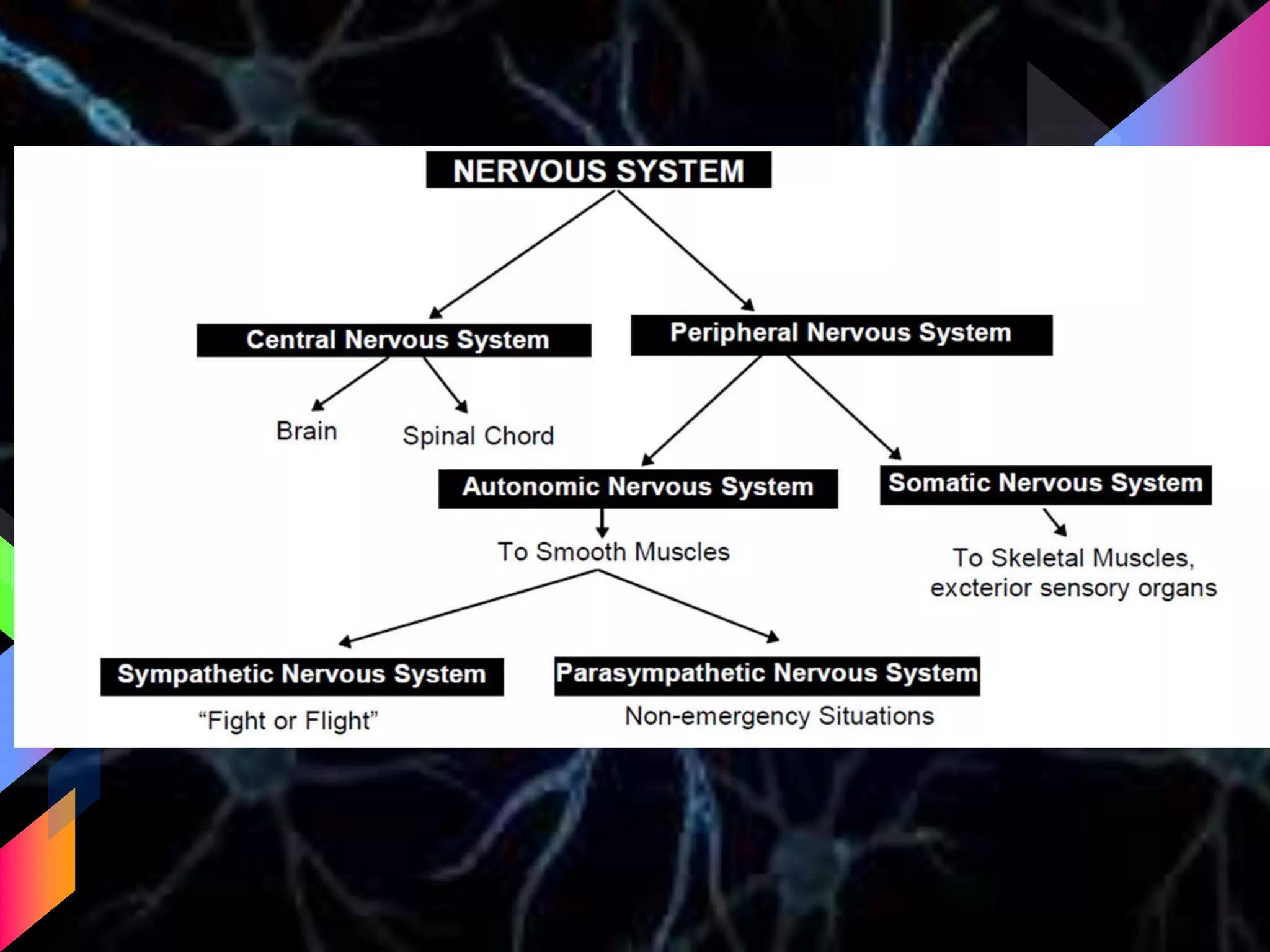
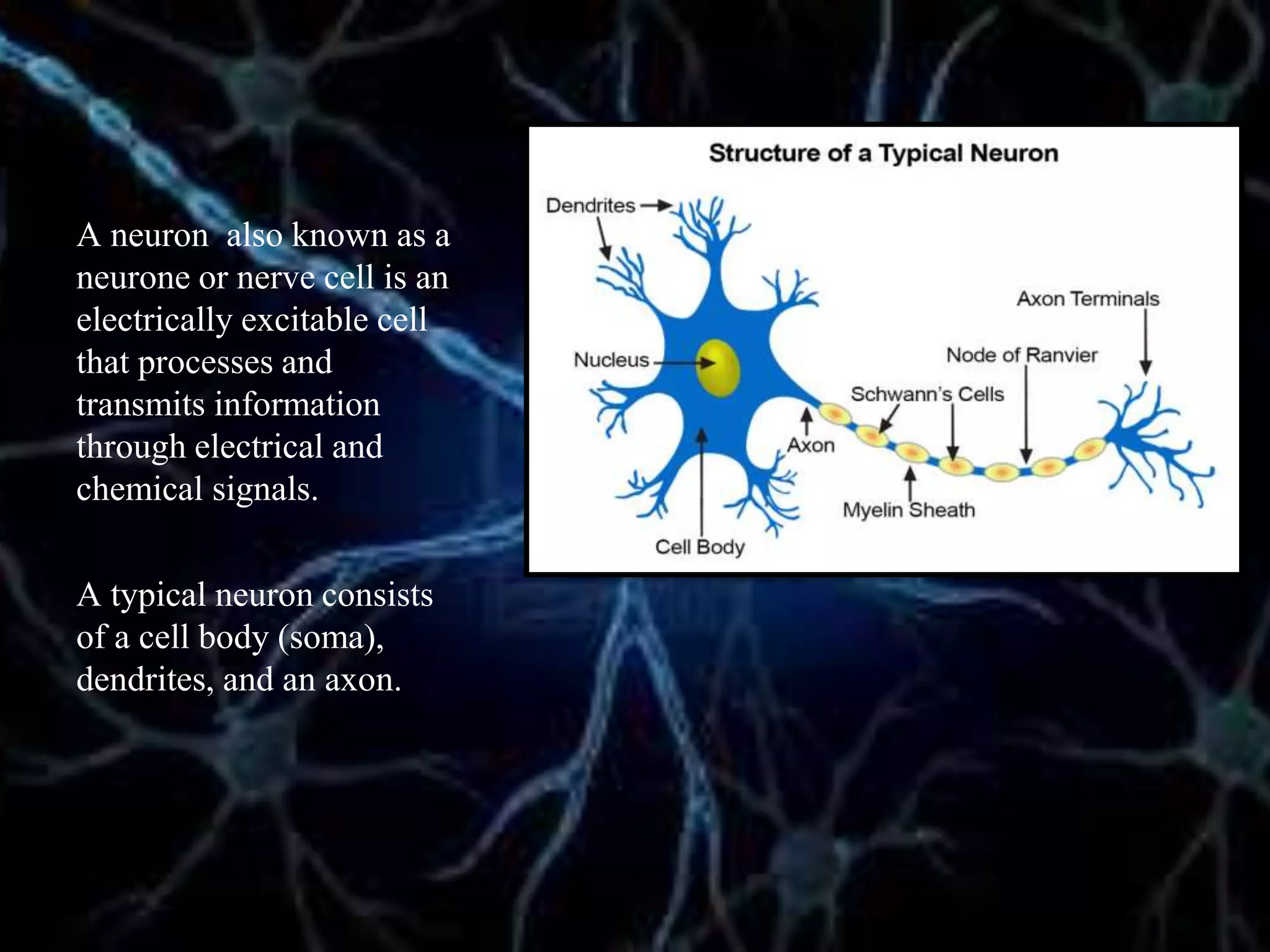
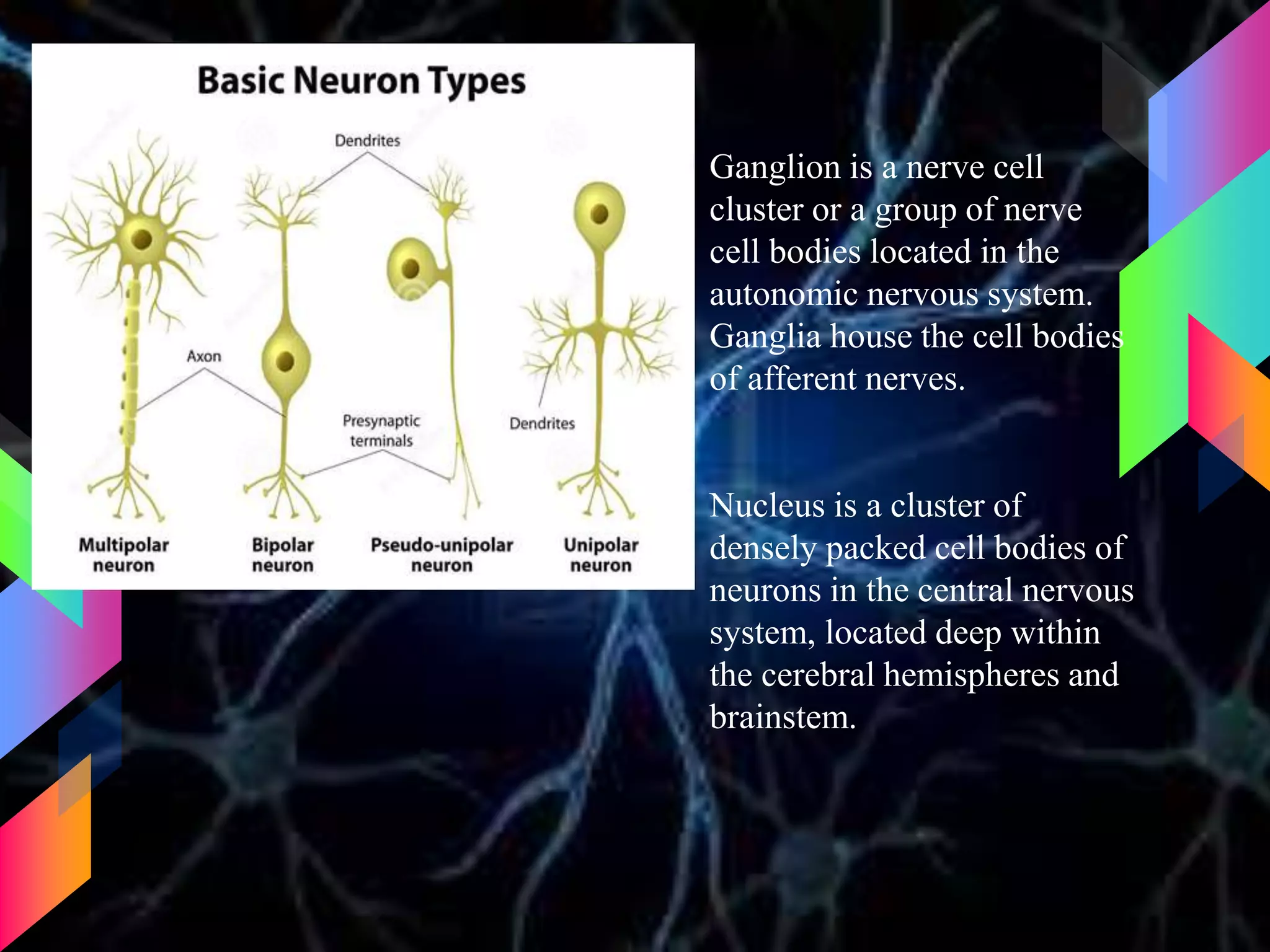
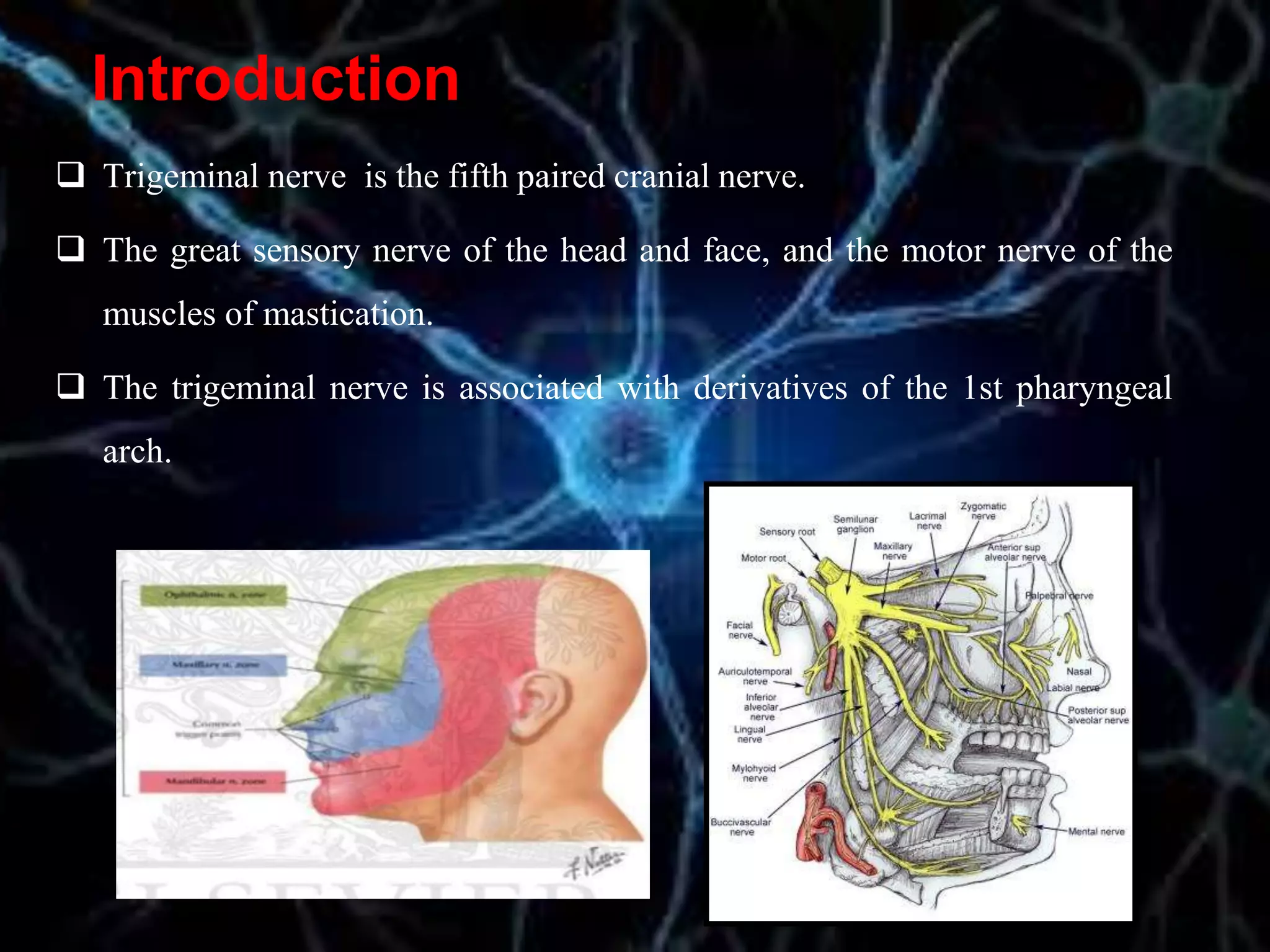
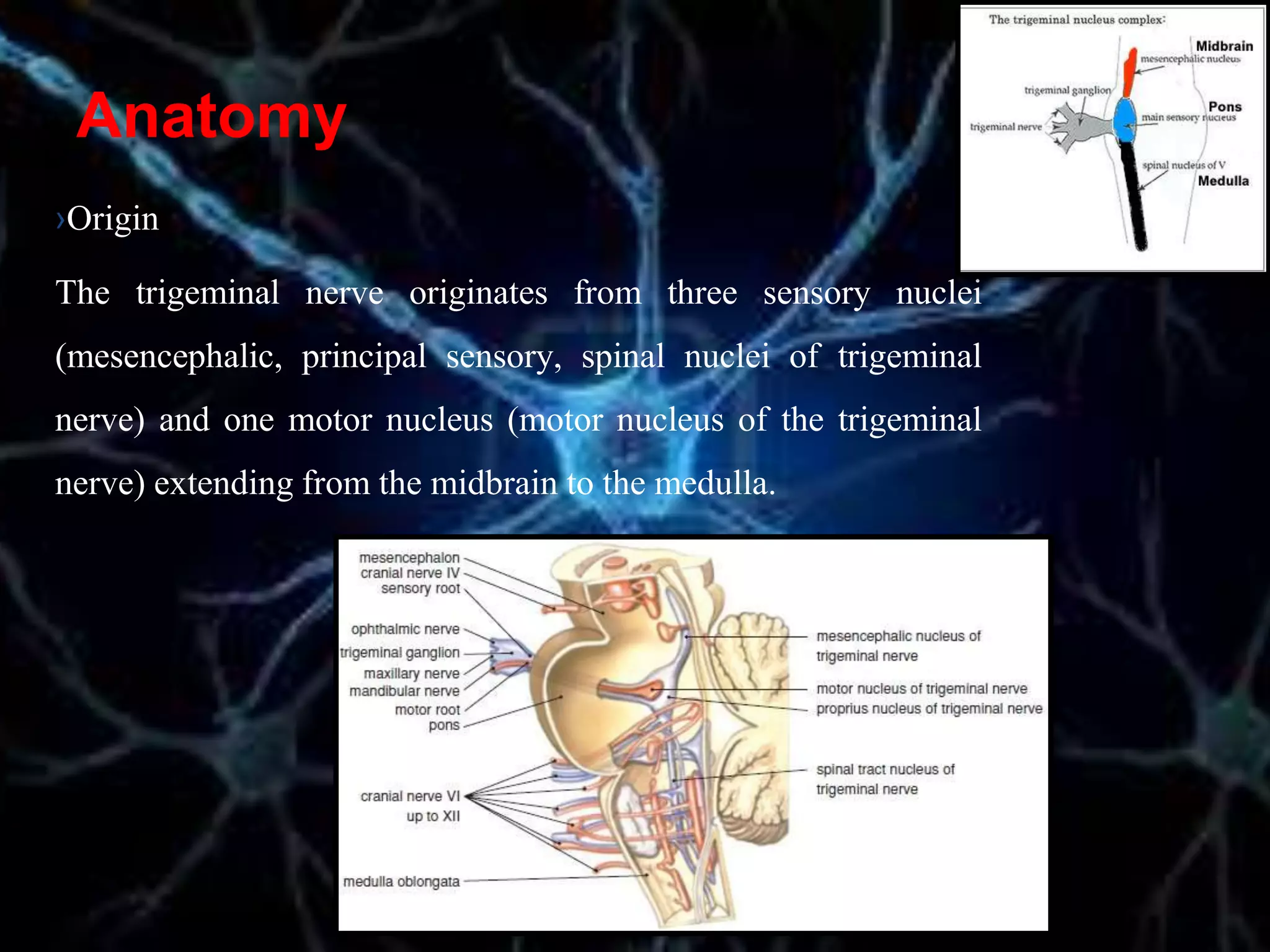
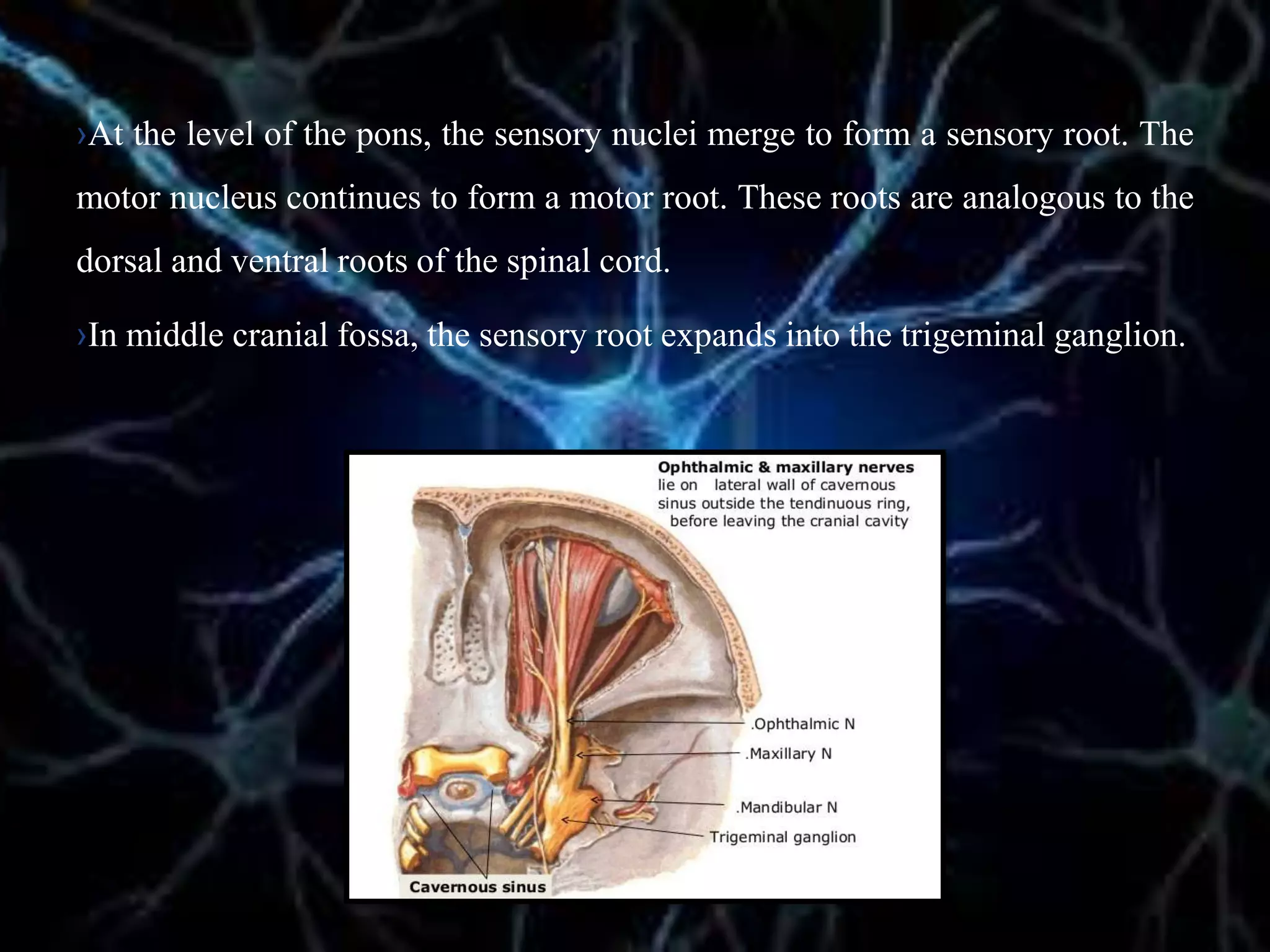
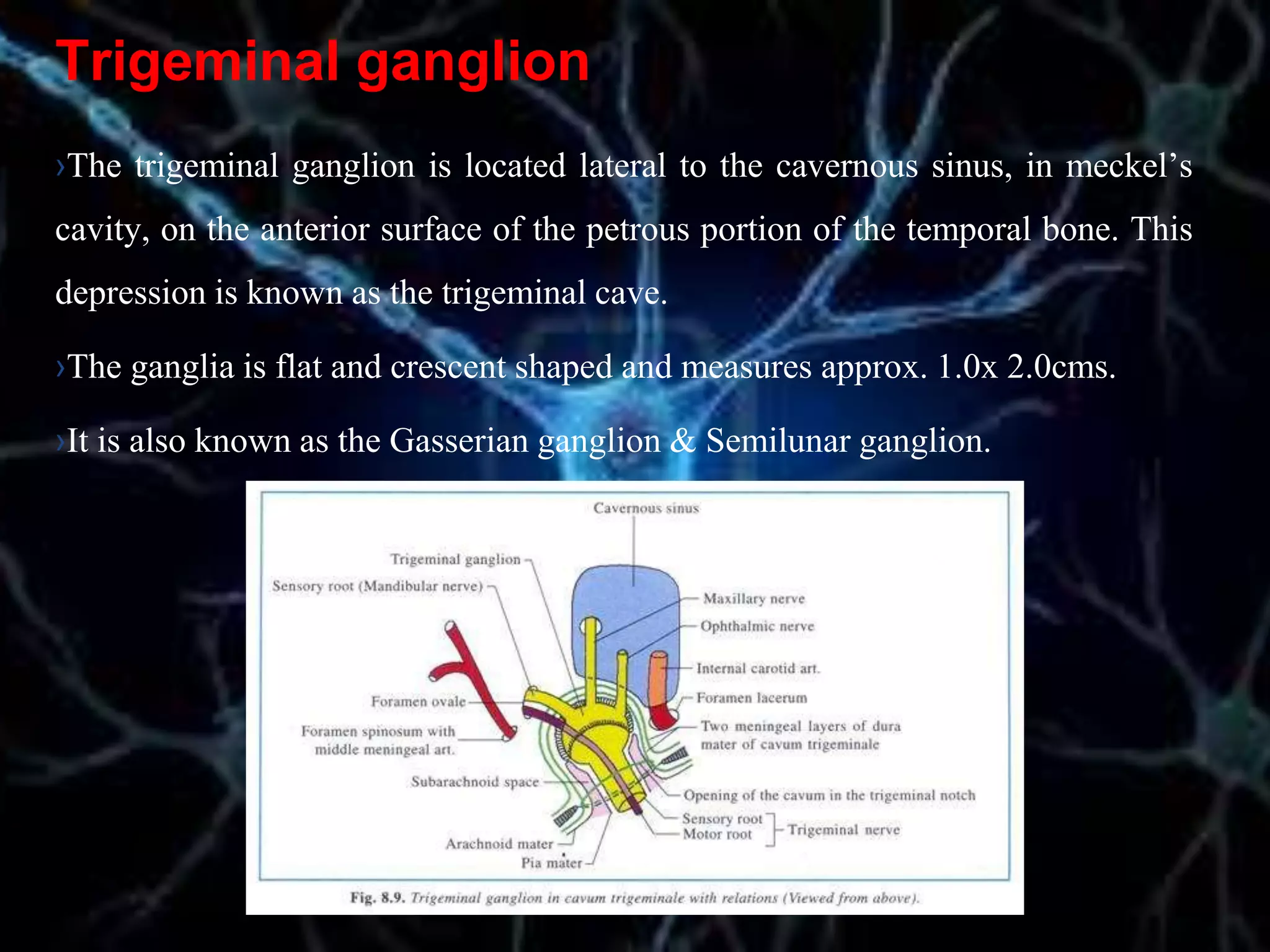
