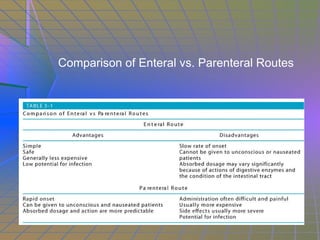
This document summarizes key principles of therapeutics in dentistry, including pharmacology basics like indications, contraindications, dose, and side effects. It discusses medication names, routes of drug administration, essential components of prescriptions, and Latin abbreviations commonly used. Key information covered includes Clark's Rule for calculating pediatric doses, factors to consider before prescribing drugs like interactions and patient factors, and legal responsibilities of the prescribing dentist.



























![Feel free to use this PowerPoint presentation for your personal, educational and business. Do Make a copy for backups on your harddrive or local network. Use the presentation for your presentations and projects. Print hand outs or other promotional items. Don‘t Make it available on a website , portal or social network website for download . (Incl. groups, file sharing networks, Slideshare etc.) Edit or modify the downloaded presentation and claim / pass off as your own work. All copyright and intellectual property rights, without limitation, are retained by Dr. Iyad Abou Rabii. By downloading and using this presentatione, you agree to this statement. Please feel free to contact me, if you do have any questions about usage. Dr Iyad Abou Rabii [email_address] Copyright notice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therapeuticsindentistrygeneralprinciples-111203084902-phpapp02/85/Therapeutics-in-dentistry-general-principles-30-320.jpg)