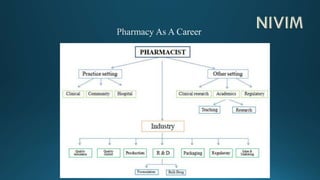
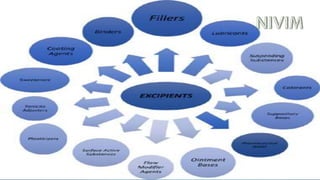
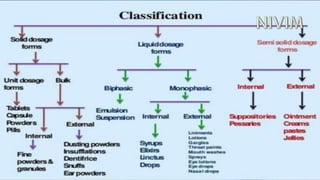
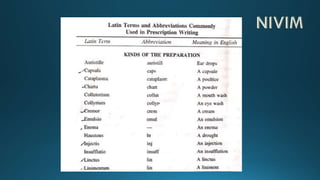
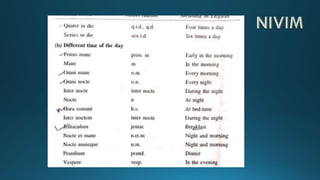
This document provides an overview of pharmacy topics including the history and development of pharmacy as a profession in India, pharmacopoeias, medicines, active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients and their uses. It defines various dosage forms like tablets, capsules, pills, and discusses topics like prescriptions, posology, dose calculation factors and formulas. The key information covered includes the historical background of pharmacy in India, definitions of common dosage forms and medicines, factors affecting drug doses, and formulas to calculate doses for children and infants.