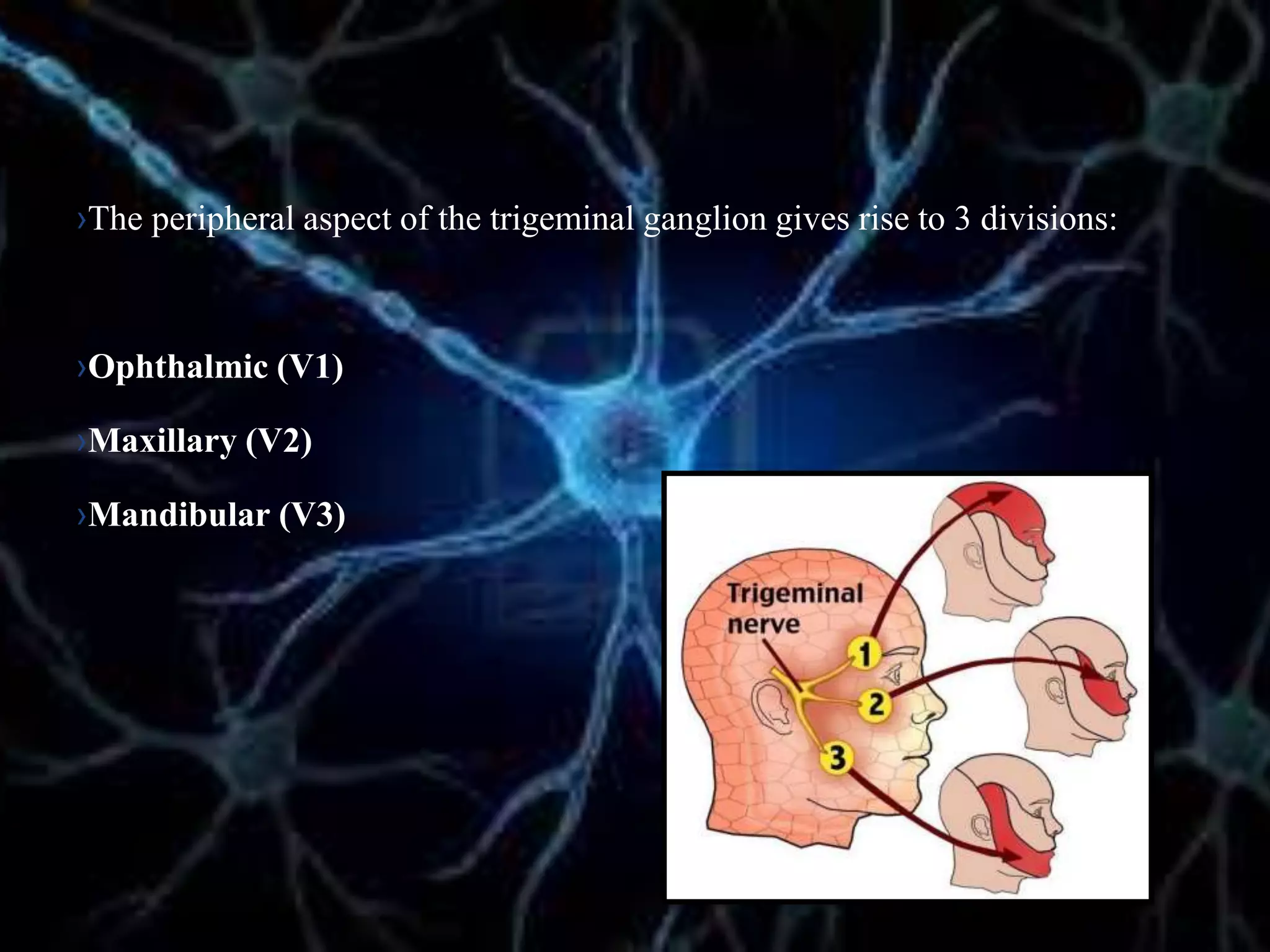
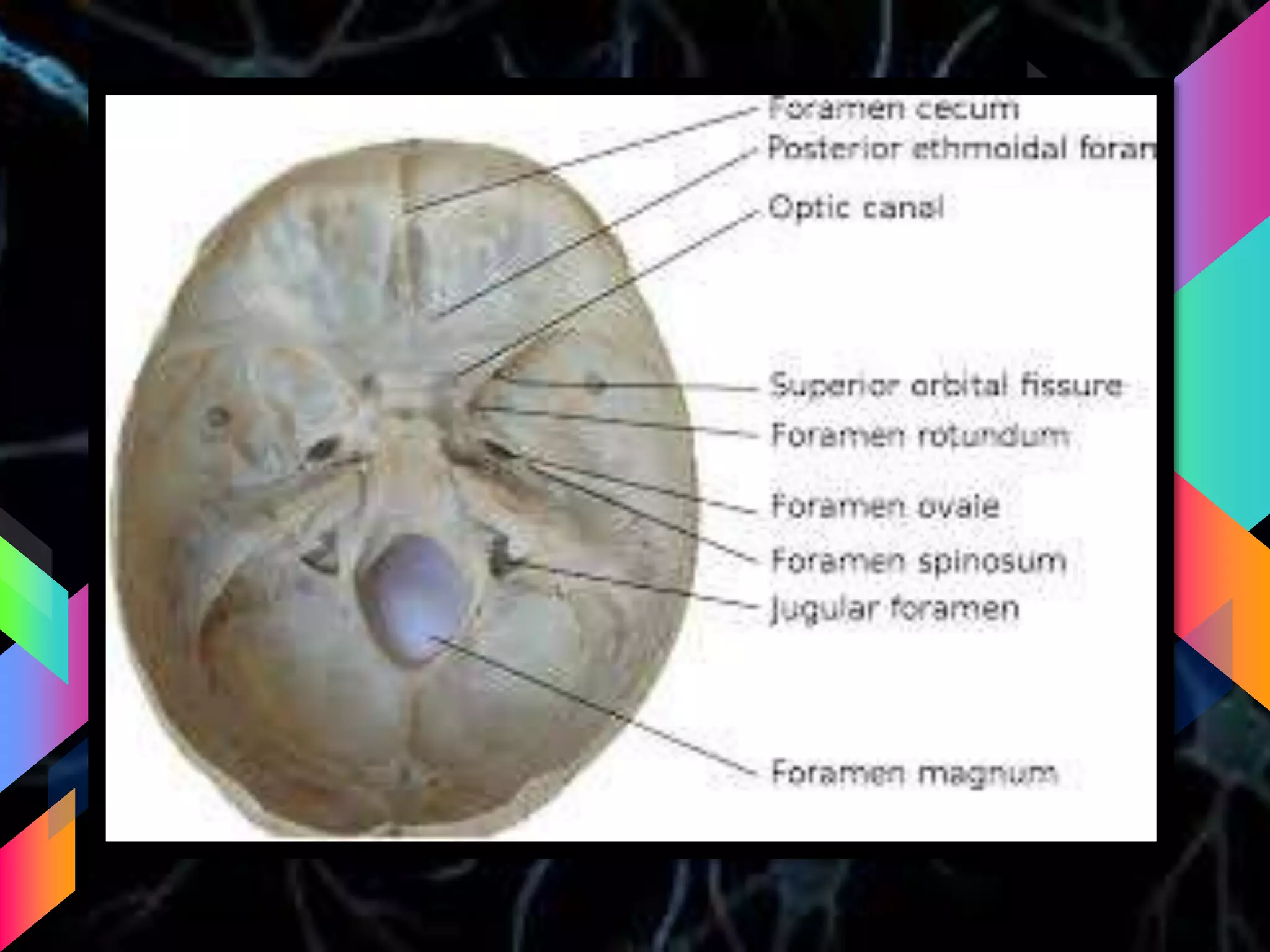
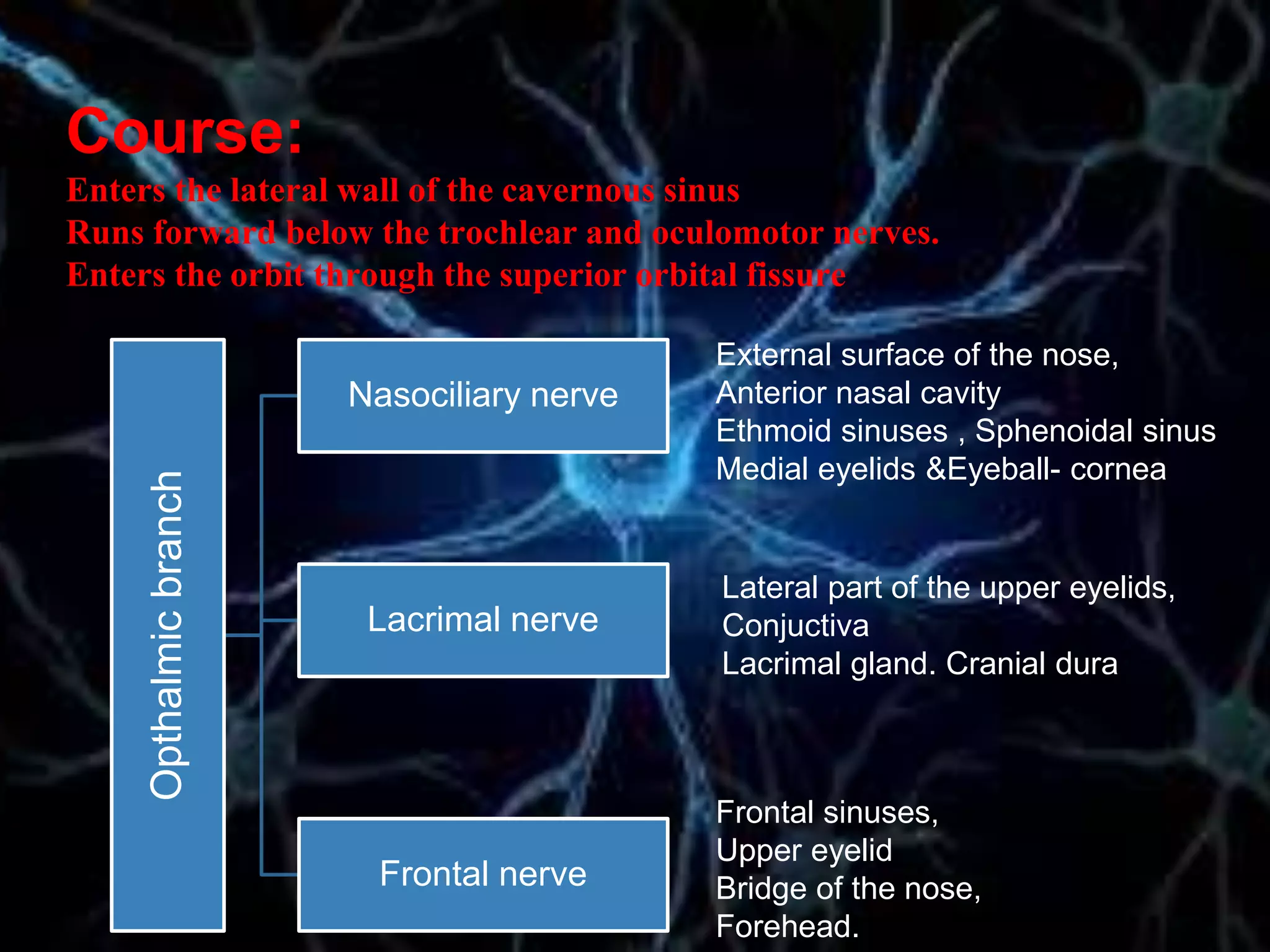
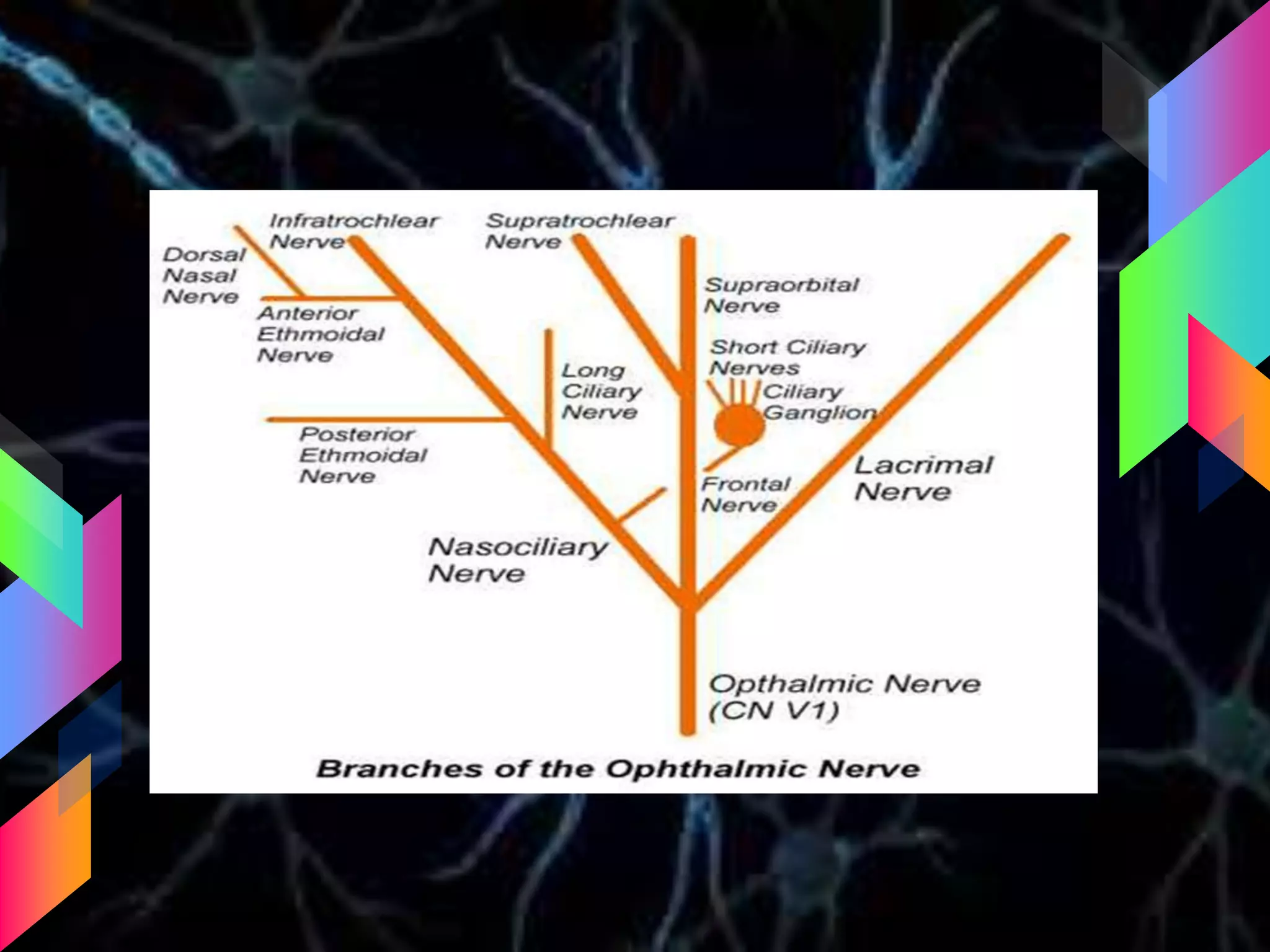
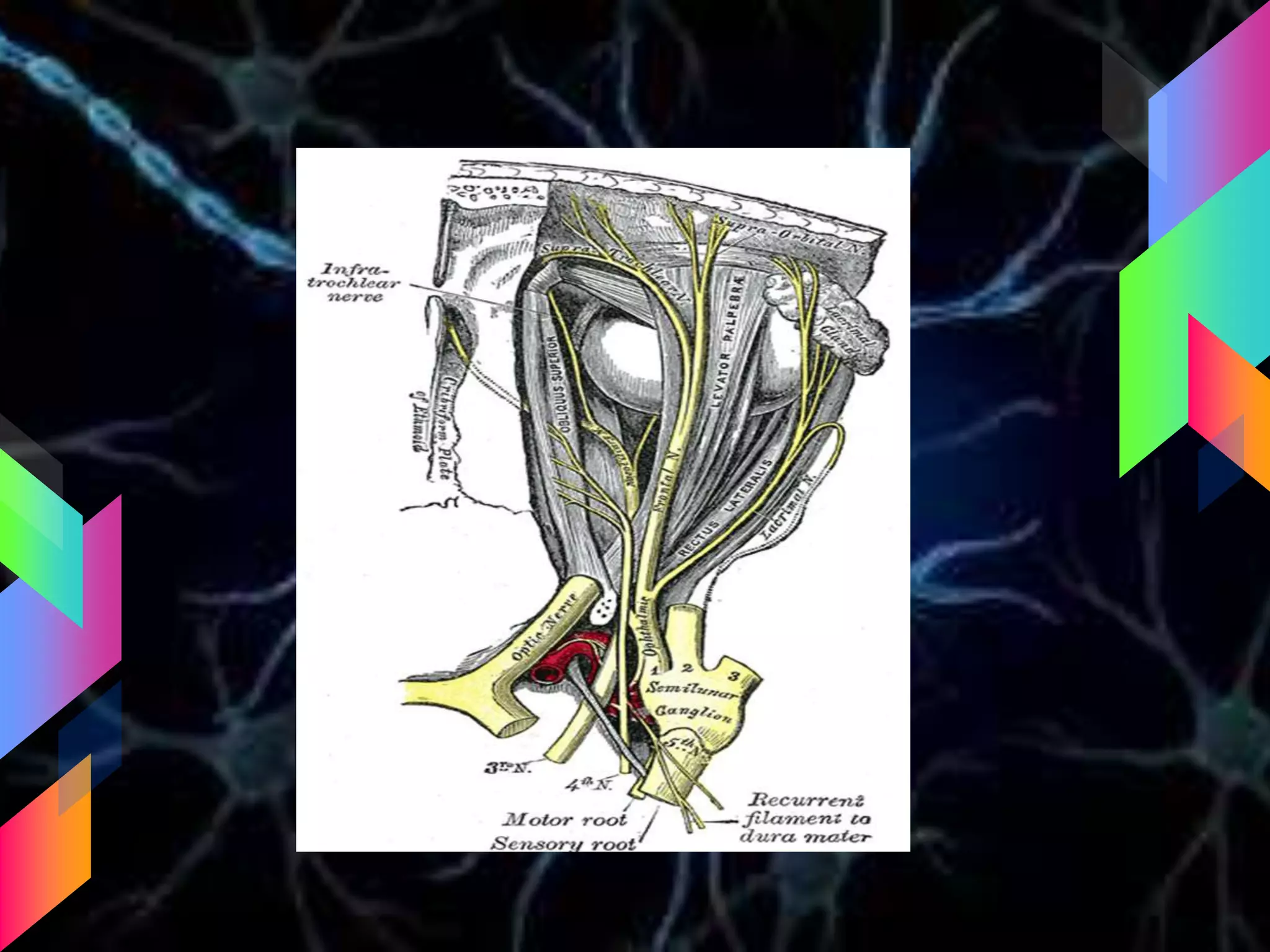
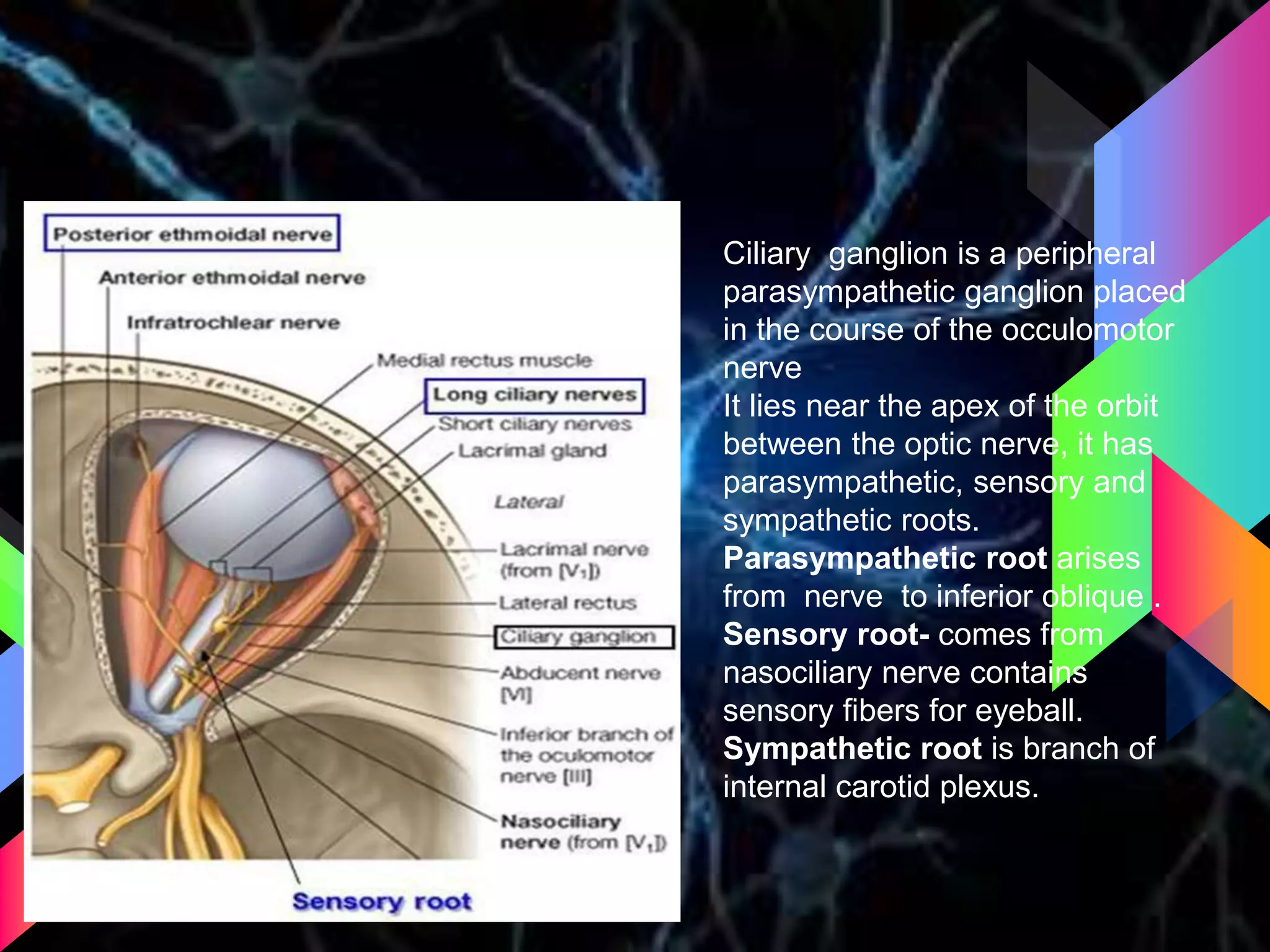
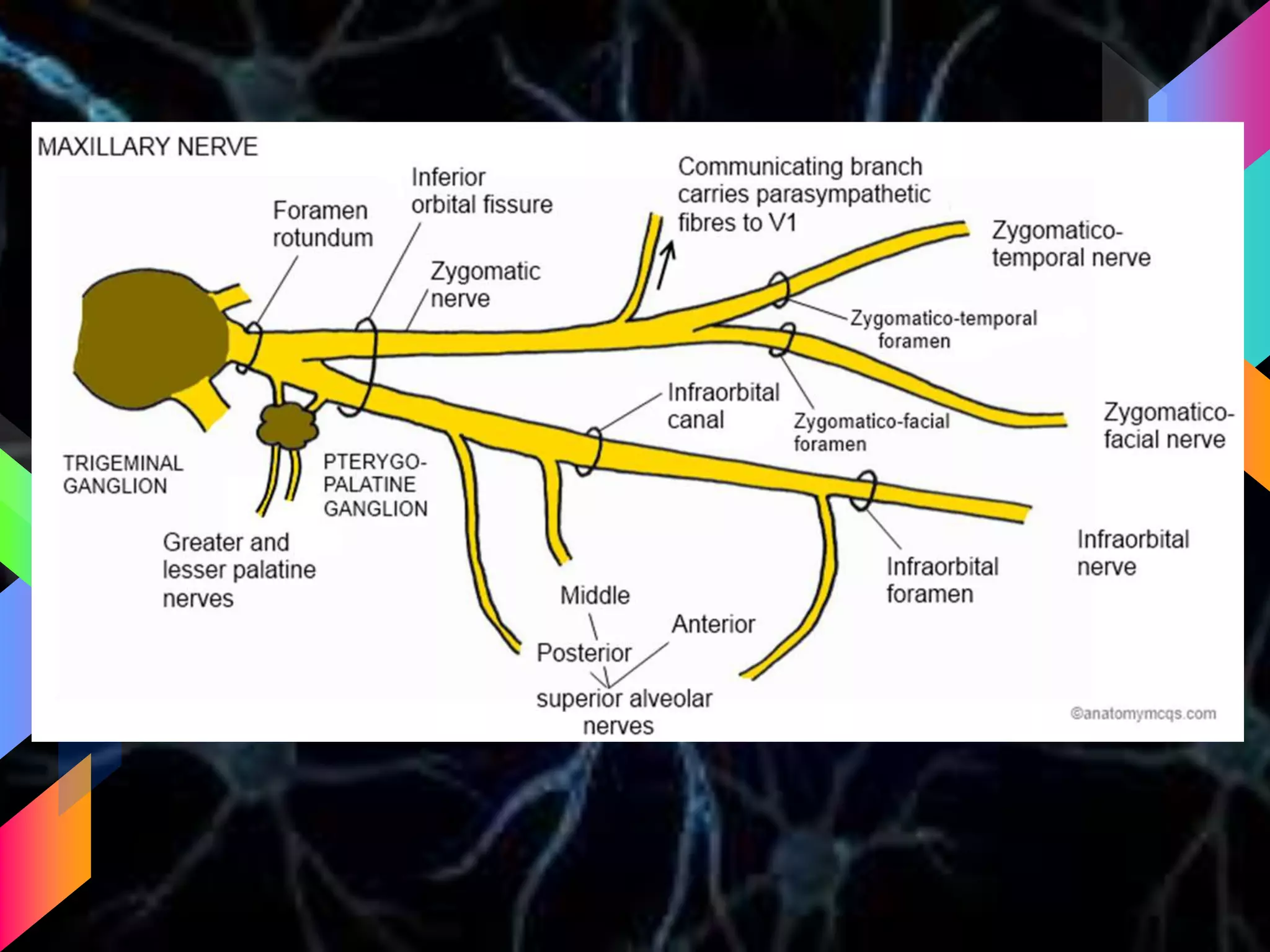
