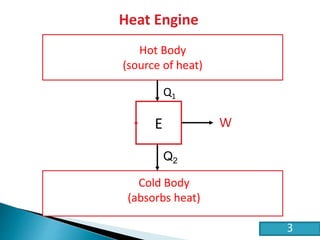
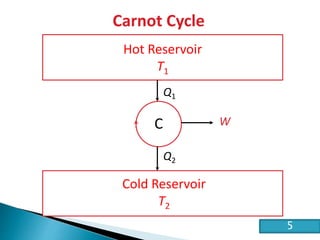
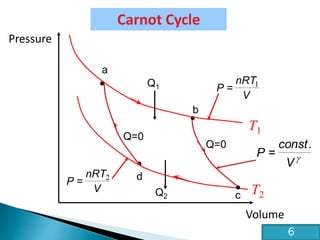
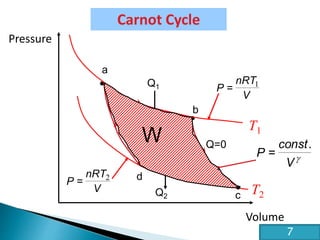
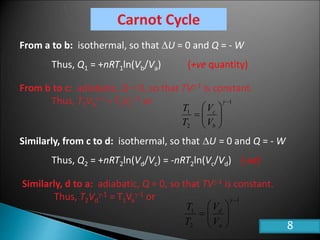
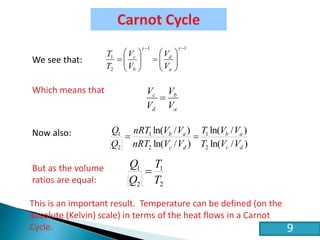
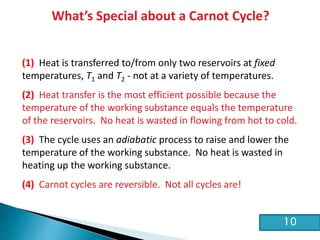
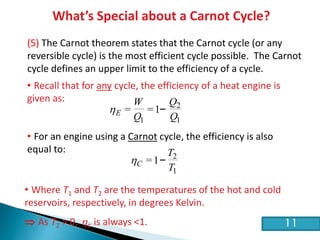
This document discusses the Carnot cycle and the second law of thermodynamics. It defines a heat engine and describes the key components of the Carnot cycle, including the isothermal and adiabatic processes. It explains that the Carnot cycle is reversible and defines the maximum possible efficiency for converting heat into work. The document concludes by stating the Kelvin-Planck and Clausius formulations of the second law - that it is impossible to convert all heat from a single body into work or to spontaneously transfer heat from a cold to hot body.