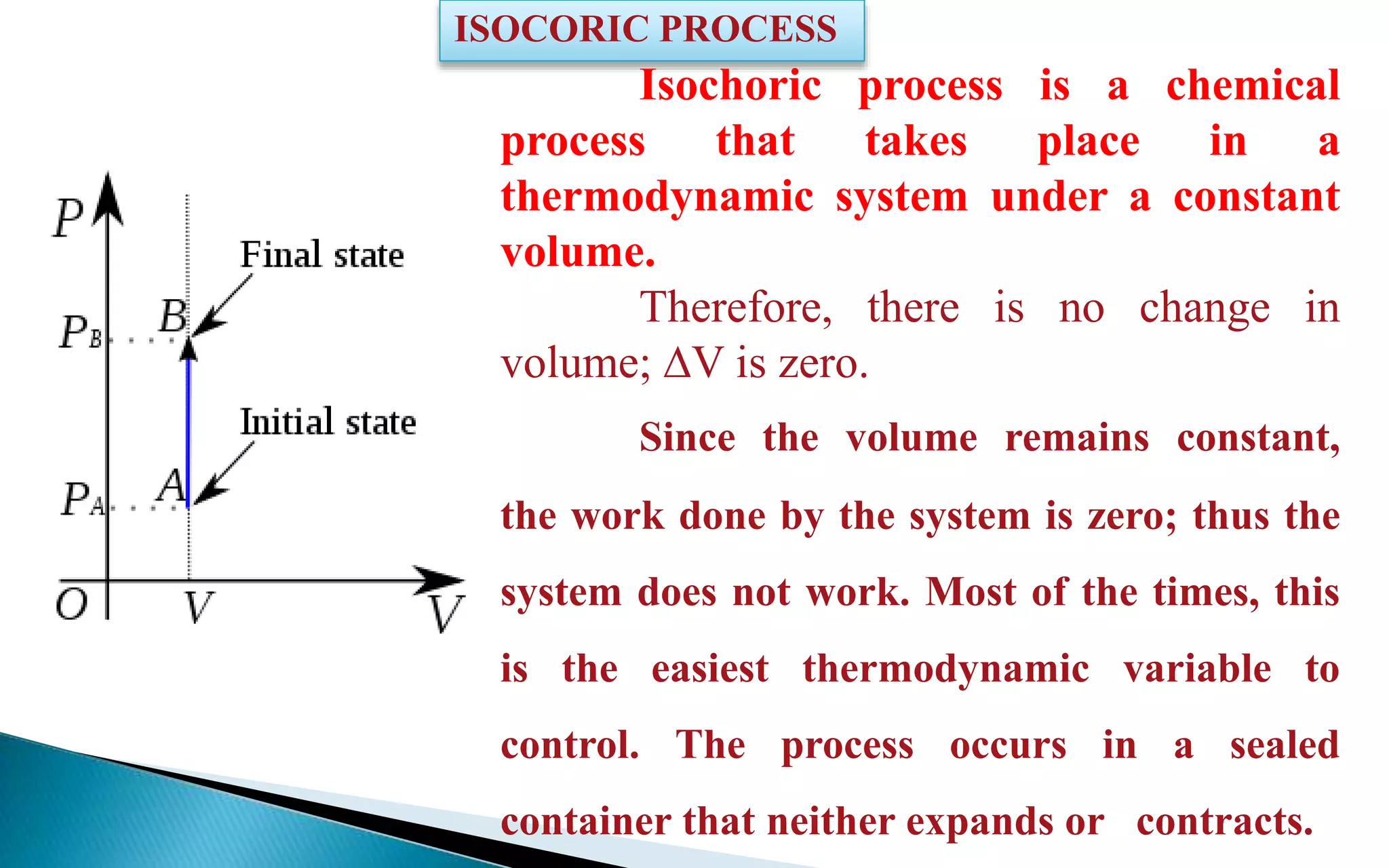
This document discusses different thermodynamic processes. It defines a thermodynamic process as a chemical or physical process that changes a system from an initial state to a final state. It then describes four main types of thermodynamic processes: isolated, closed, open, isothermal, isochoric, isobaric, and adiabatic. For each process, it provides the key characteristics, such as whether the system can exchange energy and mass with its surroundings.