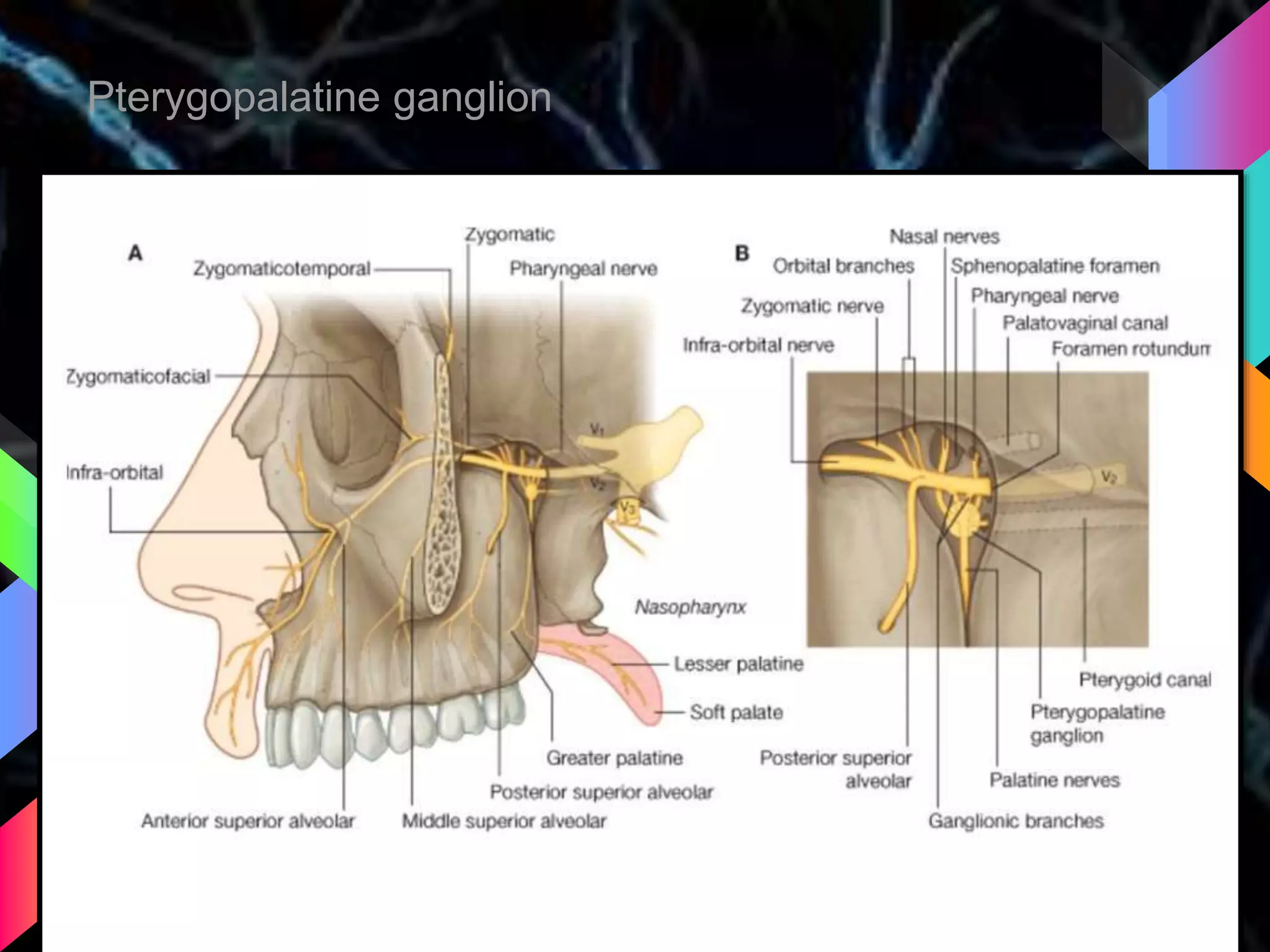
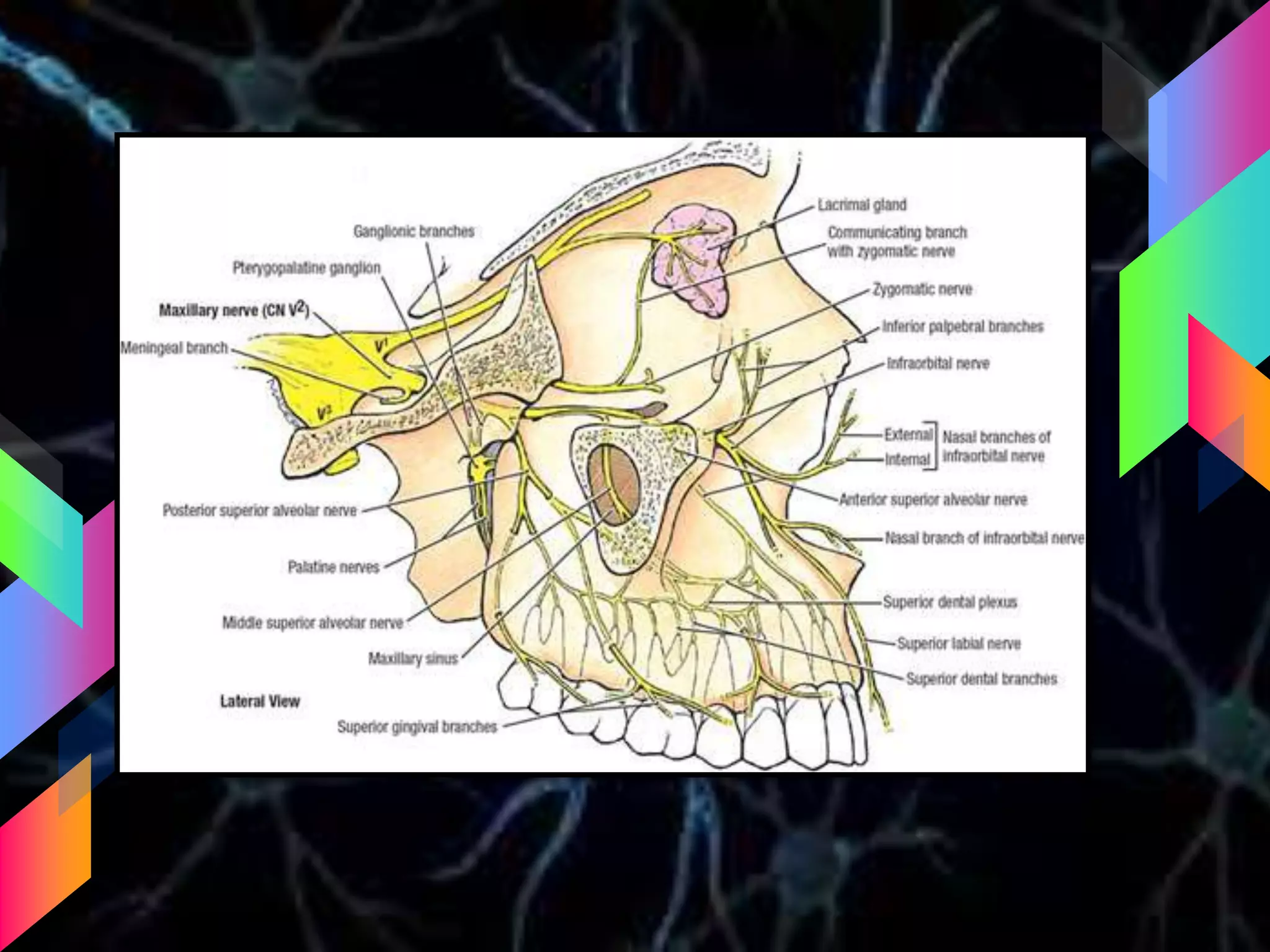
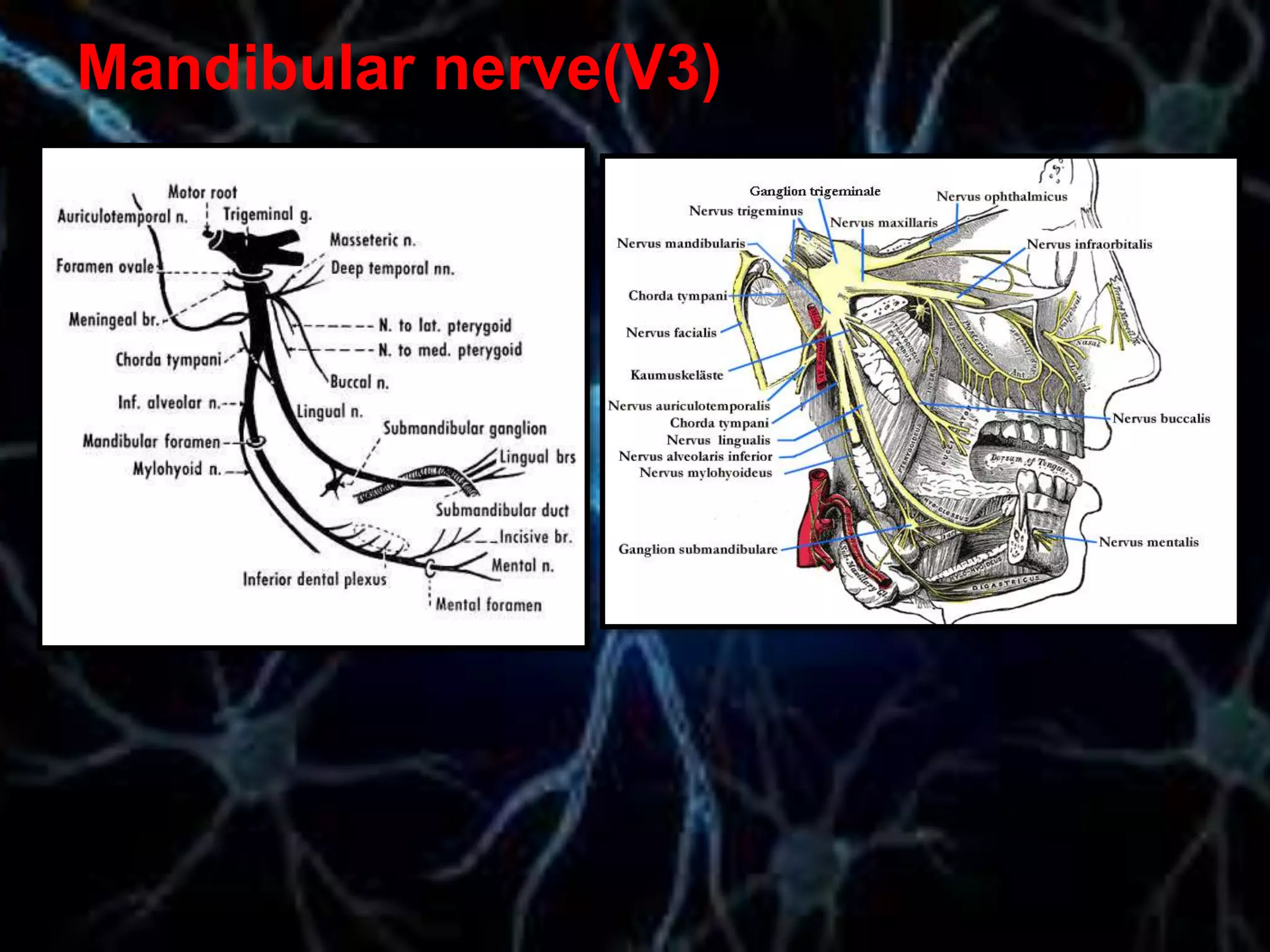
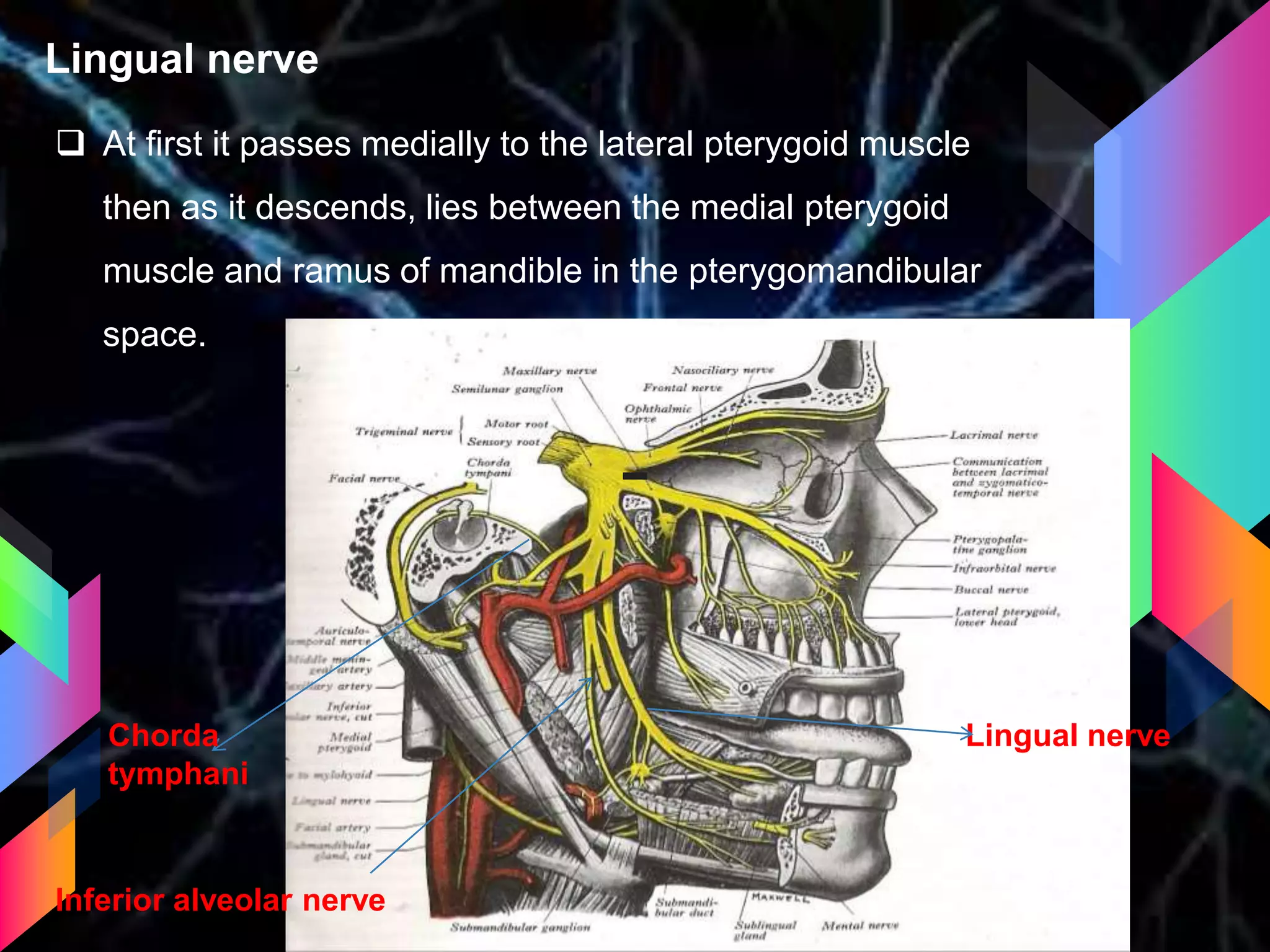
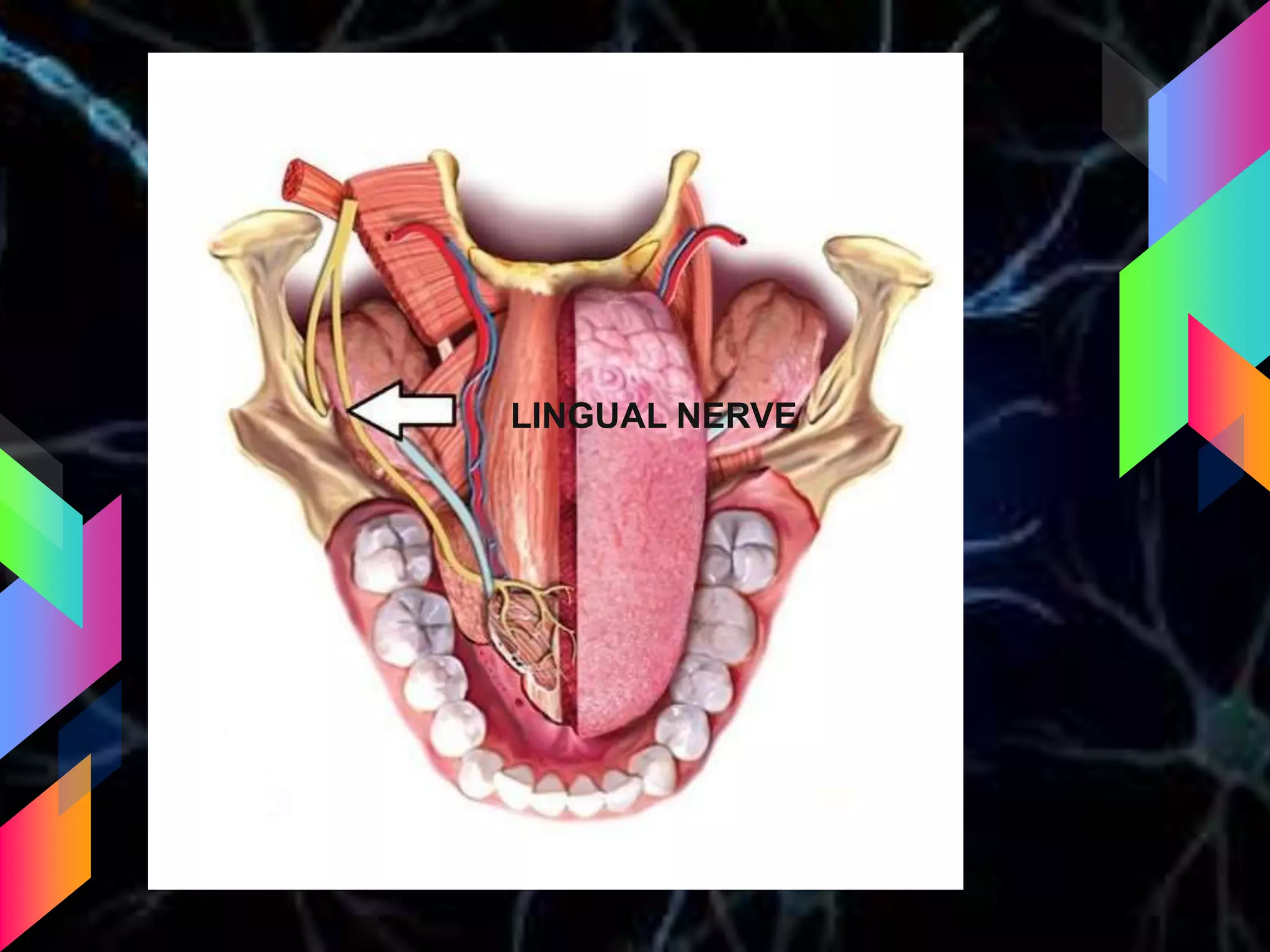
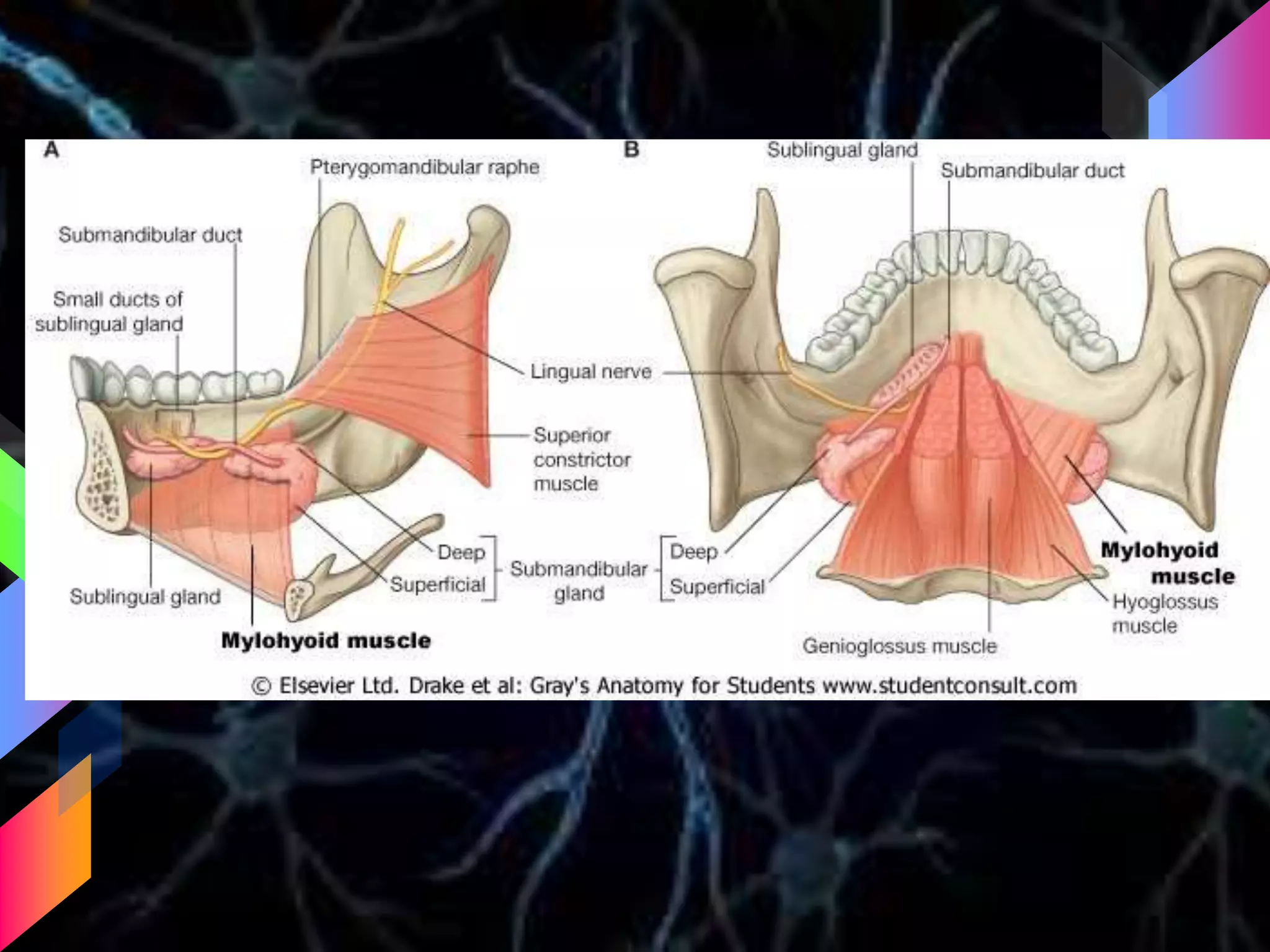
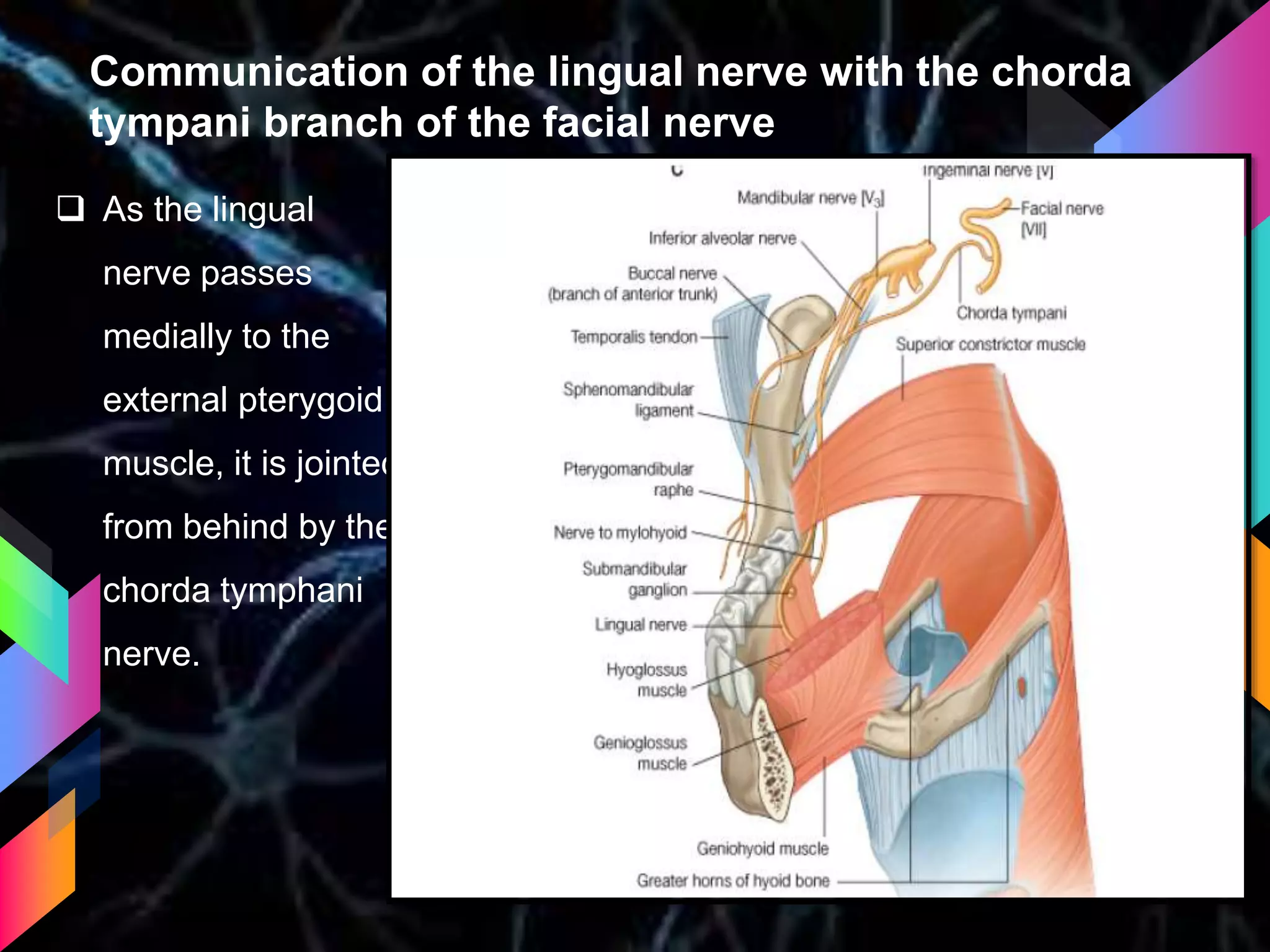
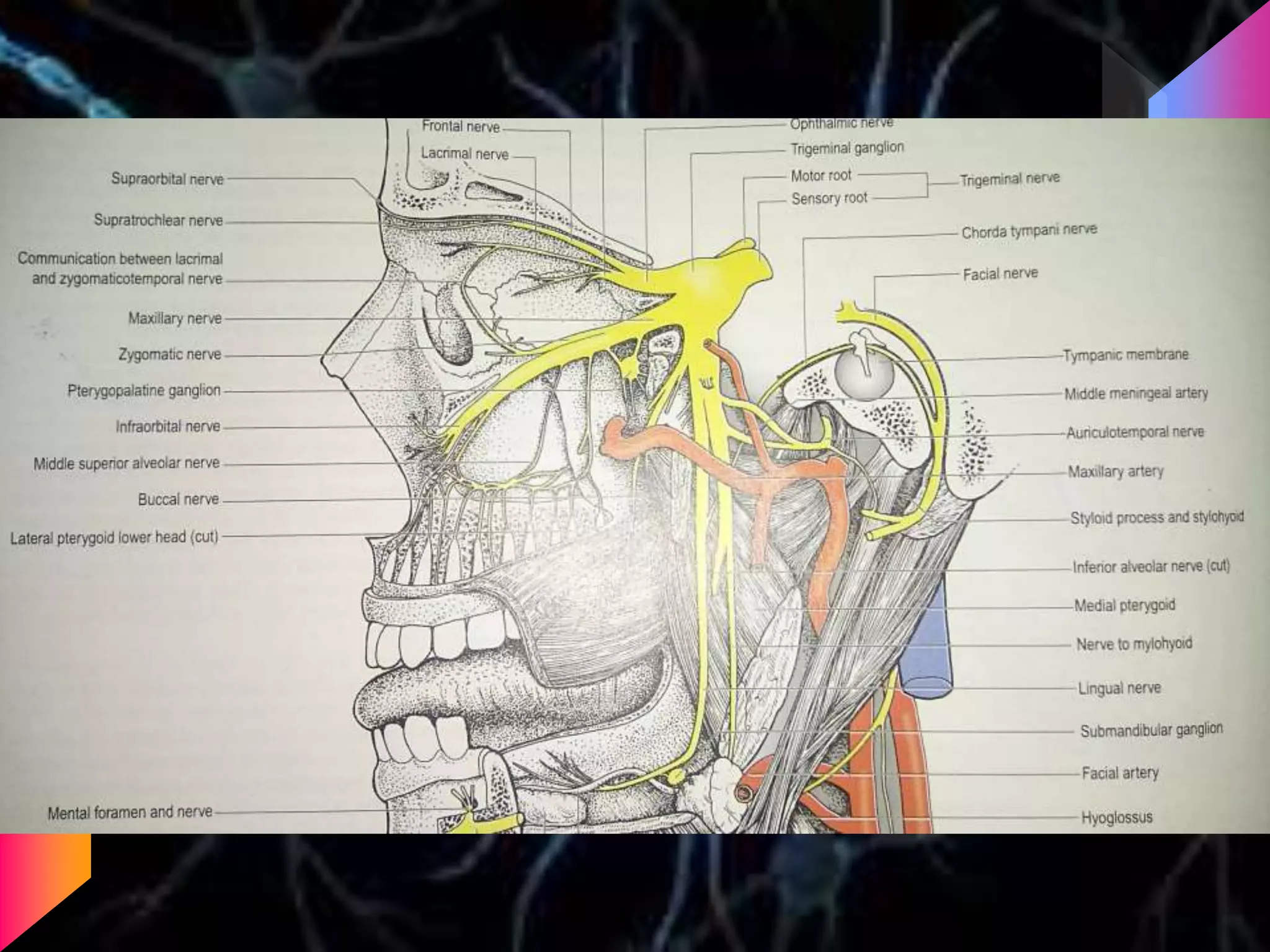
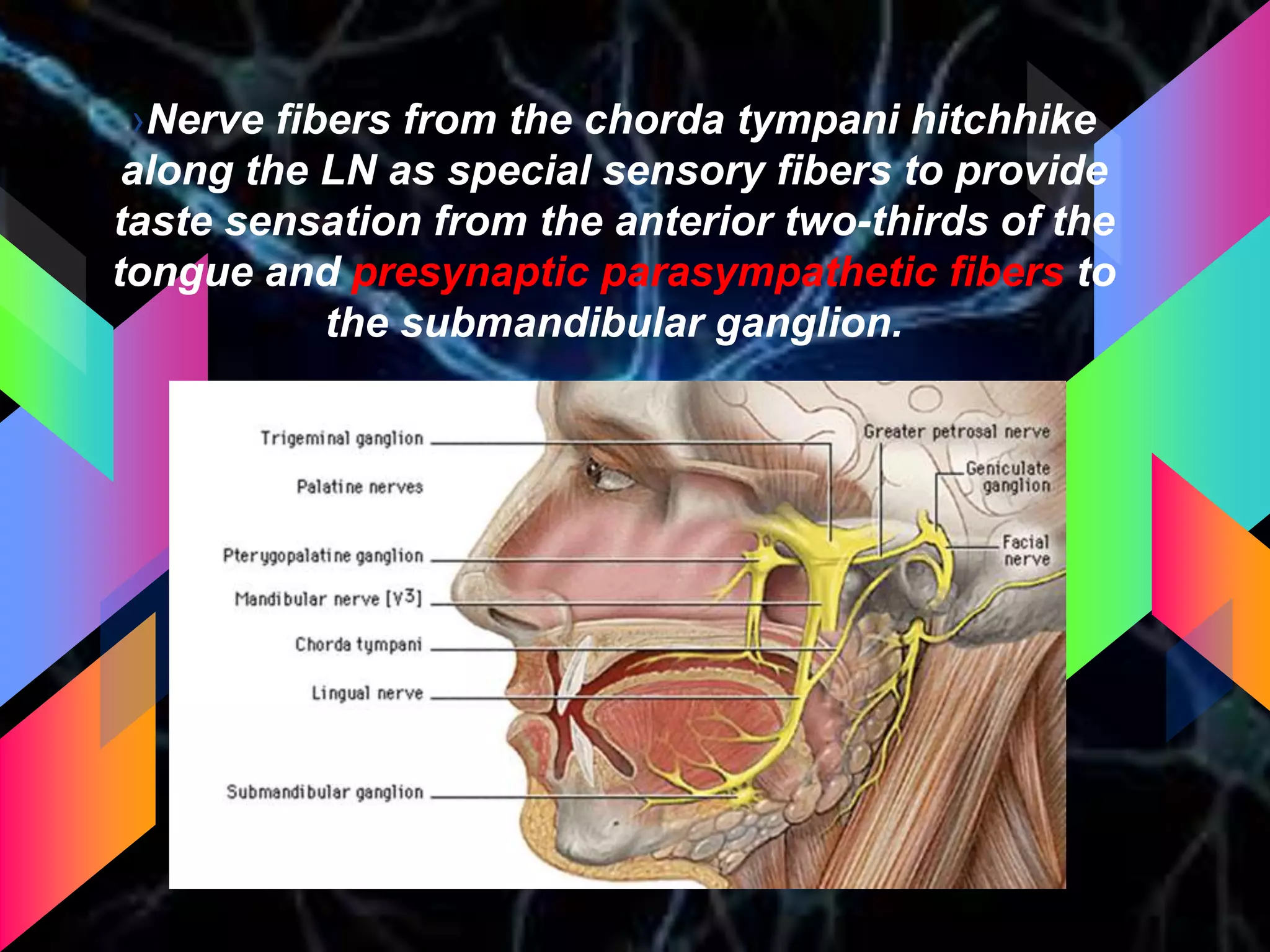
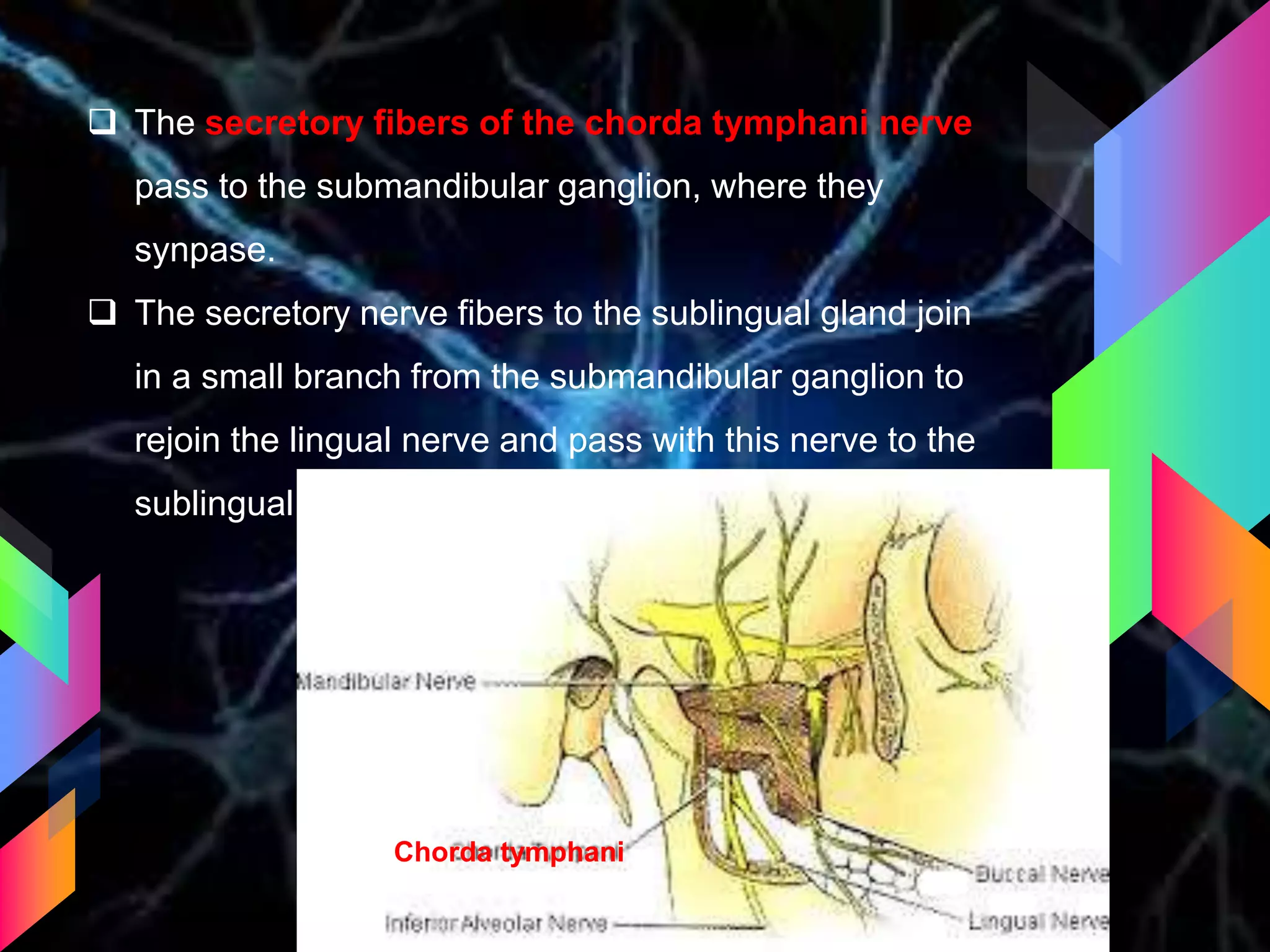
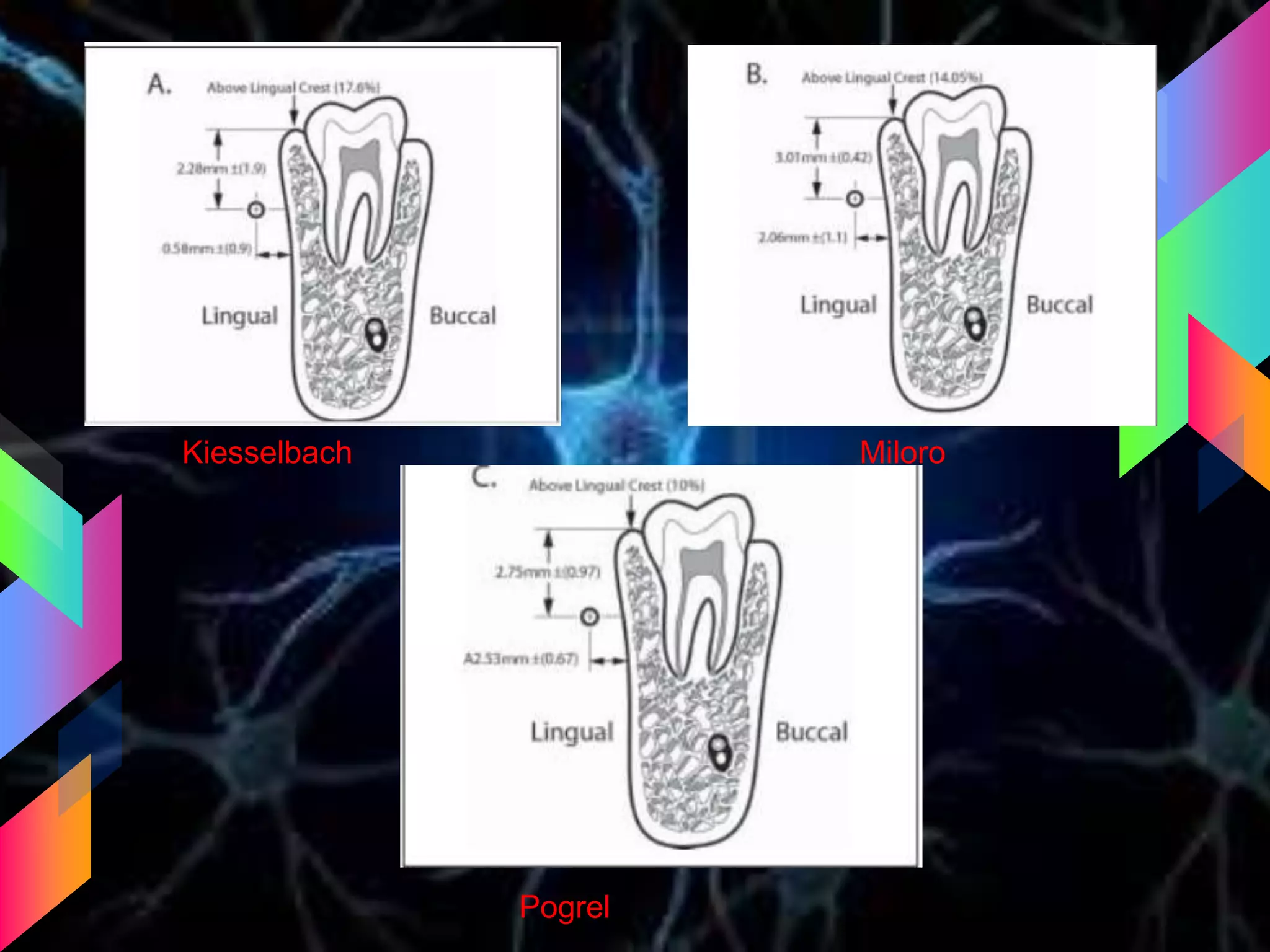
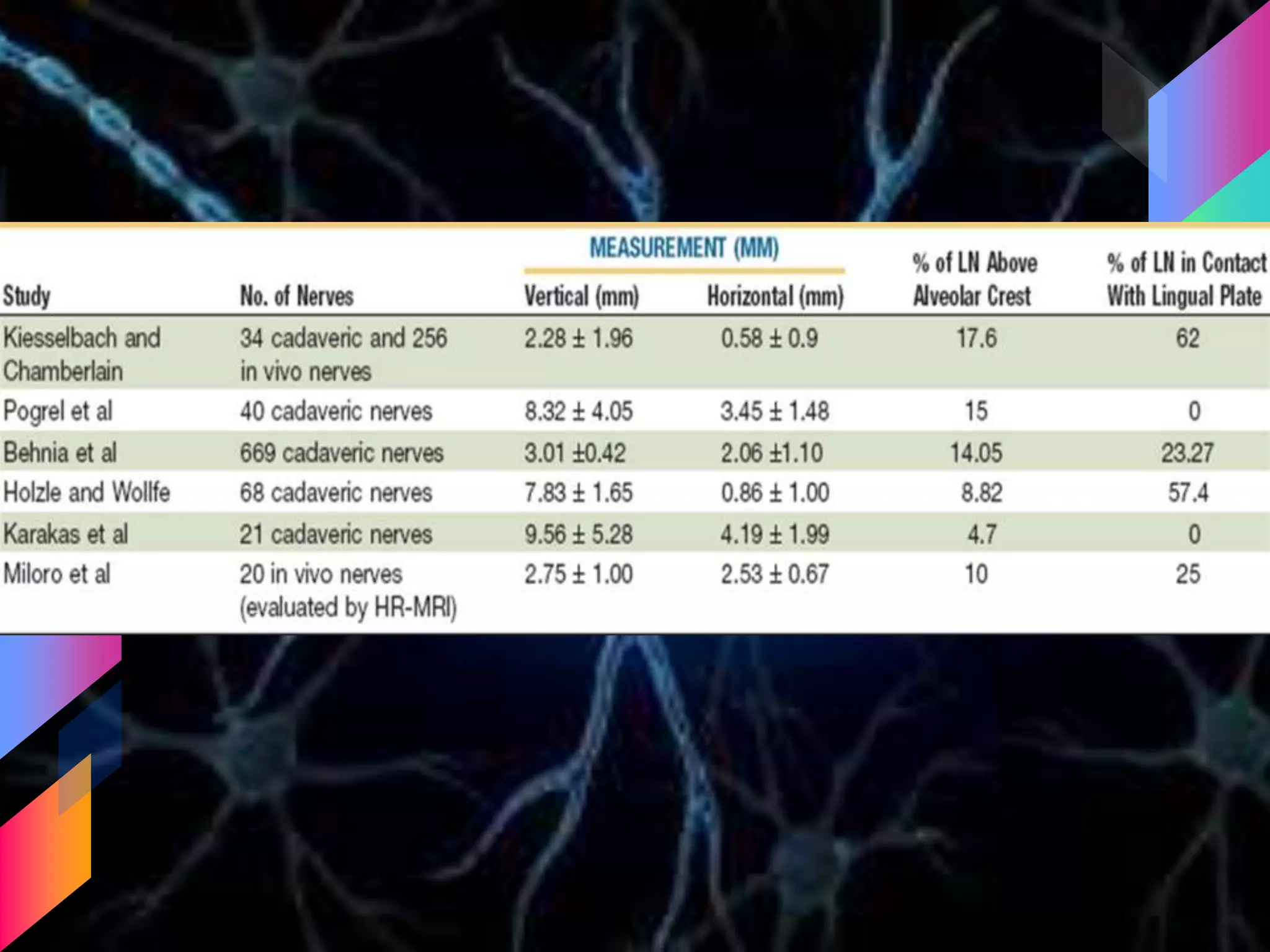
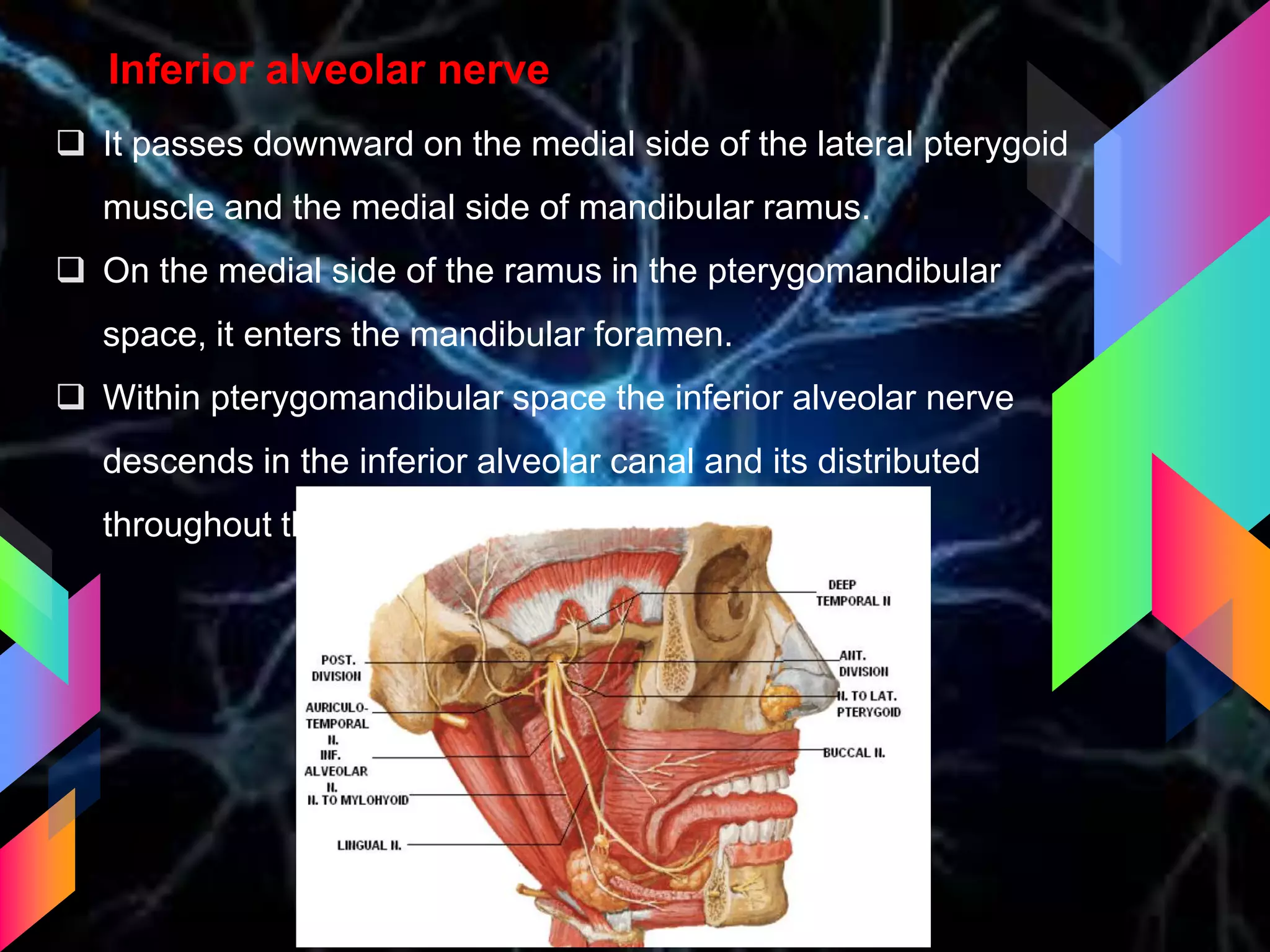
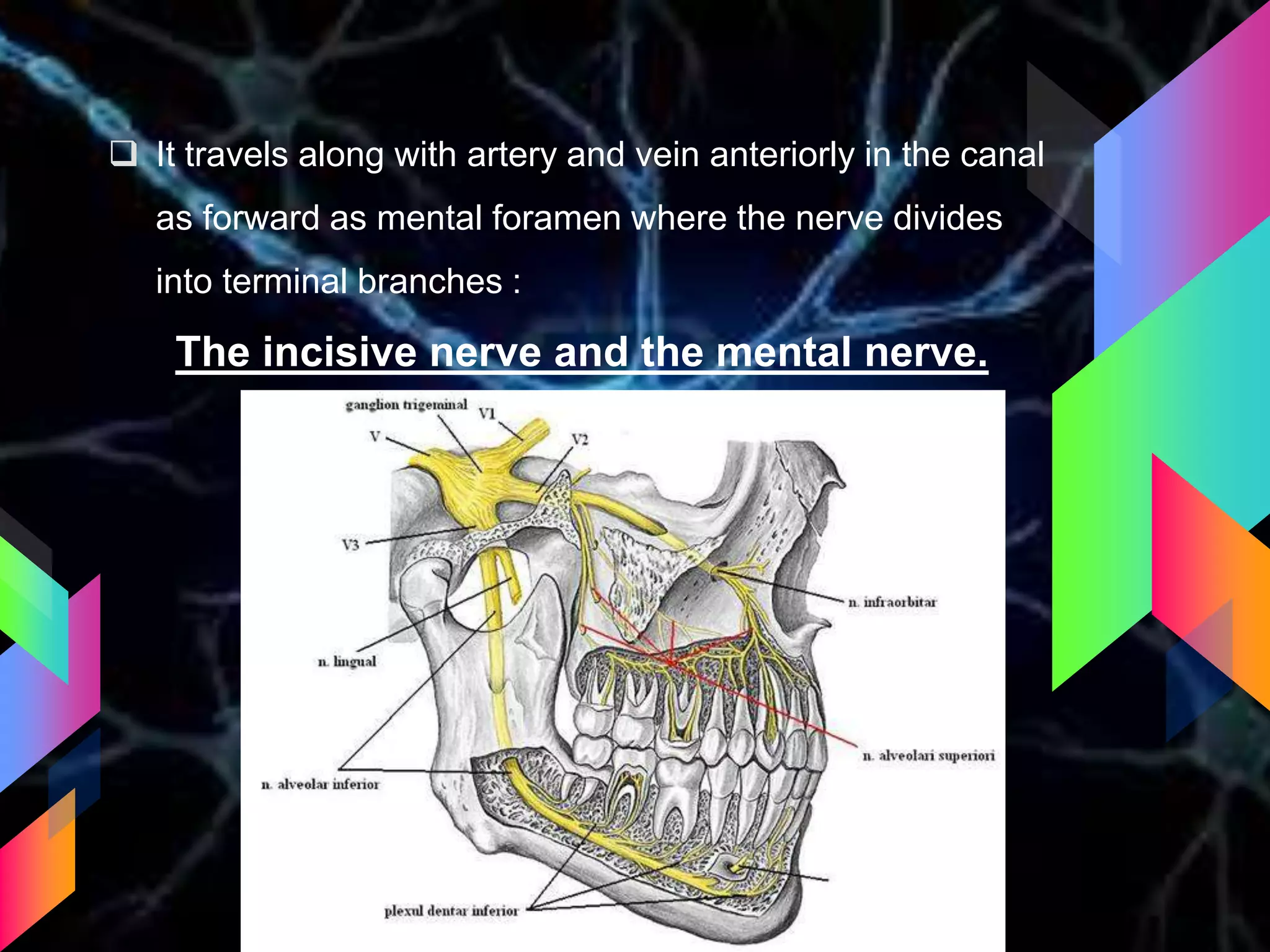
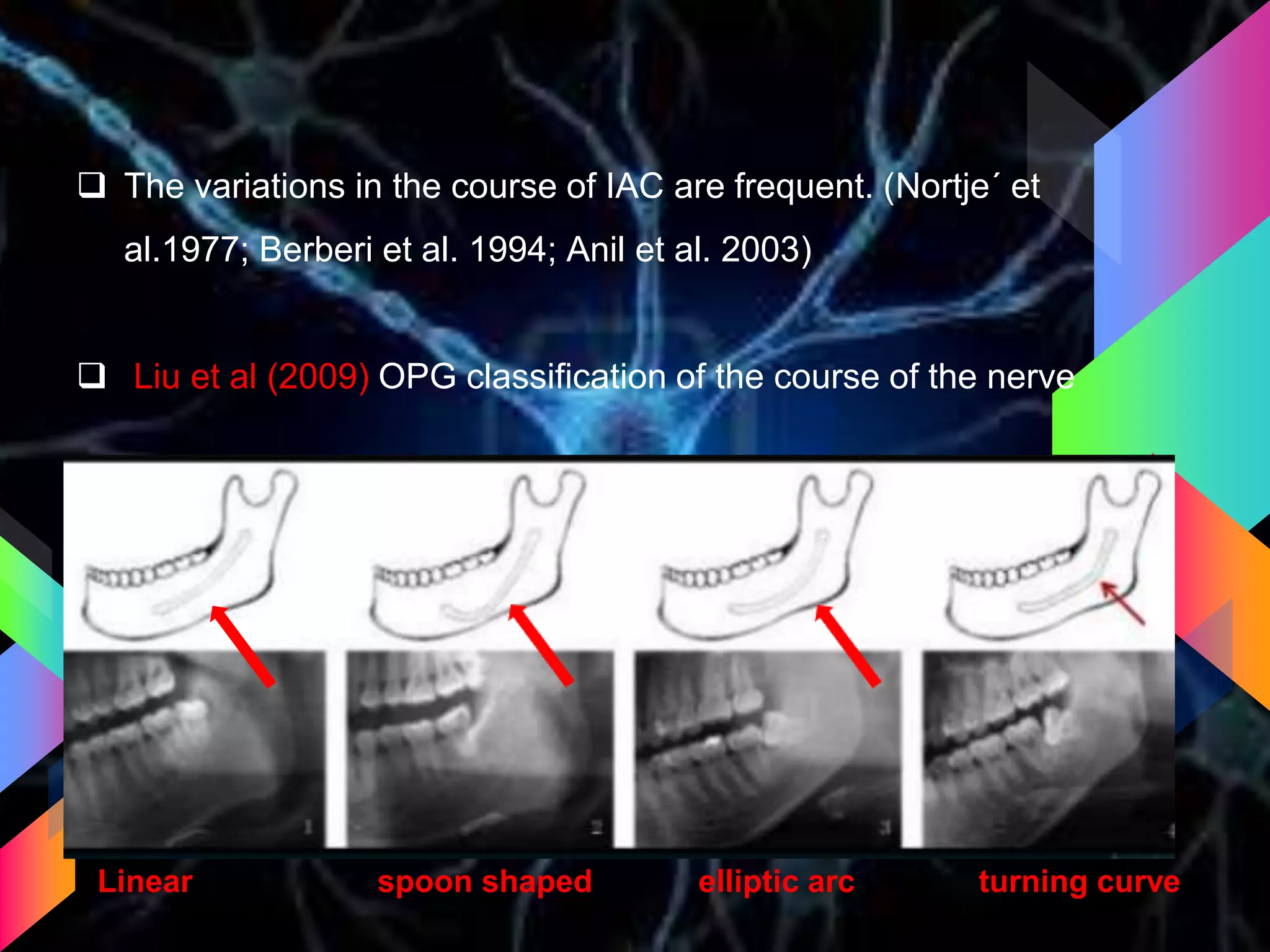
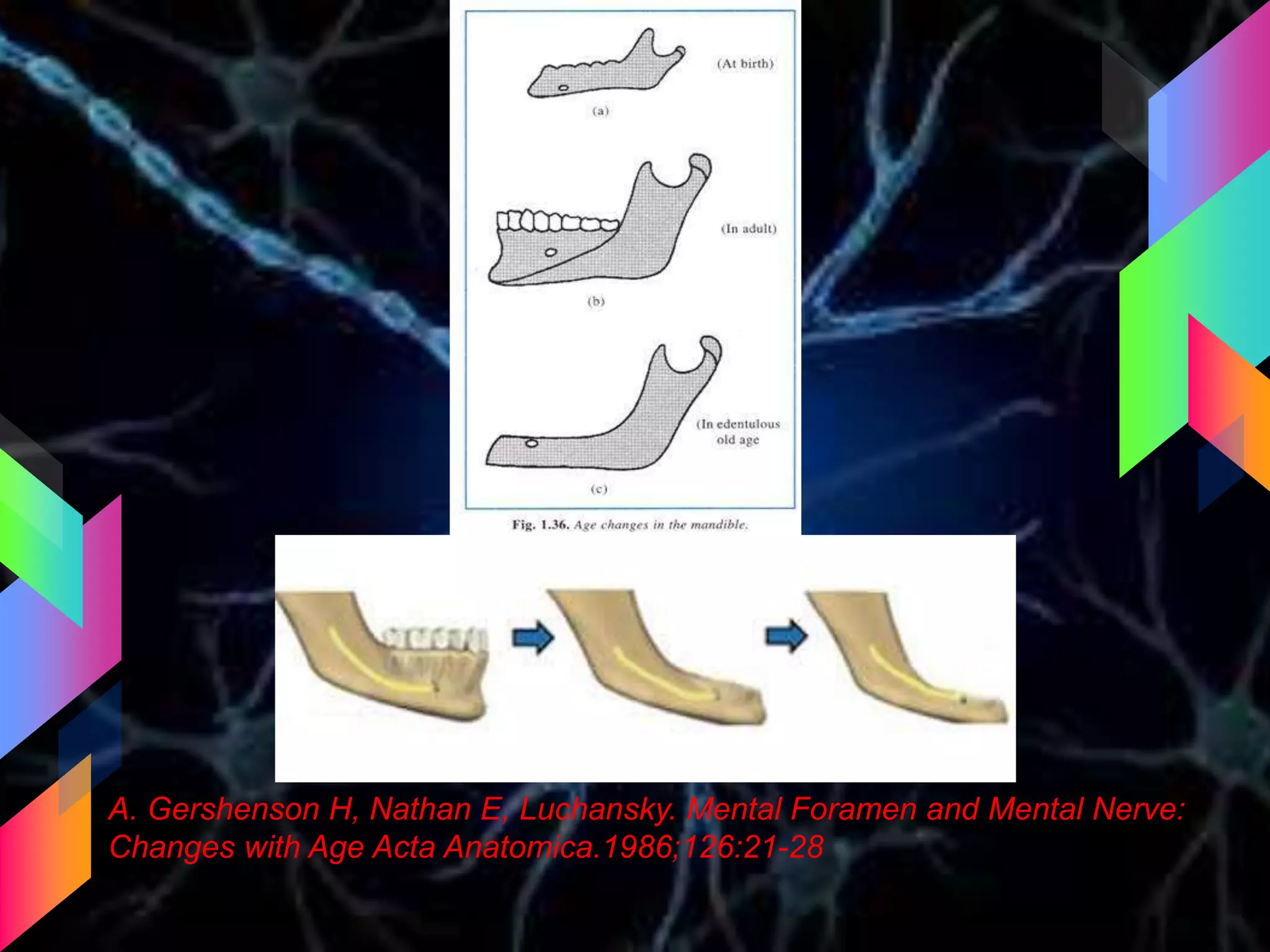
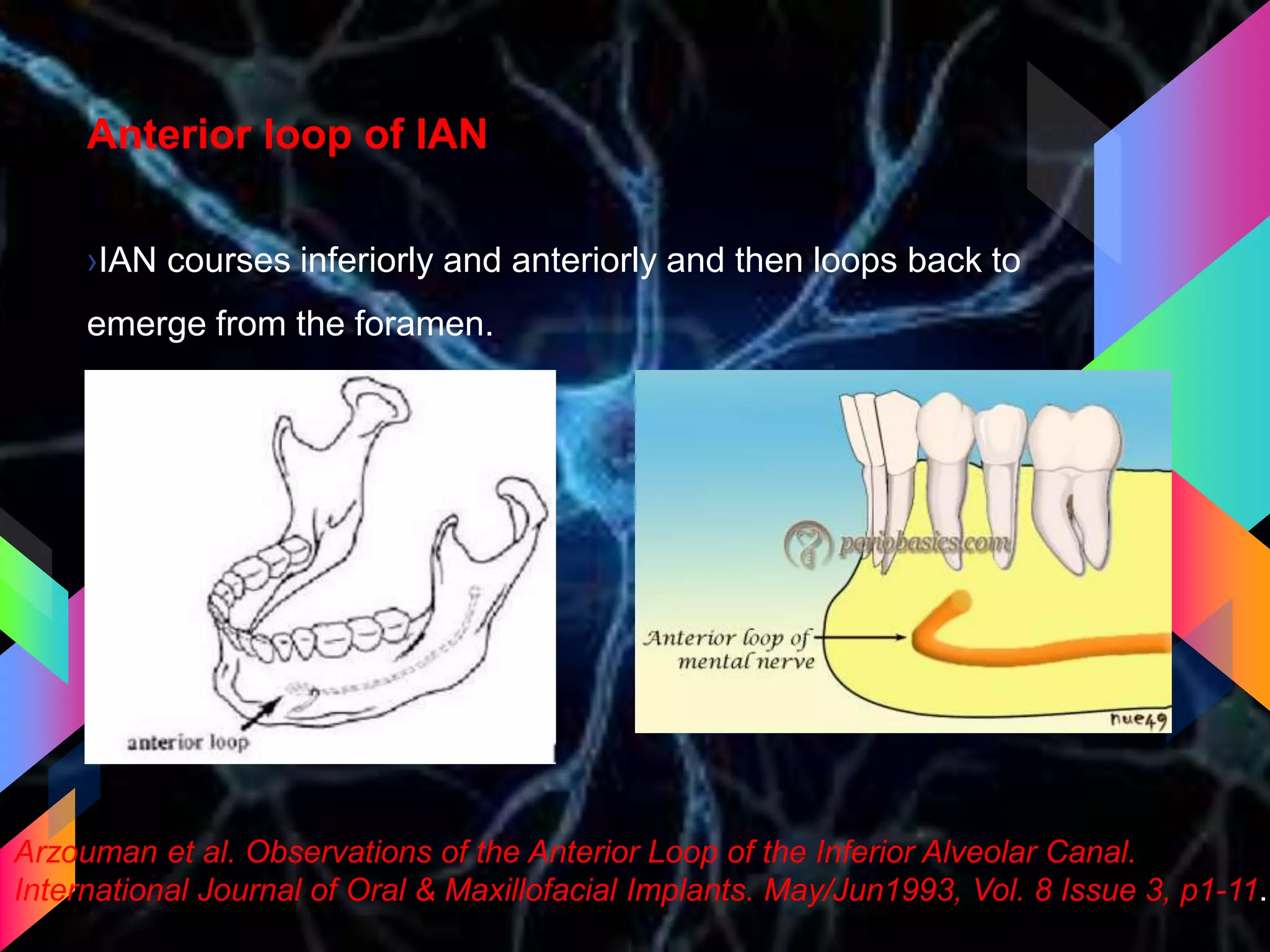
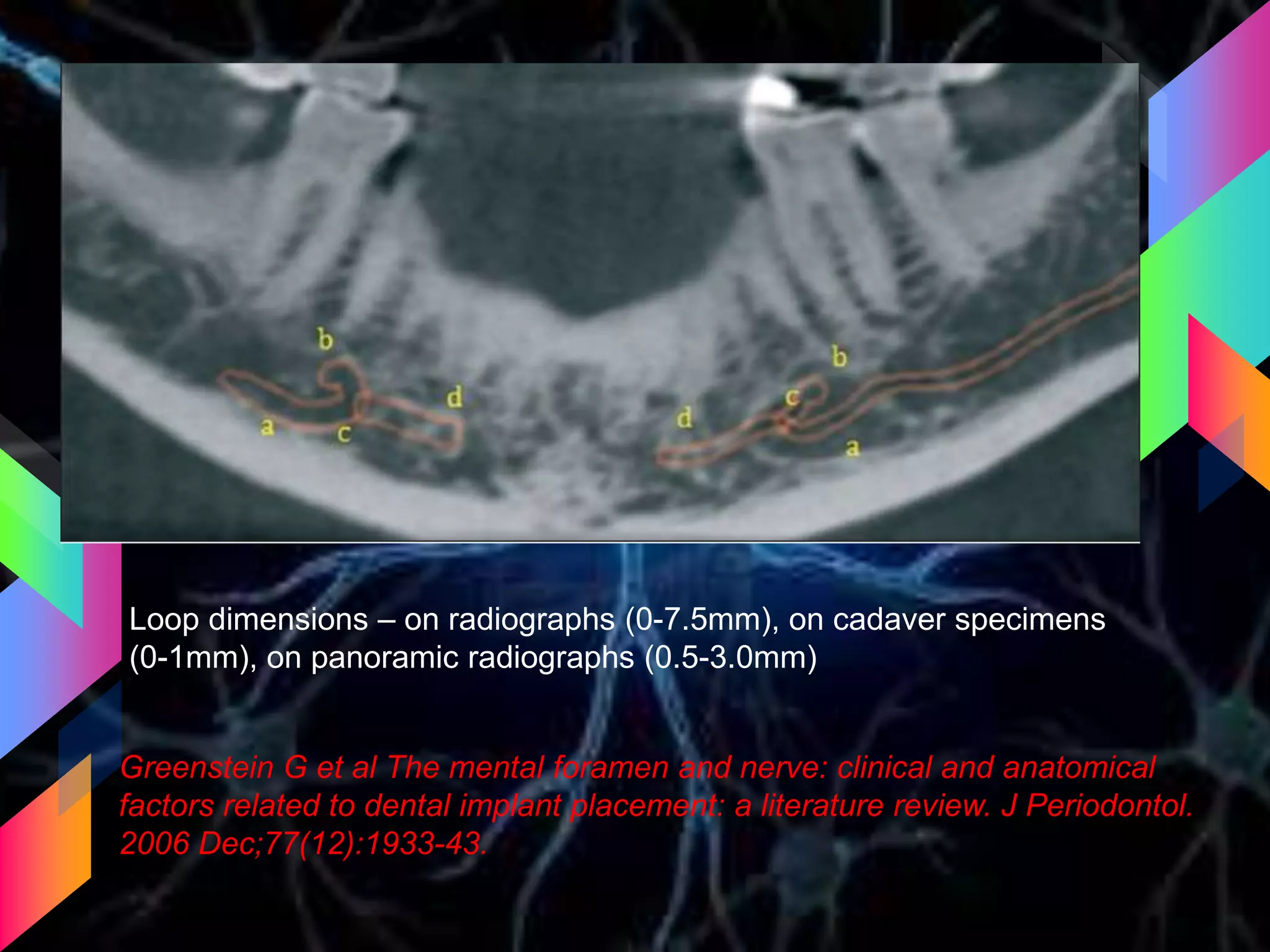
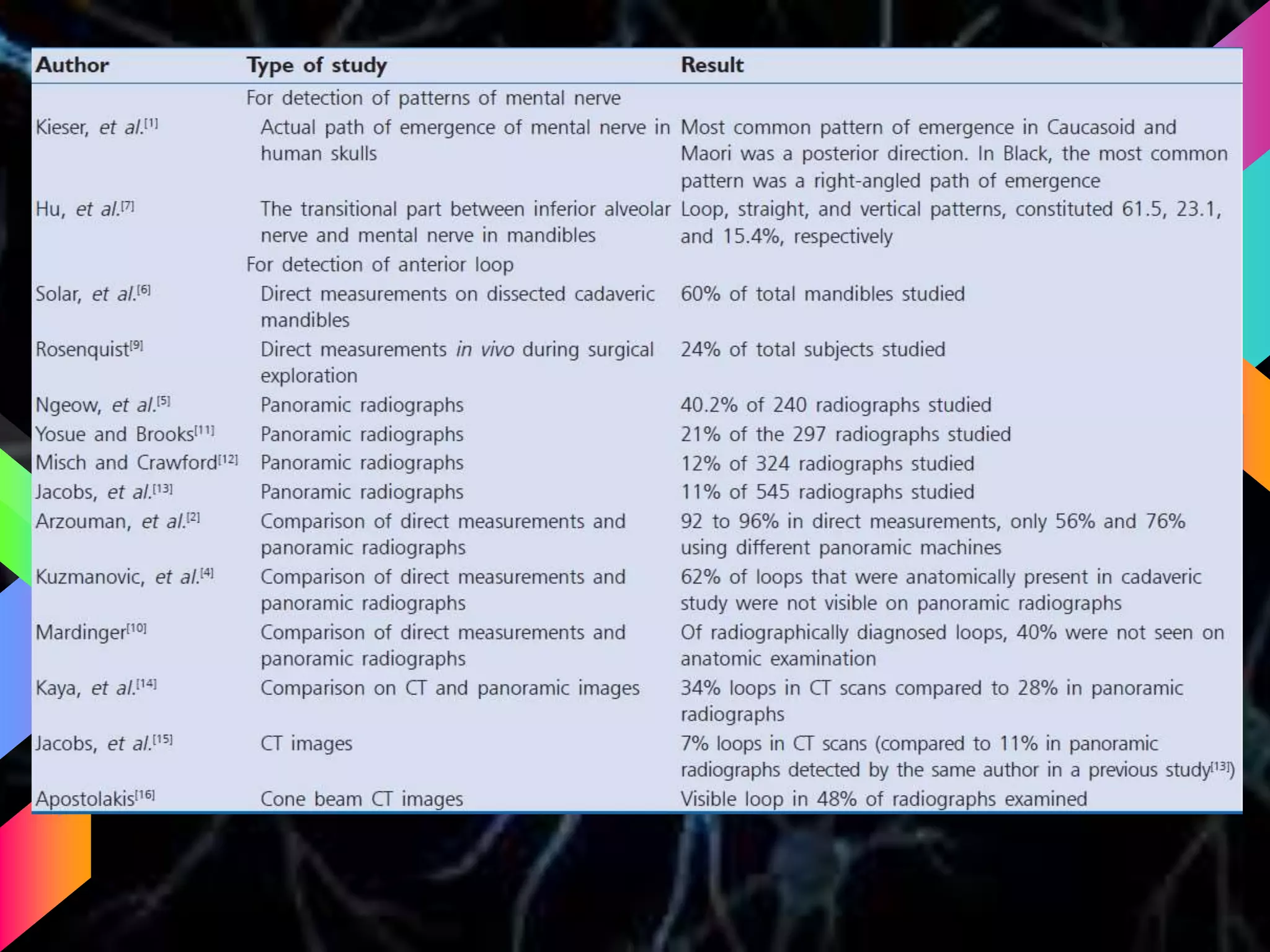
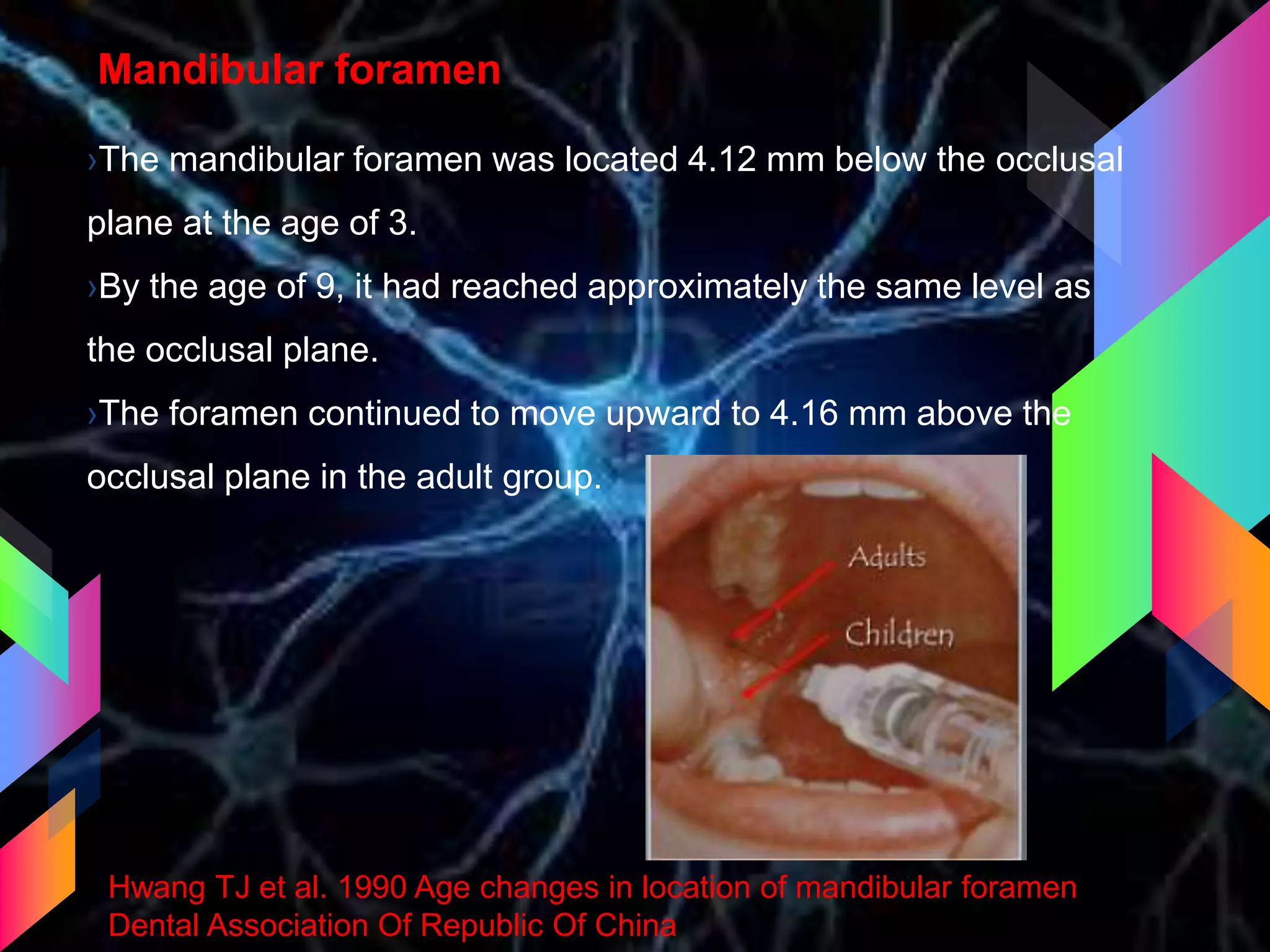
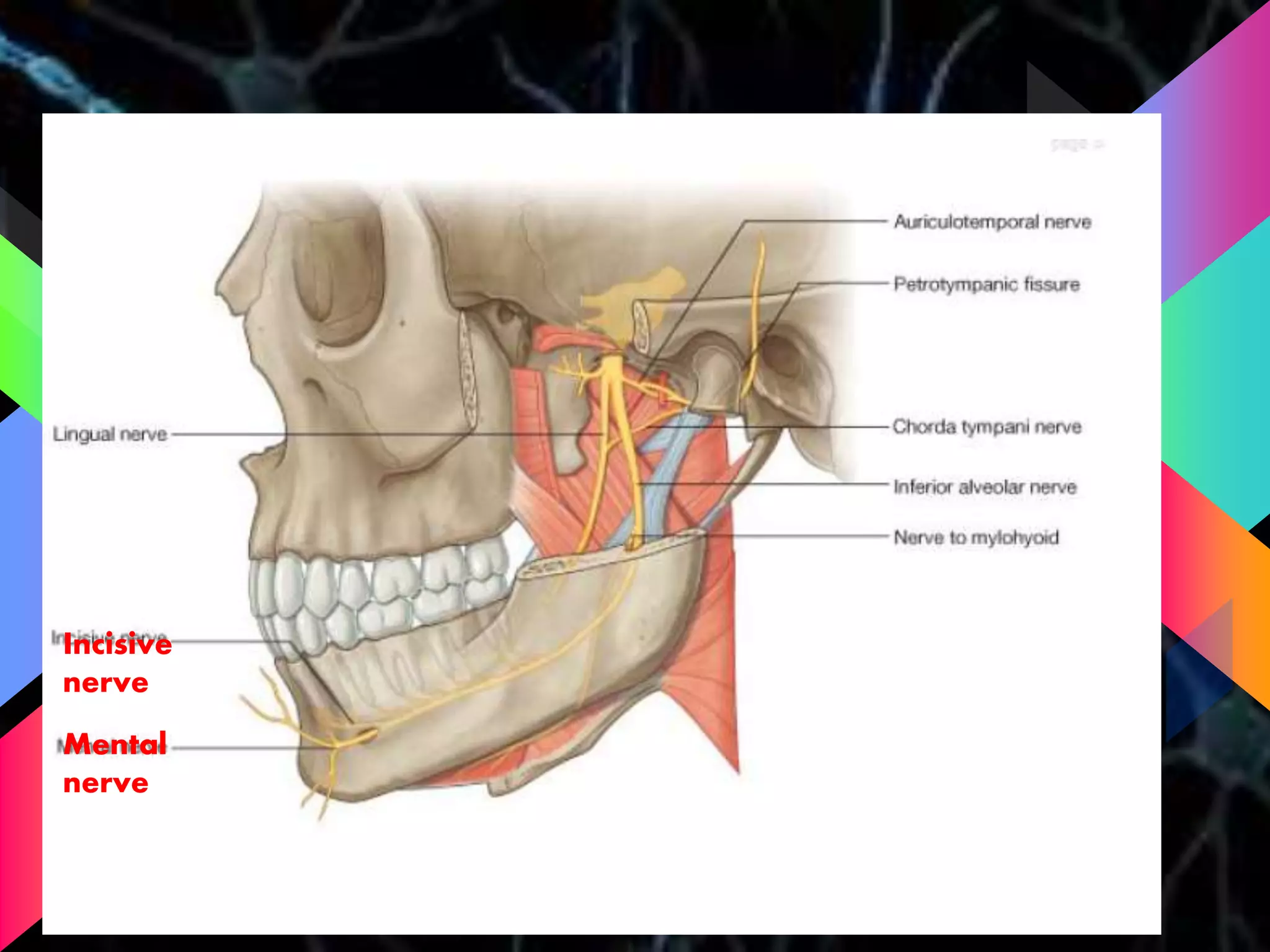
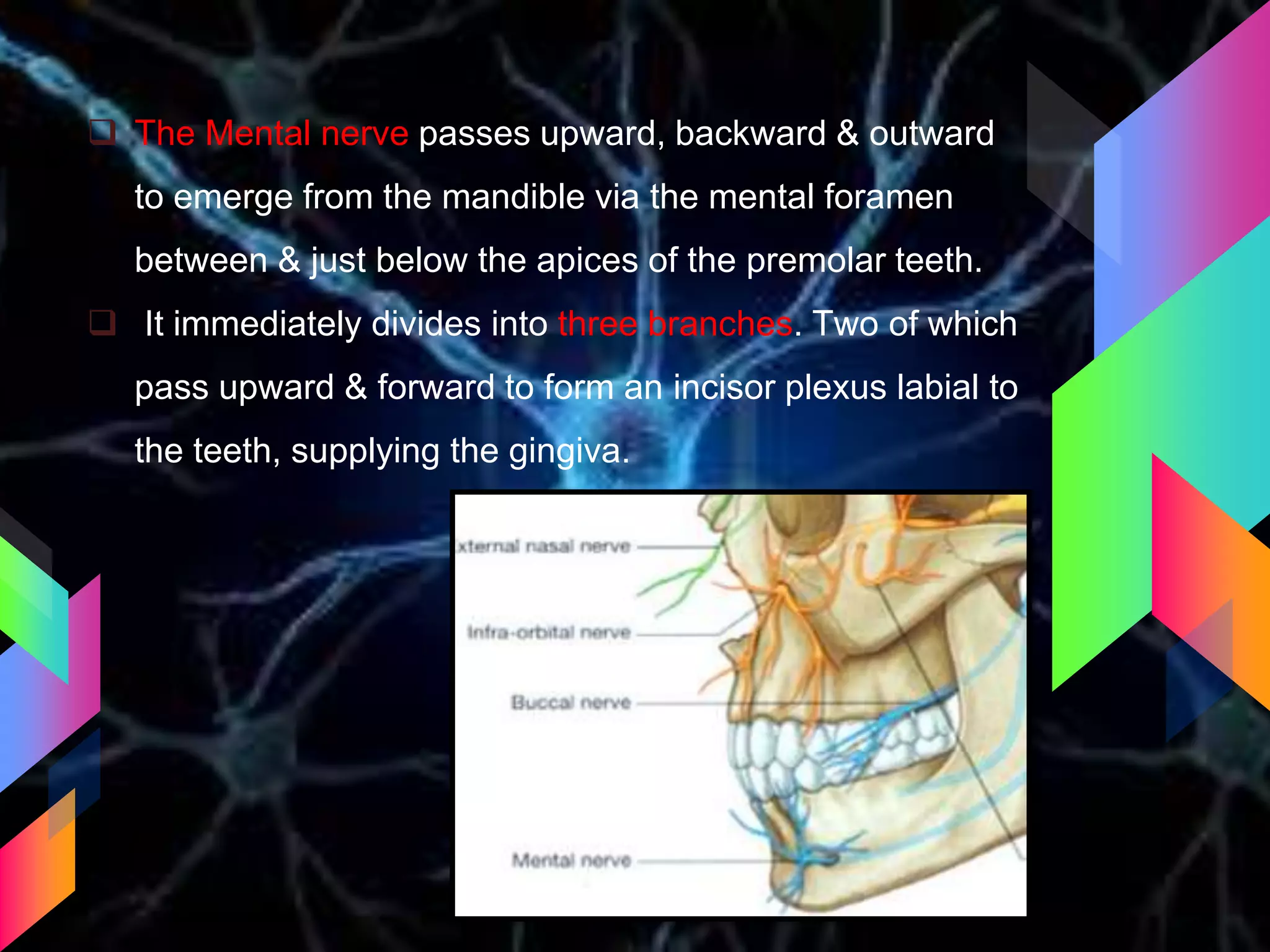
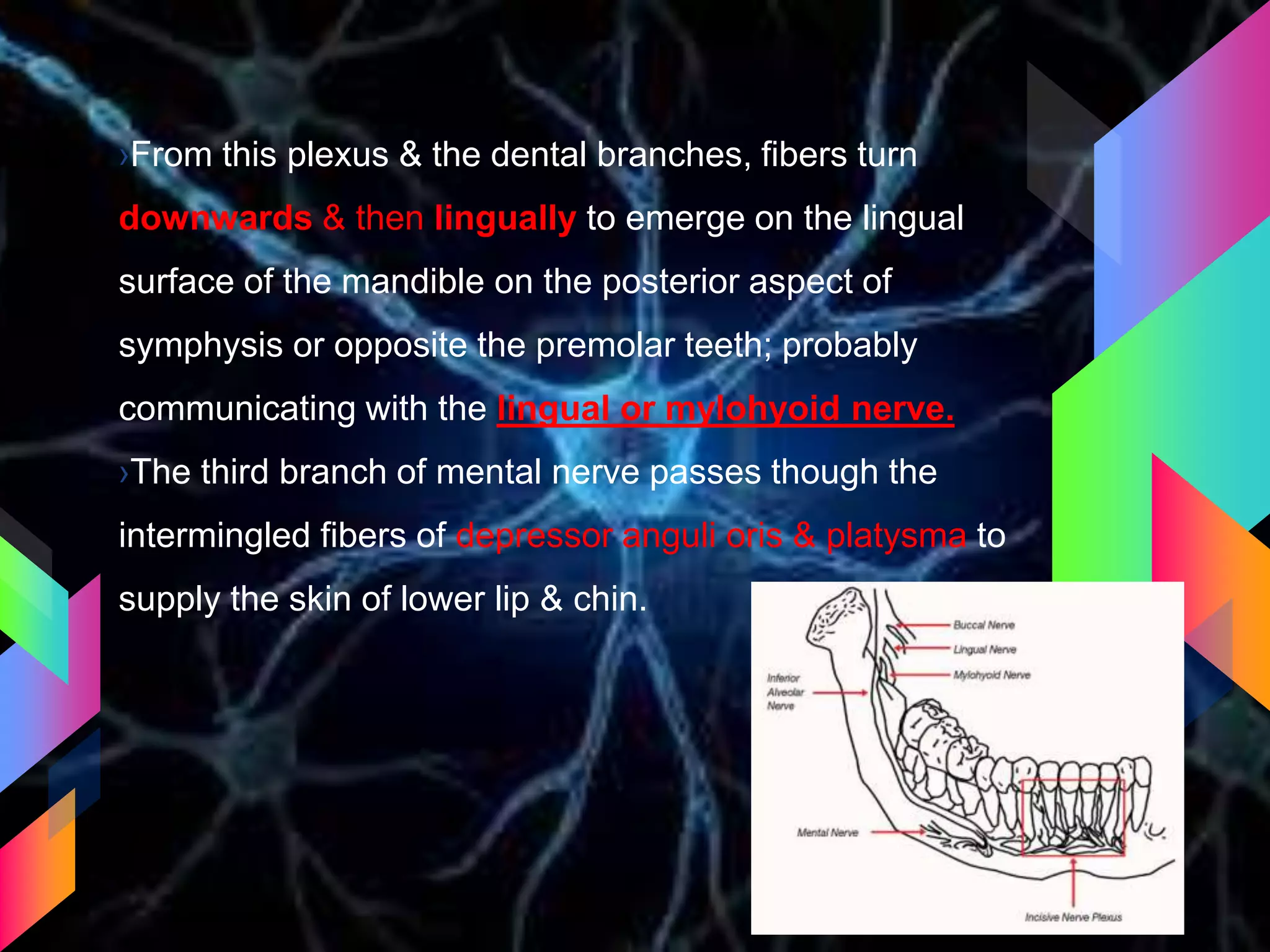
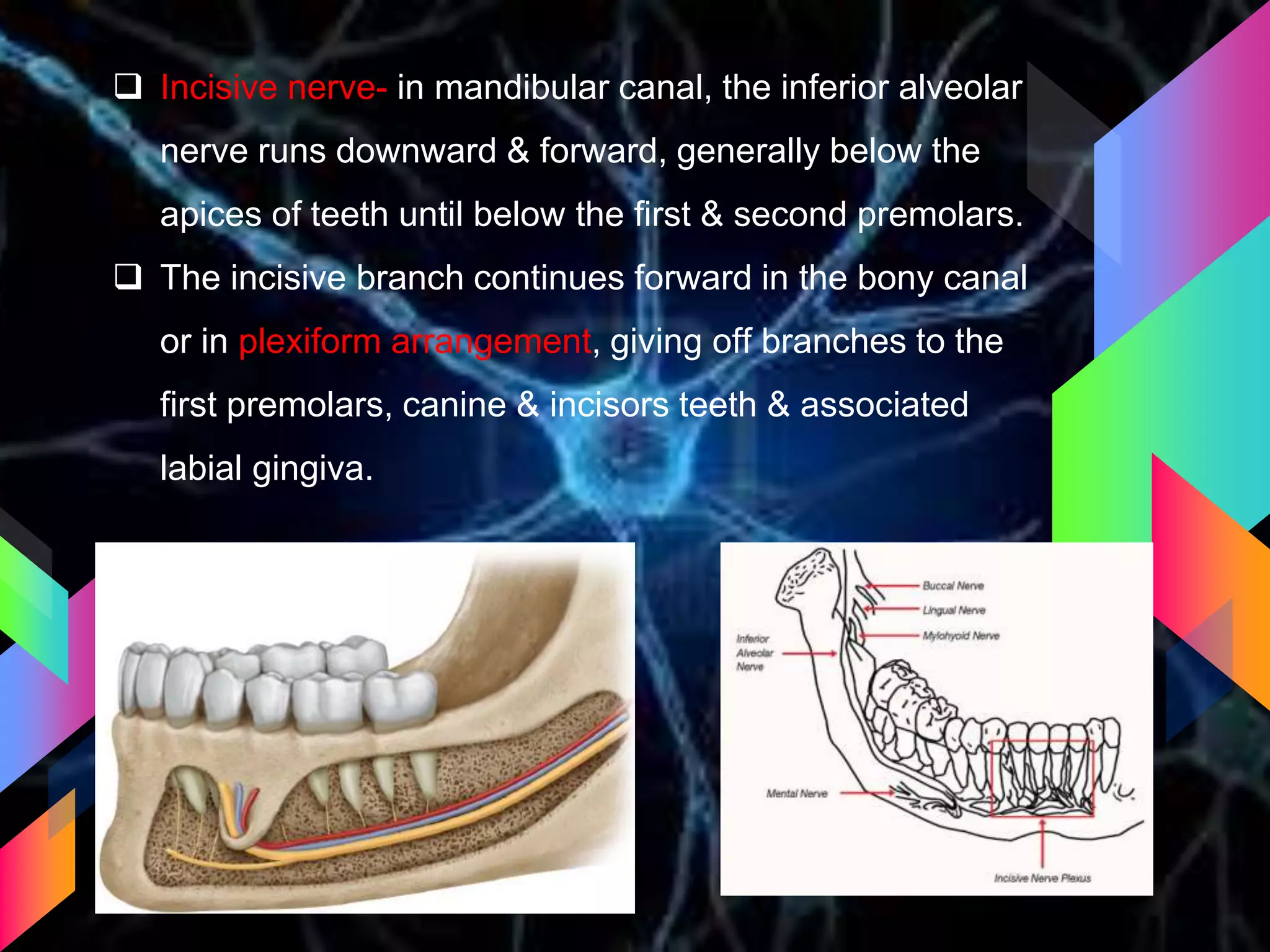
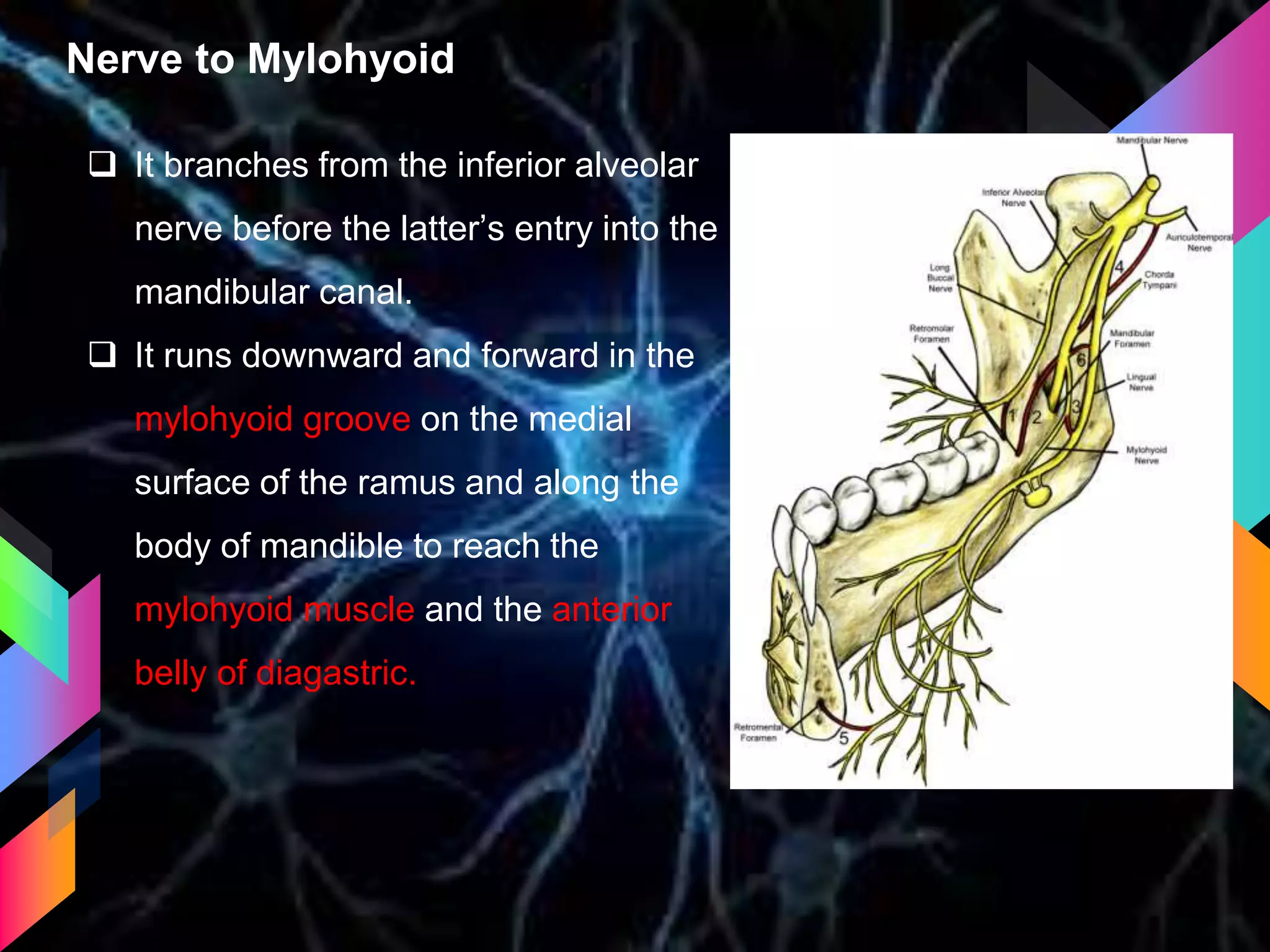
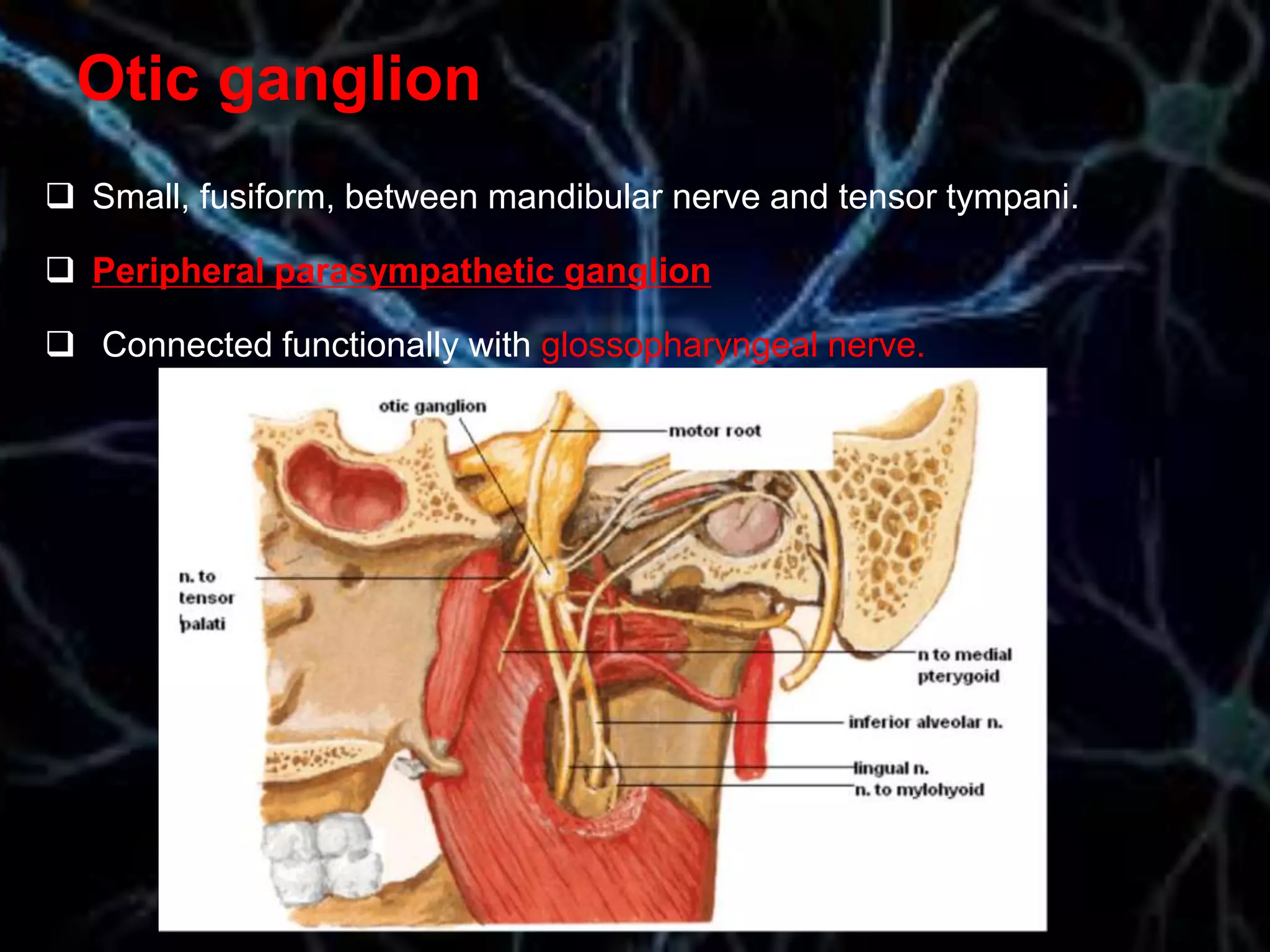
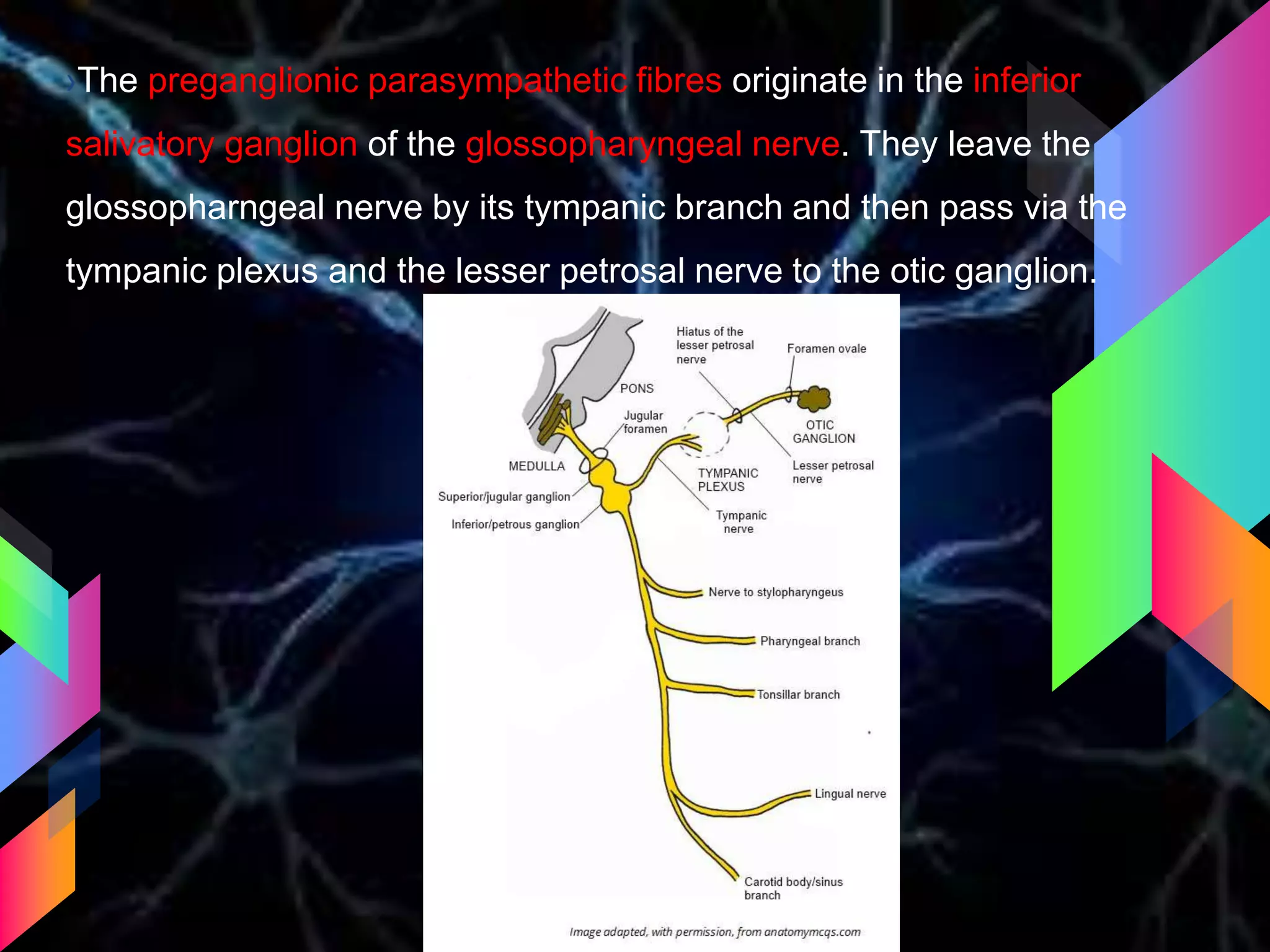
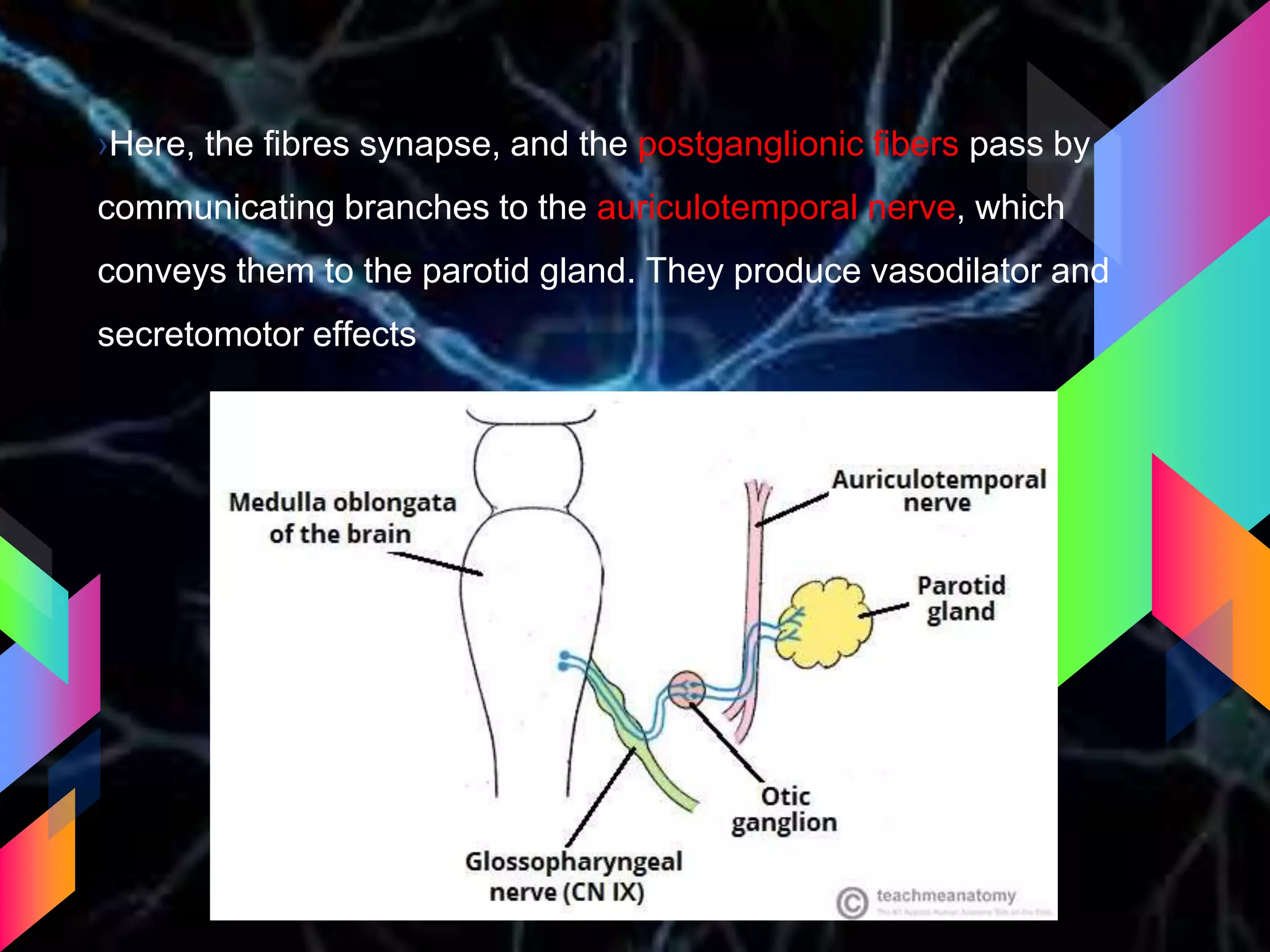
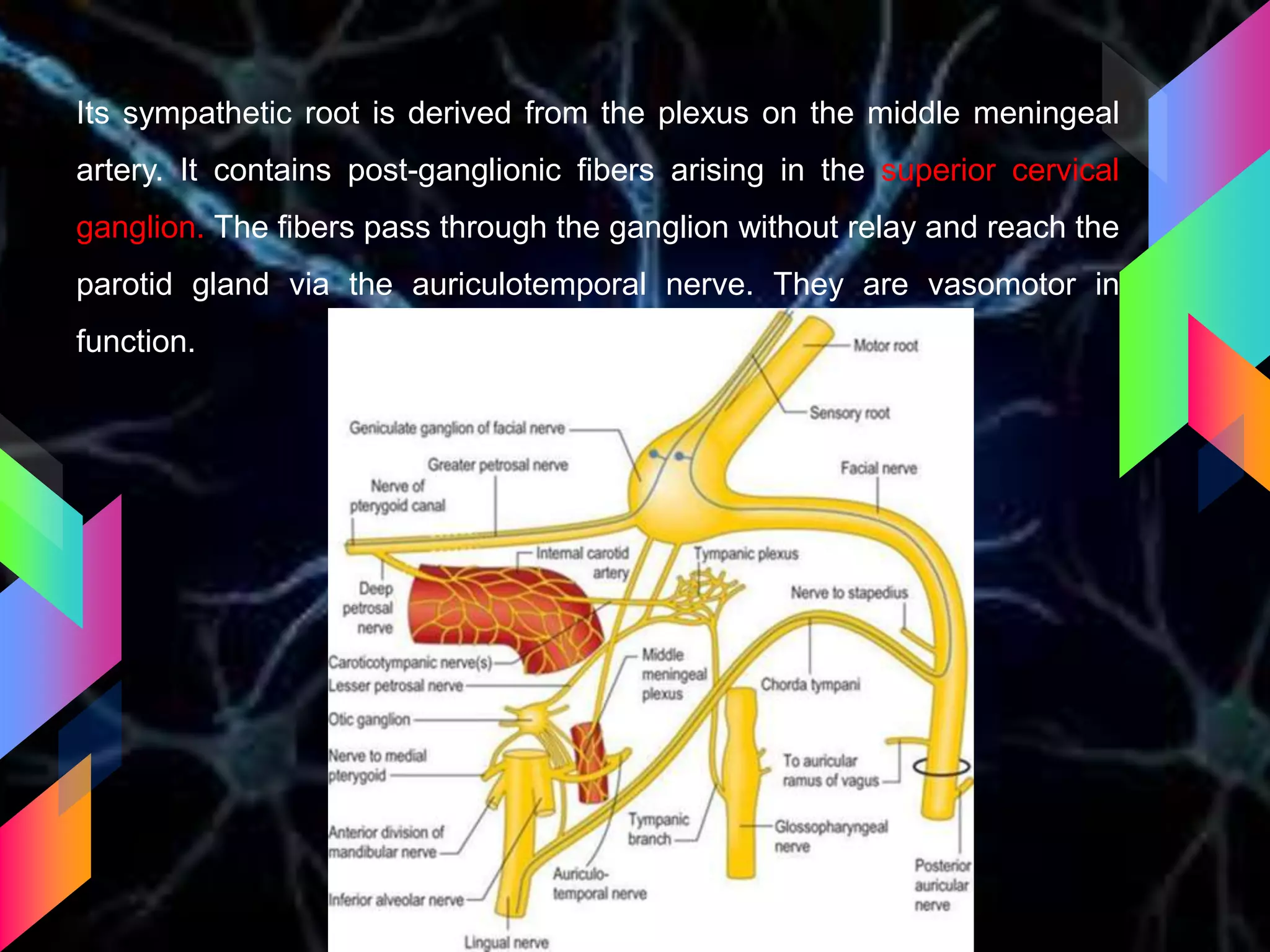
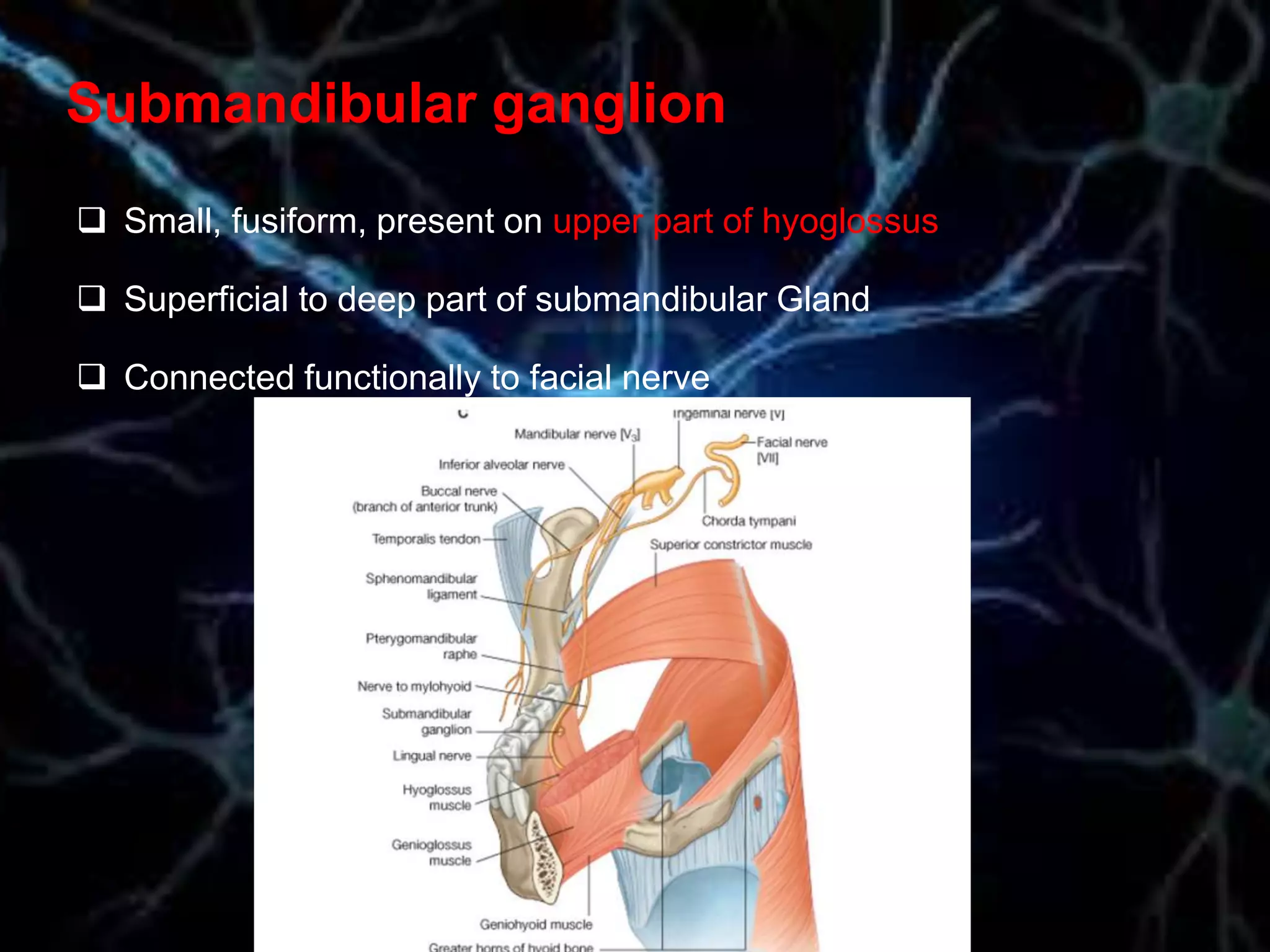
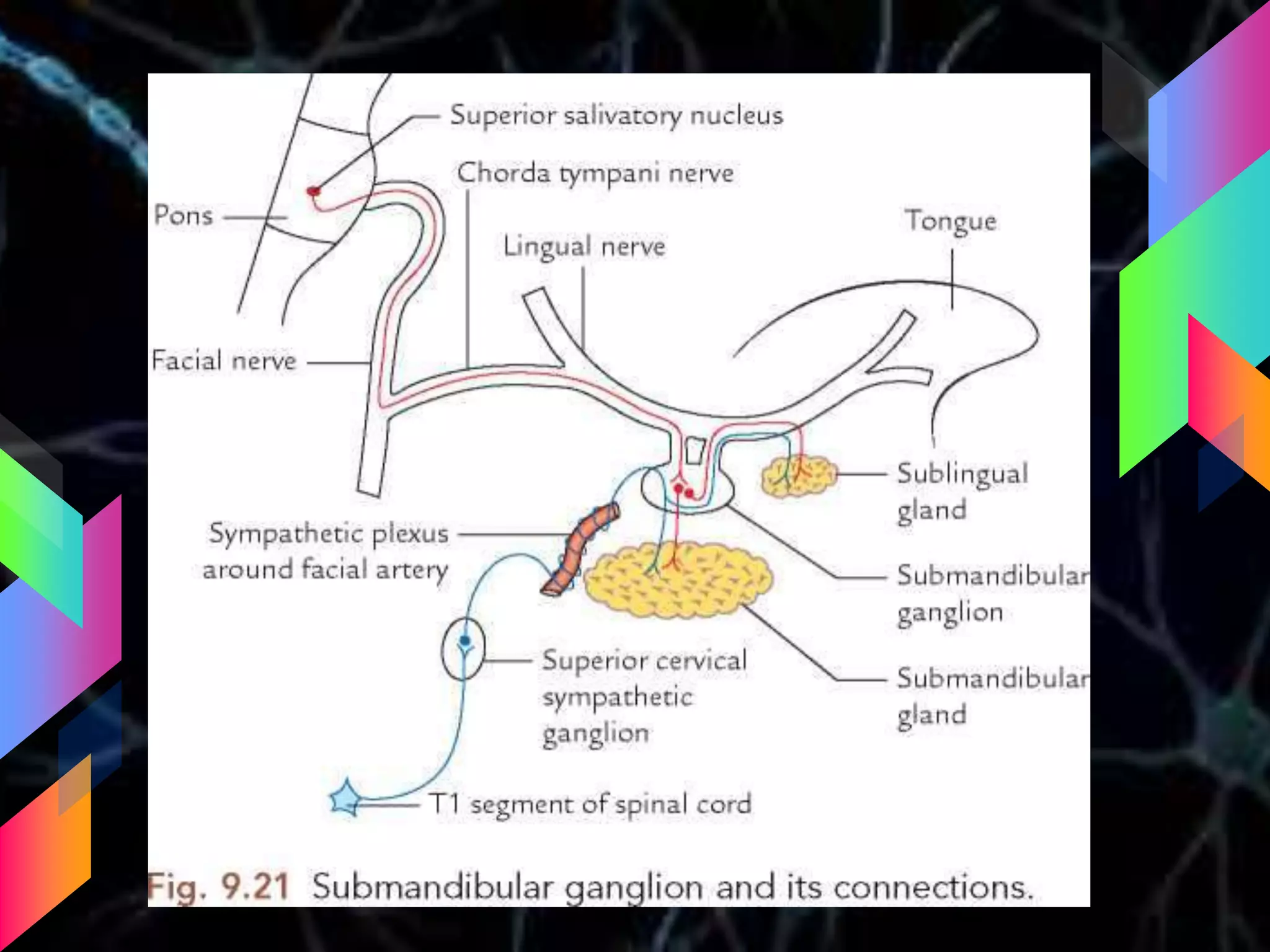
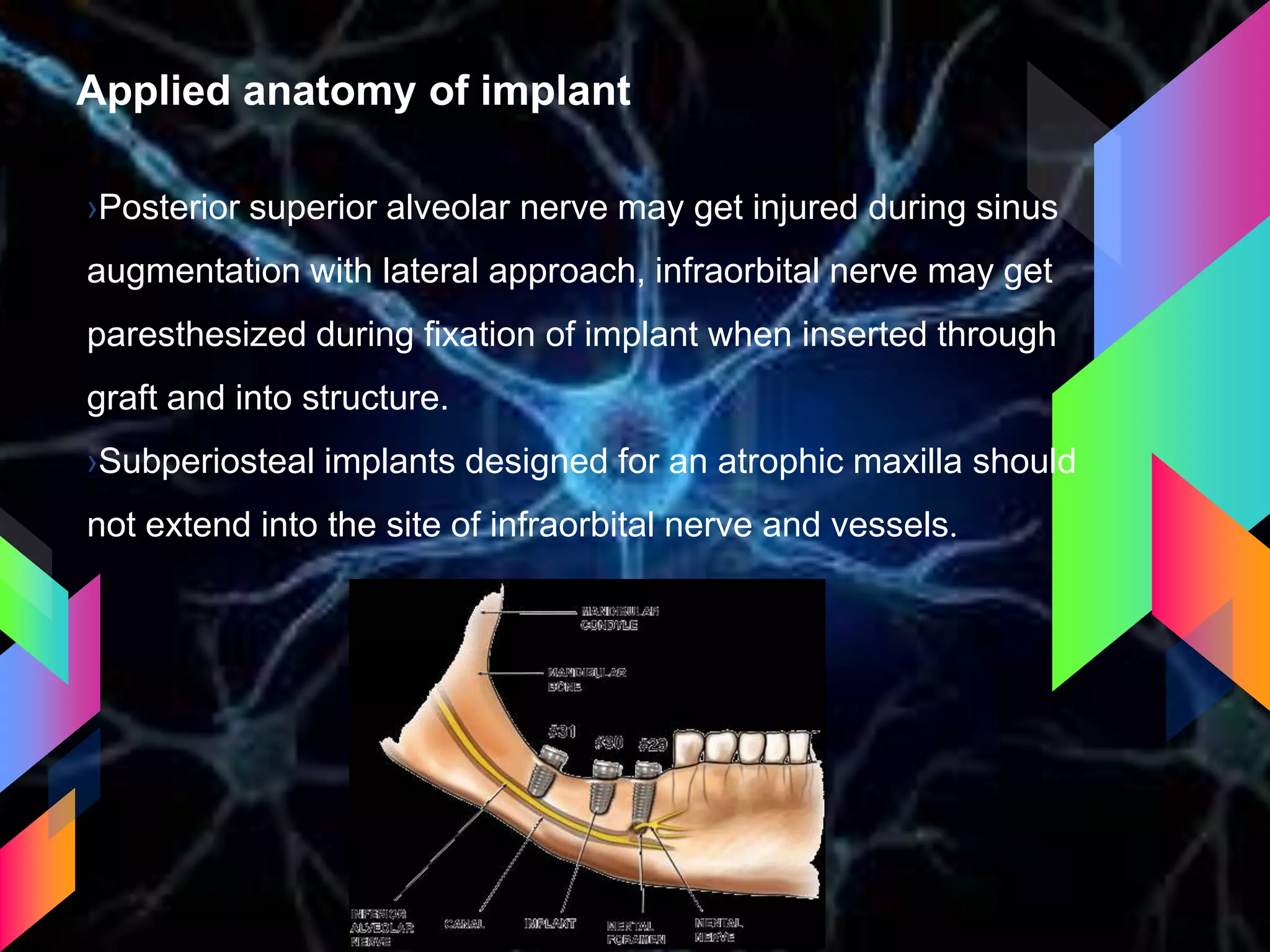
The document details the trigeminal nerve, its anatomy, origin, course, and branches, highlighting its significance as the main sensory nerve of the head and face. It covers the implications of this nerve in periodontal health and provides an extensive overview of its anatomical relationships, including branches to various facial structures. The content is presented by Dr. Aishvarya Hajare as part of a postgraduate presentation.